Abstract
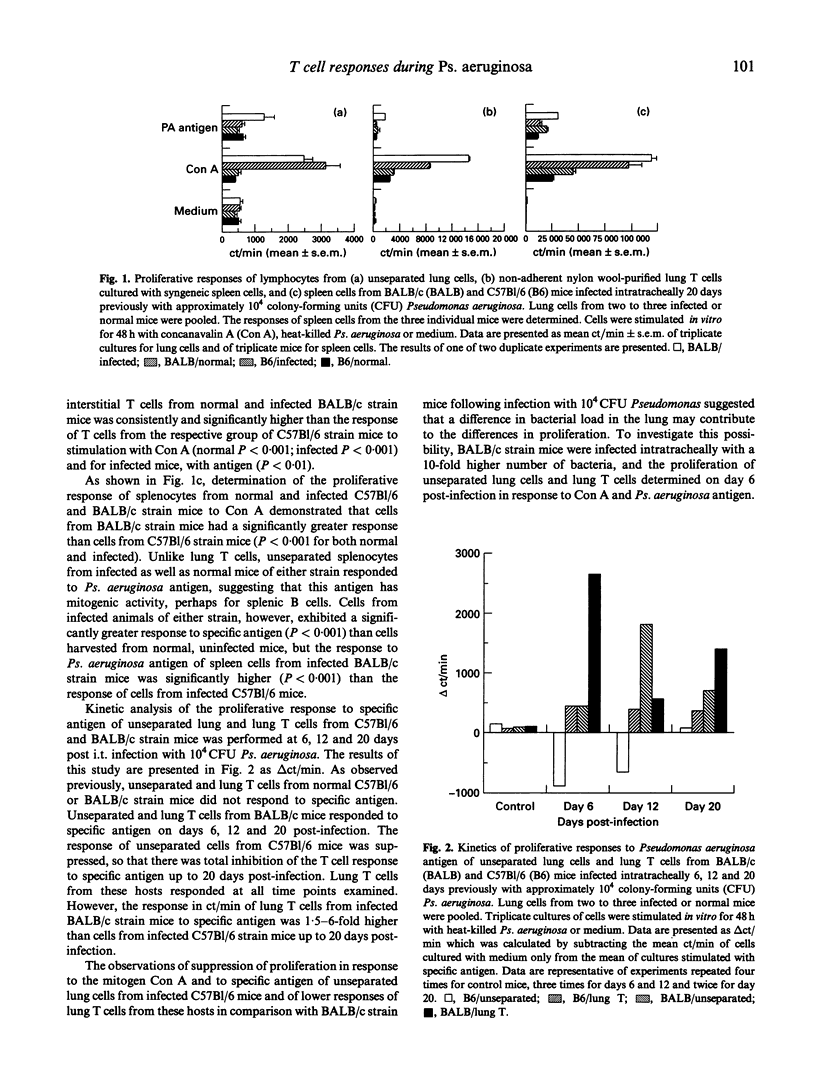
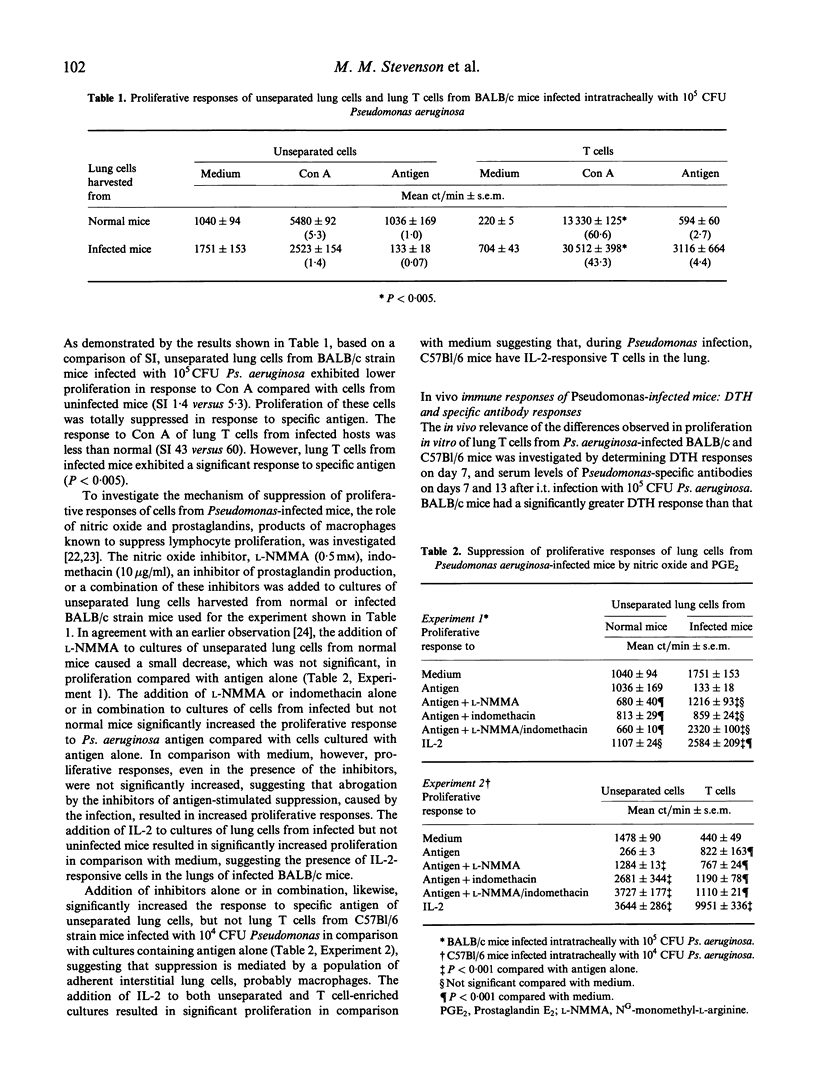
In vitro and in vivo T cell responses were determined during the course of bronchopulmonary infection with mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. T cell responses were compared in two inbred mouse strains, namely BALB/c mice, which are resistant to the establishment of chronic bronchopulmonary Ps. aeruginosa infection, and C57Bl/6 mice, which have high numbers of bacteria in the lungs through 14 days post-infection. Unseparated lung cells and lung T cells from BALB/c mice exhibited significantly higher in vitro proliferative responses to both heat-killed Ps. aeruginosa and concanavalin A (Con A) than cells from C57Bl/6 mice through 20 days post-intratracheal infection with 10(4) colony-forming units (CFU) Ps. aeruginosa. Proliferation of unseparated lung cells but not lung T cells from BALB/c mice infected 6 days previously with 10(5) CFU Ps. aeruginosa was suppressed in response to Con A; these cells were unresponsive to specific antigen. Suppression of lymphocyte proliferation in the lungs of C57Bl/6 mice infected with 10(4) CFU Ps. aeruginosa and in BALB/c mice infected with 10(5) CFU was found to be mediated by adherent lung cells via the production of nitric oxide and prostaglandins. Determination of in vivo T cell-mediated responses in infected mice demonstrated that resistant BALB/c mice had high DTH and low Pseudomonas-specific antibody responses, while C57Bl/6 mice had low DTH and high antibody levels, in particular, IgG2b and IgM.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apt A. S., Kramnik I. B., Moroz A. M. Regulation of T-cell proliferative responses by cells from solid lung tissue of M. tuberculosis-infected mice. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):173–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. Inflammation in the lung in cystic fibrosis. A vicious cycle that does more harm than good? Clin Rev Allergy. 1991 Spring-Summer;9(1-2):119–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-0475-6_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Preston M., Montgomery I. N., Hazlett L. D., Tse H. Y. Antibody hyporesponsiveness in resistant BALB/cJ mice intracorneally infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Reg Immunol. 1990;3(4):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash H. A., Woods D. E., McCullough B., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Welte K., Mertelsmann R., Dupont B. Prostaglandin E2 acts at two distinct pathways of T lymphocyte activation: inhibition of interleukin 2 production and down-regulation of transferrin receptor expression. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1172–1179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Shearer G. M. A TH1-->TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: immune status in patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):628–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.628-635.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorin J. R., Dickinson P., Alton E. W., Smith S. N., Geddes D. M., Stevenson B. J., Kimber W. L., Fleming S., Clarke A. R., Hooper M. L. Cystic fibrosis in the mouse by targeted insertional mutagenesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):211–215. doi: 10.1038/359211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Høiby N. Longitudinal study of immune response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):197–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.197-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greally P., Cook A. J., Sampson A. P., Coleman R., Chambers S., Piper P. J., Price J. F. Atopic children with cystic fibrosis have increased urinary leukotriene E4 concentrations and more severe pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Jan;93(1 Pt 1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Oliver J., Bilyk N., McMenamin C., McMenamin P. G., Kraal G., Thepen T. Downregulation of the antigen presenting cell function(s) of pulmonary dendritic cells in vivo by resident alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):397–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Robinson B. W., Reid M., Kees U. R., Warton A., Dawson V. H., Rose A., Schon-Hegrad M., Papadimitriou J. M. Extraction of immune and inflammatory cells from human lung parenchyma: evaluation of an enzymatic digestion procedure. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):188–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Isobe K. I., Hasegawa Y., Nakashima I., Shimokata K. Immunosuppressive activity induced by nitric oxide in culture supernatant of activated rat alveolar macrophages. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):72–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagacé J., Mercier J., Fréchette M., Fournier D., Dubreuil M., Lamarre A., Lapointe J. R., Montplaisir S. Circulating immune complexes, antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and pulmonary status in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1989 Sep;30(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. D. Molecular basis of "suppressor" macrophages. Arginine metabolism via the nitric oxide synthetase pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2719–2723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Hickey W. F., Blackwood L. L., Arnaut M. A. Active immunization with lipopolysaccharide Pseudomonas antigen for chronic Pseudomonas bronchopneumonia in guinea pigs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1140–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI110358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Small G. J., Warren H. B. Protection against mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rodent models of endobronchial infections. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):537–540. doi: 10.1126/science.2116663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porwoll J. M., Gebel H. M., Rodey G. E., Markham R. B. In vitro response of human T cells to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):670–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.670-674.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. W., Mansfield J. M. Suppressor macrophages in African trypanosomiasis inhibit T cell proliferative responses by nitric oxide and prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5492–5503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Coffman R. L. Regulation of immunity to parasites by T cells and T cell-derived cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:385–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snouwaert J. N., Brigman K. K., Latour A. M., Malouf N. N., Boucher R. C., Smithies O., Koller B. H. An animal model for cystic fibrosis made by gene targeting. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1083–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Chase P. A., Polmar S. H. Changes in lymphocyte reactivity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospitalized patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):37–41. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Chase P., Polmar S. H. Defective cellular immunity to gram-negative bacteria in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):398–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.398-402.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Polmar S. H. Cellular immunity to bacteria: impairment of in vitro lymphocyte responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.735-740.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Polmar S. H. Lymphocyte responsiveness to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: Relationship to status of pulmonary disease in sibling pairs. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke J. R., Edwards M. S., Langston C., Baker C. J. A mouse model of chronic pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia. Pediatr Res. 1987 Dec;22(6):698–702. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198712000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street N. E., Mosmann T. R. Functional diversity of T lymphocytes due to secretion of different cytokine patterns. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):171–177. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.1825981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Klinger J. D., Winnie G. B., Wood R. E., Burtner C., Tomashefski J. F., Horowitz J. G., Tandler B. Pulmonary cellular response to chronic irritation and chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in cats. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):741–747. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.741-747.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


