Abstract
In autoimmune rheumatic diseases, retroviruses have been repeatedly discussed as important etiologic factors. However, despite a considerable amount of indirect evidence that retroviruses might indeed be involved in triggering or perpetuating autoimmune rheumatic diseases, clear cut direct evidence is still missing. Studies on arthropathies associated with HIV-1 or HTLV-1 infection as well as new experimental animal models like the Tax transgene mice and new data from the MLR/lpr mouse model might help to answer the questions how and by what mechanisms retroviral infection may lead to autoimmune rheumatic diseases. From data obtained in the MLR/lpr mouse it seems obvious that a potential link of retroviruses, apoptosis and autogenes to autoimmune diseases opens exciting new approaches to the study of rheumatic disease pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Watanabe-Fukunaga R., Nagata S. Aberrant transcription caused by the insertion of an early transposable element in an intron of the Fas antigen gene of lpr mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1756–1760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aicher W. K., Heer A. H., Trabandt A., Bridges S. L., Jr, Schroeder H. W., Jr, Stransky G., Gay R. E., Eibel H., Peter H. H., Siebenlist U. Overexpression of zinc-finger transcription factor Z-225/Egr-1 in synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5940–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akbar A. N., Salmon M., Savill J., Janossy G. A possible role for bcl-2 in regulating T-cell memory--a 'balancing act' between cell death and survival. Immunol Today. 1993 Nov;14(11):526–532. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90181-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks K. L., Jutila M. A., Jacobs C. A., Michaels F. H. Augmentation of lymphocyte and macrophage proliferation by caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus contributes to the development of progressive arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(3-5):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00271868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman A., Espinoza L. R., Diaz J. D., Aguilar J. L., Rolando T., Vasey F. B., Germain B. F., Lockey R. F. Rheumatic manifestations of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Med. 1988 Jul;85(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom E. J., Abrams D. I., Rodgers G. Lupus anticoagulant in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1986 Jul 25;256(4):491–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumpas D. T., Popovic M., Mann D. L., Balow J. E., Tsokos G. C. Type C retroviruses of the human T cell leukemia family are not evident in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Feb;29(2):185–188. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brancato L., Itescu S., Skovron M. L., Solomon G., Winchester R. Aspects of the spectrum, prevalence and disease susceptibility determinants of Reiter's syndrome and related disorders associated with HIV infection. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(3-5):137–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00271870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese L. H. The rheumatic manifestations of infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1989 May;18(4):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Ribeiro J. M. Apoptosis and disease. Lancet. 1993 May 15;341(8855):1251–1254. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91154-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J. L., Drappa J., Parnassa A., Elkon K. B. The defect in Fas mRNA expression in MRL/lpr mice is associated with insertion of the retrotransposon, ETn. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):723–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang H., Dauphinée M. J., Talal N., Garry R. F., Seibold J. R., Medsger T. A., Jr, Alexander S., Feghali C. A. Serum antibody to retroviral gag proteins in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1336–1337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A., Sobelman S. Multiple overlapping homologies between two rheumatoid antigens and immunosuppressive viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6328–6332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flescher E., Dauphinée M. J., Fossum D., Ledbetter J., Talal N. Signal transduction in Sjögren's syndrome T cells. Abnormalities associated with a newly described human A-type retrovirus. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Sep;35(9):1068–1074. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. F. Extensive antigenic mimicry by retrovirus capsid proteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Dec;6(12):1361–1362. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. F., Fermin C. D., Hart D. J., Alexander S. S., Donehower L. A., Luo-Zhang H. Detection of a human intracisternal A-type retroviral particle antigenically related to HIV. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.1701273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Gay R. E. Cellular basis and oncogene expression of rheumatoid joint destruction. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(3-5):105–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00271866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
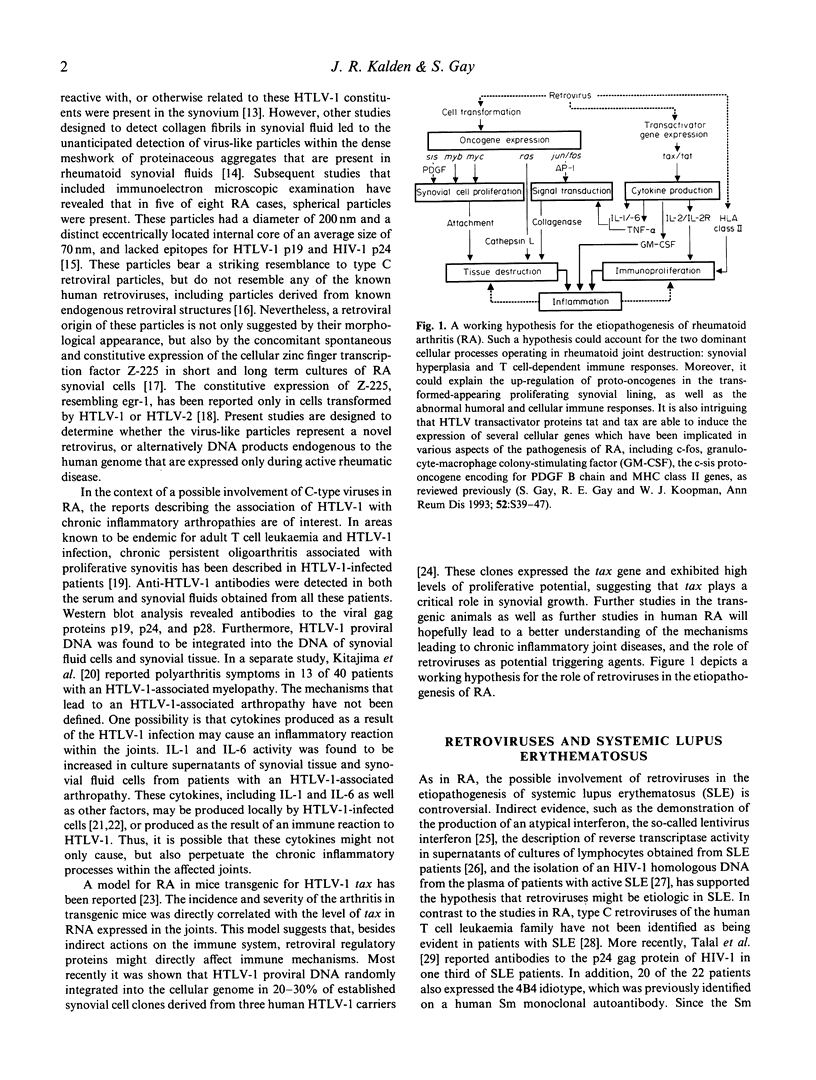
- Green J. E., Hinrichs S. H., Vogel J., Jay G. Exocrinopathy resembling Sjögren's syndrome in HTLV-1 tax transgenic mice. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):72–74. doi: 10.1038/341072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkiss G. D., Watt N. J., King T. J., Williams J., Hopkins J. Retroviral arthritis: phenotypic analysis of cells in the synovial fluid of sheep with inflammatory synovitis associated with visna virus infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jul;60(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90116-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Baur A., Nebel-Schickel H., Vornhagen R., Jahn G., Krapf F. E., Kalden J. R. Antibodies against p24 of HIV-1 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus? Viral Immunol. 1992 Fall;5(3):229–231. doi: 10.1089/vim.1992.5.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura Y., Tosu M., Yoshida E., Takiguchi M., Sato K., Kitajima I., Nishioka K., Yamamoto K., Takeda T., Hatanaka M. Induction of inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in mice transgenic for HTLV-I. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.1887217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalden J. R., Herrmann M. Autoimmune diseases in humans, e.g. autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Intervirology. 1993;35(1-4):176–185. doi: 10.1159/000150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy-Stoskopf S. Pathogenesis of lentivirus-induced arthritis. A review. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(3-5):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00271869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima I., Maruyama I., Maruyama Y., Ijichi S., Eiraku N., Mimura Y., Osame M. Polyarthritis in human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Oct;32(10):1342–1344. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Gay S. The MRL-lpr/lpr mouse. A model for the study of rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:284–289. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg A. M., Gourley M. F., Perl A. Endogenous retroviruses: potential etiologic agents in autoimmunity. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2537–2544. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1592206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E., Kato N., Cohen M. Human endogenous proviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;148:115–132. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74700-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer-Siuta R., Keil L. B., DeBari V. A. Autoantibodies and circulating immune complexes in subjects infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1988;177(4):189–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00211218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountz J. D., Talal N. Retroviruses, apoptosis and autogenes. Immunol Today. 1993 Nov;14(11):532–536. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90182-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Aono H., Hasunuma T., Yamamoto K., Maruyama I., Nosaka T., Hatanaka M., Nishioka K. Overgrowth of human synovial cells driven by the human T cell leukemia virus type I tax gene. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):186–193. doi: 10.1172/JCI116548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka K., Nakajima T., Hasunuma T., Sato K. Rheumatic manifestation of human leukemia virus infection. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993 May;19(2):489–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. G., Tarr M. J., Mathes L. E., Whisler R., Du Plessis D., Schulz E. J., Blakeslee J. R. Serological and virological evidence of human T-lymphotropic virus in systemic lupus erythematosus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(2):53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00200675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotz P. H. Autoantibodies are anti-idiotype antibodies to antiviral antibodies. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):824–826. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki A., Kurki P., Riepponen S., Stephansson E. Antibodies to retroviral proteins in autoimmune connective tissue disease. Relation to clinical manifestations and ribonucleoprotein autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Dec;35(12):1483–1491. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Bennett J. C. The infectious etiology of chronic rheumatic diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Aug;17(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(87)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Markham P. D., Lindner S. G., Gootenberg J., Popovic M., Hemmi H., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C. Lymphokine production by cultured human T cells transformed by human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus-I. Science. 1984 Feb 17;223(4637):703–707. doi: 10.1126/science.6320367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Maruyama I., Maruyama Y., Kitajima I., Nakajima Y., Higaki M., Yamamoto K., Miyasaka N., Osame M., Nishioka K. Arthritis in patients infected with human T lymphotropic virus type I. Clinical and immunopathologic features. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jun;34(6):714–721. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stransky G., Vernon J., Aicher W. K., Moreland L. W., Gay R. E., Gay S. Virus-like particles in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Dec;32(12):1044–1048. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.12.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Dauphinée M. J., Dang H., Alexander S. S., Hart D. J., Garry R. F. Detection of serum antibodies to retroviral proteins in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (autoimmune exocrinopathy). Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):774–781. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Garry R. F., Schur P. H., Alexander S., Dauphinée M. J., Livas I. H., Ballester A., Takei M., Dang H. A conserved idiotype and antibodies to retroviral proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1866–1871. doi: 10.1172/JCI114647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wano Y., Hattori T., Matsuoka M., Takatsuki K., Chua A. O., Gubler U., Greene W. C. Interleukin 1 gene expression in adult T cell leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):911–916. doi: 10.1172/JCI113152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Fukunaga R., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Nagata S. Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):314–317. doi: 10.1038/356314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Stanley S. D., Austin A. A., Matthews T. J., Bolognesi D. P. HIV-1 GP120-mediated immune suppression and lymphocyte destruction in the absence of viral infection. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3091–3097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. J., Gunter K. C., Mitsuya H., Irving S. G., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Expression of a zinc finger gene in HTLV-I- and HTLV-II-transformed cells. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):588–591. doi: 10.1126/science.2110381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Zhou T., He J., Mountz J. D. Autoimmune disease in mice due to integration of an endogenous retrovirus in an apoptosis gene. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):461–468. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Clerck L. S., Couttenye M. M., de Broe M. E., Stevens W. J. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome mimicking Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Feb;31(2):272–275. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


