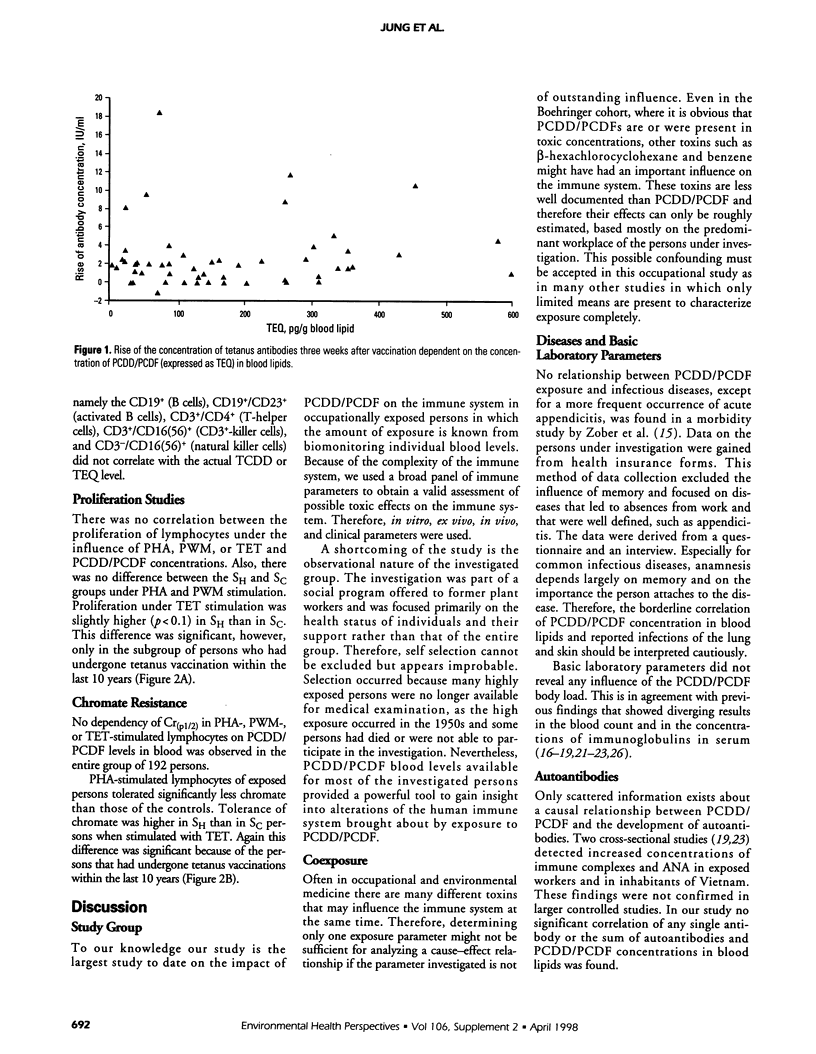
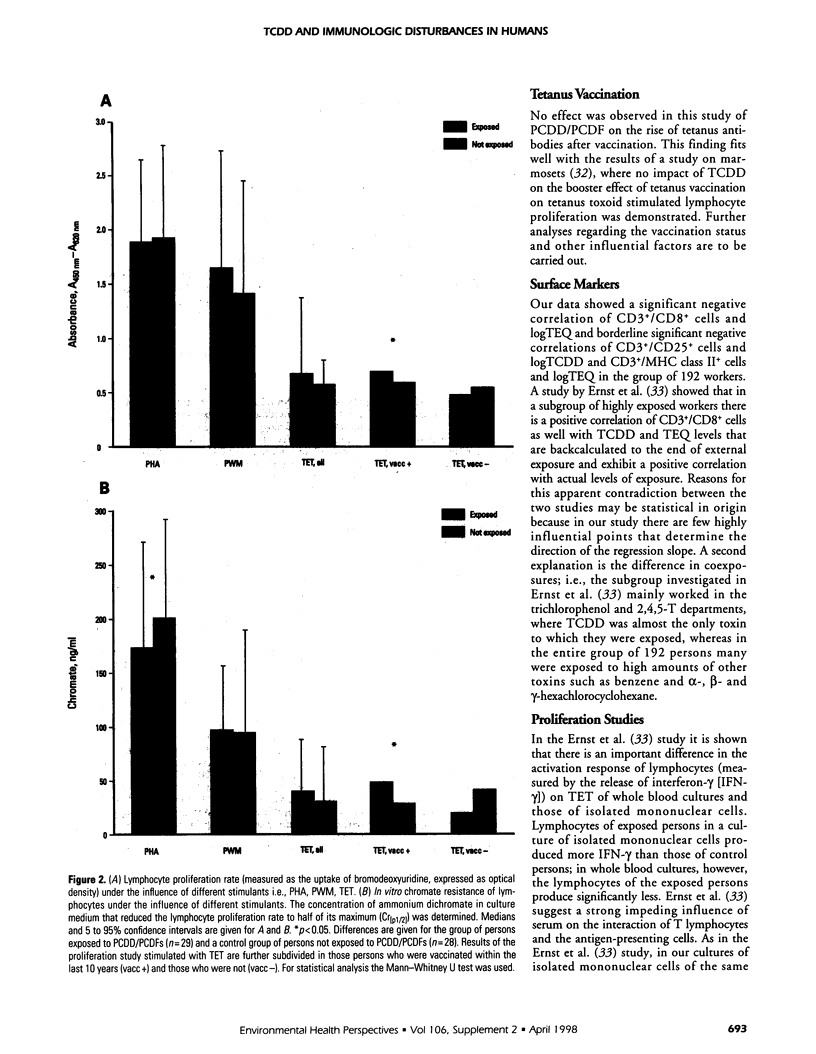
Abstract
One hundred ninety-two workers in a German pesticide factory who were exposed to polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and -furans (PCDD/PCDF) were investigated for former and present diseases and laboratory changes of the immune system. Moreover, in a subgroup of 29 highly exposed and 28 control persons, proliferation studies were performed. In addition to assays such as blood count, immunoglobulins, serum electrophoresis, monoclonal bands, surface markers, autoantibodies, and lymphocyte proliferation, two new methods, the rise of tetanus antibody concentration after vaccination and the in vitro resistance of lymphocytes to chromate, were used to diagnose the morphologic and functional state of the immune system. There was no stringent correlation of actual PCDD/PCDF concentrations with the occurrence of infections or with one of the immune parameters. In addition, outcomes of the tetanus vaccination and the chromate resistance test were not correlated with PCDD/PCDF. However, the chromate resistance of lymphocytes stimulated by phytohemagglutinin of highly exposed persons was significantly lower than that for the control group. These findings indicate that the function of lymphocytes can be stressed and possibly impaired by high exposure to PCDD/PCDF.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M. F., Gasiewicz T. A., Lamm K. R., Germolec D. R., Luster M. I. Selective inhibition of polymorphonuclear neutrophil activity by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;101(3):470–480. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. C., Blank J. A., Germolec D. R., Luster M. I. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation in B lymphocytes: potential role in immunosuppression. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;39(4):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Krey G. K., Kerkvliet N. I. Suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin occurs in vivo, but not in vitro, and is independent of corticosterone elevation. Toxicology. 1995 Mar 31;97(1-3):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(94)02929-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waal E. J., Schuurman H. J., Loeber J. G., Van Loveren H., Vos J. G. Alterations in the cortical thymic epithelium of rats after in vivo exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD): an (immuno)histological study. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;115(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(92)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst M., Flesch-Janys D., Morgenstern I., Manz A. Immune cell functions in industrial workers after exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: dissociation of antigen-specific T-cell responses in cultures of diluted whole blood and of isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Environ Health Perspect. 1998 Apr;106 (Suppl 2):701–705. doi: 10.1289/ehp.98106701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. G., Webb K. B., Knutsen A. P., Roodman S. T., Roberts D. W., Bagby J. R., Garrett W. A., Jr, Andrews J. S., Jr A medical follow-up of the health effects of long-term exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Arch Environ Health. 1988 Jul-Aug;43(4):273–278. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1988.10545949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch-Janys D., Becher H., Gurn P., Jung D., Konietzko J., Manz A., Päpke O. Elimination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in occupationally exposed persons. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1996 Mar;47(4):363–378. doi: 10.1080/009841096161708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funseth E., Ilbäck N. G. Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on blood and spleen natural killer (NK) cell activity in the mouse. Toxicol Lett. 1992 May;60(3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(92)90282-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. D., Smialowicz R. J. Evaluation of the effect of low-level 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure on cell mediated immunity. Toxicology. 1994 Mar 11;88(1-3):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(94)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. E., Stehr-Green P. A., Webb K. B., Evans R. G., Knutsen A. P., Schramm W. F., Staake J. L., Gibson B. B., Steinberg K. K. Health effects of long-term exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. JAMA. 1986 Apr 18;255(15):2031–2038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. M., Wild G., Ward J. D., Ward A. M. Immunological abnormalities 17 years after accidental exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Oct;45(10):701–704. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.10.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karras J. G., Holsapple M. P. Inhibition of calcium-dependent B cell activation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;125(2):264–270. doi: 10.1006/taap.1994.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer J., Gleichmann E., Esser C. Thymic stroma exposed to arylhydrocarbon receptor-binding xenobiotics fails to support proliferation of early thymocytes but induces differentiation. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2778–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. S., Becker S., Clark G. C., Devlin R. B., Koren H. S. Lack of direct immunosuppressive effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on human peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in vitro. Arch Toxicol. 1994;68(5):296–302. doi: 10.1007/s002040050072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L., Karras J. G., Holsapple M. P. Direct effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by isolated murine B-cells. Immunopharmacology. 1993 Sep-Oct;26(2):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(93)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert R., Helge H., Neubert D. Proliferative capacity of marmoset lymphocytes after tetanus vaccination and lack of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to reduce a booster effect. Life Sci. 1995;56(6):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00908-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert R., Jacob-Müller U., Helge H., Stahlmann R., Neubert D. Polyhalogenated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and the immune system. 2. In vitro effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on lymphocytes of venous blood from man and a non-human primate (Callithrix jacchus). Arch Toxicol. 1991;65(3):213–219. doi: 10.1007/BF02307311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert R., Maskow L., Delgado I., Helge H., Neubert D. Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and the human immune system. 2. In vitro proliferation of lymphocytes from workers with quantified moderately-increased body burdens. Life Sci. 1995;56(6):421–436. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00907-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert R., Maskow L., Webb J., Jacob-Müller U., Nogueira A. C., Delgado I., Helge H., Neubert D. Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and the human immune system. 1. Blood cell receptors in volunteers with moderately increased body burdens. Life Sci. 1993;53(26):1995–2006. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90021-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. G., Zober A., Germann C. Laboratory results for selected target organs in 138 individuals occupationally exposed to TCDD. Chemosphere. 1994 Nov-Dec;29(9-11):2423–2437. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(94)90411-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggiani G. Medical problems raised by the TCDD contamination in Seveso, Italy. Arch Toxicol. 1978 Jun 16;40(3):161–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00364649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstone A. E., Frazier D. E., Jr, Gasiewicz T. A. Alternate immune system targets for TCDD: lymphocyte stem cells and extrathymic T-cell development. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1994;11(2-3):94–101. doi: 10.1159/000424198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonn T., Esser C., Schneider E. M., Steinmann-Steiner-Haldenstätt W., Gleichmann E. Persistence of decreased T-helper cell function in industrial workers 20 years after exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Environ Health Perspect. 1996 Apr;104(4):422–426. doi: 10.1289/ehp.96104422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb K. B., Evans R. G., Knutsen A. P., Roodman S. T., Roberts D. W., Schramm W. F., Gibson B. B., Andrews J. S., Jr, Needham L. L., Patterson D. G. Medical evaluation of subjects with known body levels of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1989;28(2):183–193. doi: 10.1080/15287398909531339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. C., Jeong H. G., Morris D. L., Holsapple M. P. Direct effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on human tonsillar lymphocytes. Toxicology. 1993 Jul 28;81(2):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(93)90005-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. G., Lebrec H., Burleson G. R. Effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on pulmonary influenza virus titer and natural killer (NK) activity in rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1994 Jul;23(1):125–131. doi: 10.1006/faat.1994.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zober A., Ott M. G., Messerer P. Morbidity follow up study of BASF employees exposed to 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) after a 1953 chemical reactor incident. Occup Environ Med. 1994 Jul;51(7):479–486. doi: 10.1136/oem.51.7.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]