Abstract
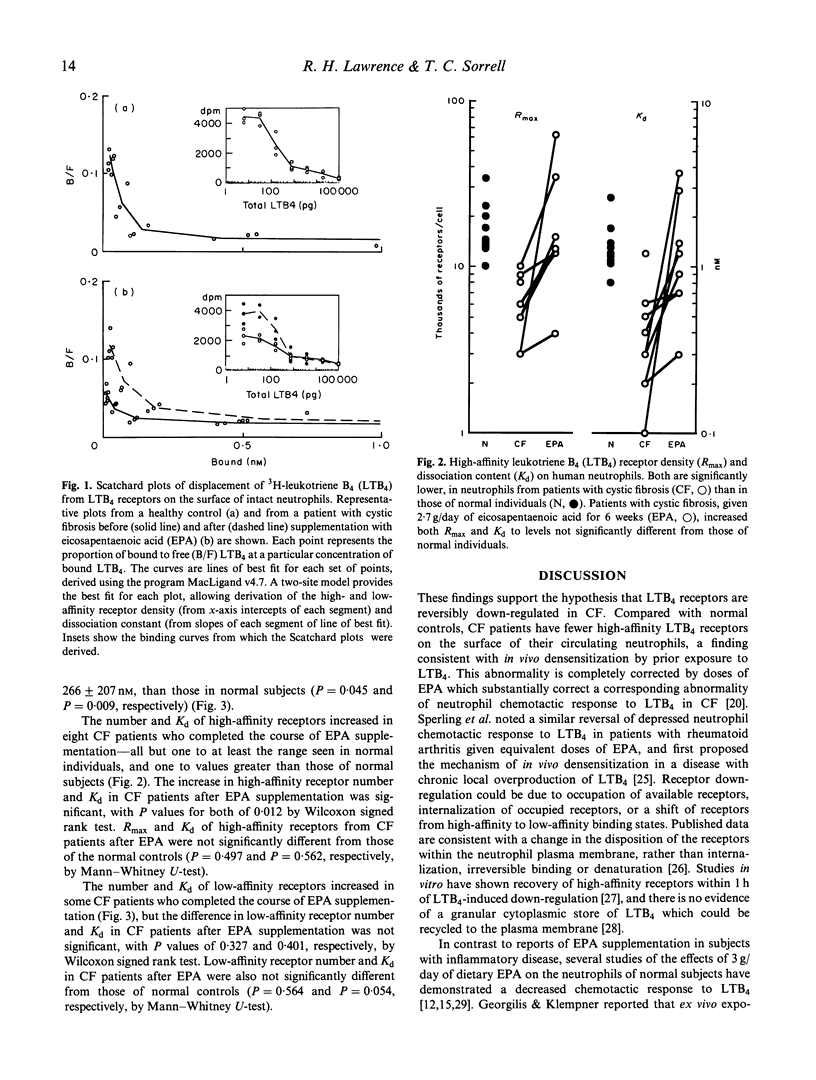
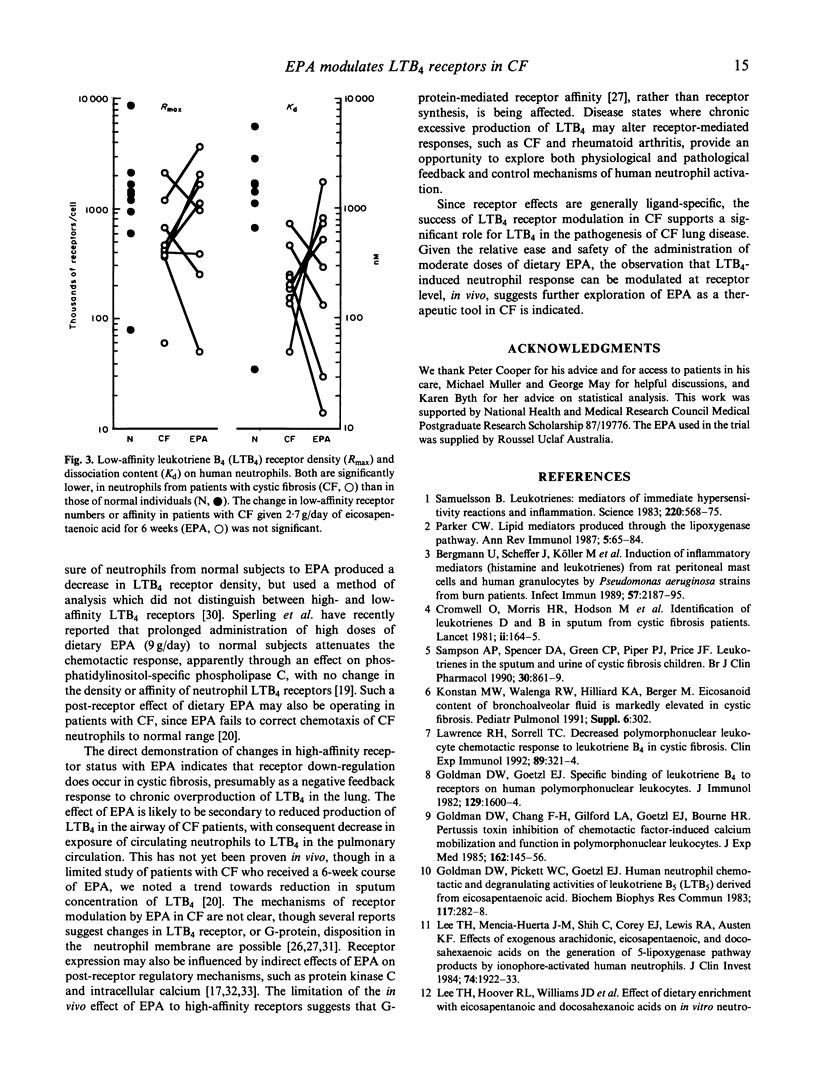
In patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), high intrapulmonary concentrations of the neutrophil chemotaxin leukotriene B4 (LTB4) are associated with specific reduction of LTB4-induced chemotaxis of circulating neutrophils. The chemotactic abnormality is partially corrected by dietary supplementation with eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). LTB4-induced neutrophil chemotaxis is mediated by specific, high-affinity, cell surface LTB4 receptors. The hypotheses that neutrophil LTB4 receptors are down-regulated in CF, and that EPA normalizes receptor expression, were tested by measuring the number (Rmax) and affinity (Kd) of LTB4 receptors on neutrophils from eight CF patients before and after EPA (6 weeks of 2.7 g/day), and from nine normal individuals. High-affinity receptor Rmax was depressed in CF patients (0.6 +/- 0.2 x 10(4)/cell (mean +/- s.d.) versus 1.8 +/- 0.7 x 10(4)/cell in normals), but corrected to normal (2.0 +/- 1.9 x 10(4)/cell) after EPA. High-affinity receptor Kd was depressed in CF patients (0.4 +/- 0.3 nM versus 1.4 +/- 0.5 nM in normals), and also corrected to normal with EPA (1.4 +/- 1.2 nM). Low-affinity receptors were depressed, but did not change significantly with EPA. These results indicate that neutrophil responses in chronic inflammatory lung disease can be influenced directly by LTB4 receptor modulation, and that this effect of EPA predominates over alterations in neutrophil signal transduction in situations of chronic exposure to LTB4.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. M., Burns D. J. Lipid activation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4661–4664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann U., Scheffer J., Köller M., Schönfeld W., Erbs G., Müller F. E., König W. Induction of inflammatory mediators (histamine and leukotrienes) from rat peritoneal mast cells and human granulocytes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from burn patients. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2187–2195. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2187-2195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. M., Koo C. H., Goetzl E. J. Down-regulation of receptor antigen in leukotriene B4-induced chemotactic deactivation of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):212–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brom J., König W. Studies on the uptake, binding and metabolism of leukotriene B4 by human neutrophils. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):479–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Walport M. J., Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Hodson M. E., Batten J., Kay A. B. Identification of leukotrienes D and B in sputum from cystic fibrosis patients. Lancet. 1981 Jul 25;2(8239):164–165. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90353-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Kelley V. E., Georgilis K., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Cannon J. G., Rogers T. S., Klempner M. S., Weber P. C. The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M., Upchurch K. S., Levine P. H., Johnson M. H., Vaudreuil C. H., Natale A., Hoogasian J. J. Effects of dietary fish oil supplementation on polymorphonuclear leukocyte inflammatory potential. Inflammation. 1986 Dec;10(4):387–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00915822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgilis K., Klempner M. S. In vitro effects of omega-3 fatty acids on neutrophil intracellular calcium homeostasis and receptor expression for FMLP and LTB4. Inflammation. 1988 Oct;12(5):475–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00919440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Chang F. H., Gifford L. A., Goetzl E. J., Bourne H. R. Pertussis toxin inhibition of chemotactic factor-induced calcium mobilization and function in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):145–156. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Gifford L. A., Marotti T., Koo C. H., Goetzl E. J. Molecular and cellular properties of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte receptors for leukotriene B4. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):200–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Goetzl E. J. Heterogeneity of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte receptors for leukotriene B4. Identification of a subset of high affinity receptors that transduce the chemotactic response. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1027–1041. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding of leukotriene B4 to receptors on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1600–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Pickett W. C., Goetzl E. J. Human neutrophil chemotactic and degranulating activities of leukotriene B5 (LTB5) derived from eicosapentaenoic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91572-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. H., Sorrelli T. C. Decreased polymorphonuclear leucocyte chemotactic response to leukotriene B4 in cystic fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):321–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R., Sorrell T. Eicosapentaenoic acid in cystic fibrosis: evidence of a pathogenetic role for leukotriene B4. Lancet. 1993 Aug 21;342(8869):465–469. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91594-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Hoover R. L., Williams J. D., Sperling R. I., Ravalese J., 3rd, Spur B. W., Robinson D. R., Corey E. J., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Effect of dietary enrichment with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on in vitro neutrophil and monocyte leukotriene generation and neutrophil function. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1217–1224. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Shih C., Corey E. J., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Effects of exogenous arachidonic, eicosapentaenoic, and docosahexaenoic acids on the generation of 5-lipoxygenase pathway products by ionophore-activated human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1922–1933. doi: 10.1172/JCI111612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. H., Ruppel P. L., Gorman R. R. Leukotriene B4 binding to human neutrophils. Prostaglandins. 1984 Dec;28(6):837–849. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(84)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Redman J. F., Jacobson D. P. Cyclical binding, processing, and functional interactions of neutrophils with leukotriene B4. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Feb;142(2):299–308. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Redman J. F., Jacobson D. P. Mechanisms involved in the bidirectional effects of protein kinase C activators on neutrophil responses to leukotriene B4. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1909–1913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Redman J. F., Jacobson D. P. Protein kinase C regulates leukotriene B4 receptors in human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80996-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W. Lipid mediators produced through the lipoxygenase pathway. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:65–84. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.000433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Wong M. Y., Chernov-Rogan T., Valone F. H., Pickett W. C., Blake V. A., Gold W. M., Goetzl E. J. Alterations in human leukocyte function induced by ingestion of eicosapentaenoic acid. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Sep;6(5):402–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00915380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson A. P., Spencer D. A., Green C. P., Piper P. J., Price J. F. Leukotrienes in the sputum and urine of cystic fibrosis children. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;30(6):861–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb05452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):568–575. doi: 10.1126/science.6301011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. B., Varming K., Pedersen J. O., Lervang H. H., Grunnet N., Jersild C., Dyerberg J. Long-term supplementation with n-3 fatty acids, II: Effect on neutrophil and monocyte chemotaxis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1992 May;52(3):229–236. doi: 10.3109/00365519209088790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speizer L. A., Watson M. J., Brunton L. L. Differential effects of omega-3 fish oils on protein kinase activities in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):E109–E114. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.1.E109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R. I., Benincaso A. I., Knoell C. T., Larkin J. K., Austen K. F., Robinson D. R. Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit phosphoinositide formation and chemotaxis in neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):651–660. doi: 10.1172/JCI116245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R. I., Weinblatt M., Robin J. L., Ravalese J., 3rd, Hoover R. L., House F., Coblyn J. S., Fraser P. A., Spur B. W., Robinson D. R. Effects of dietary supplementation with marine fish oil on leukocyte lipid mediator generation and function in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Sep;30(9):988–997. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terano T., Hirai A., Tamura Y., Kumagai A., Yoshida S. Effect of dietary supplementation of highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on arachidonic acid metabolism in leukocytes and leukocyte function in healthy volunteers. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1987;17B:880–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schacky C., Fahrer C., Fischer S. Catabolism of leukotriene B5 in humans. J Lipid Res. 1990 Oct;31(10):1831–1838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


