Abstract
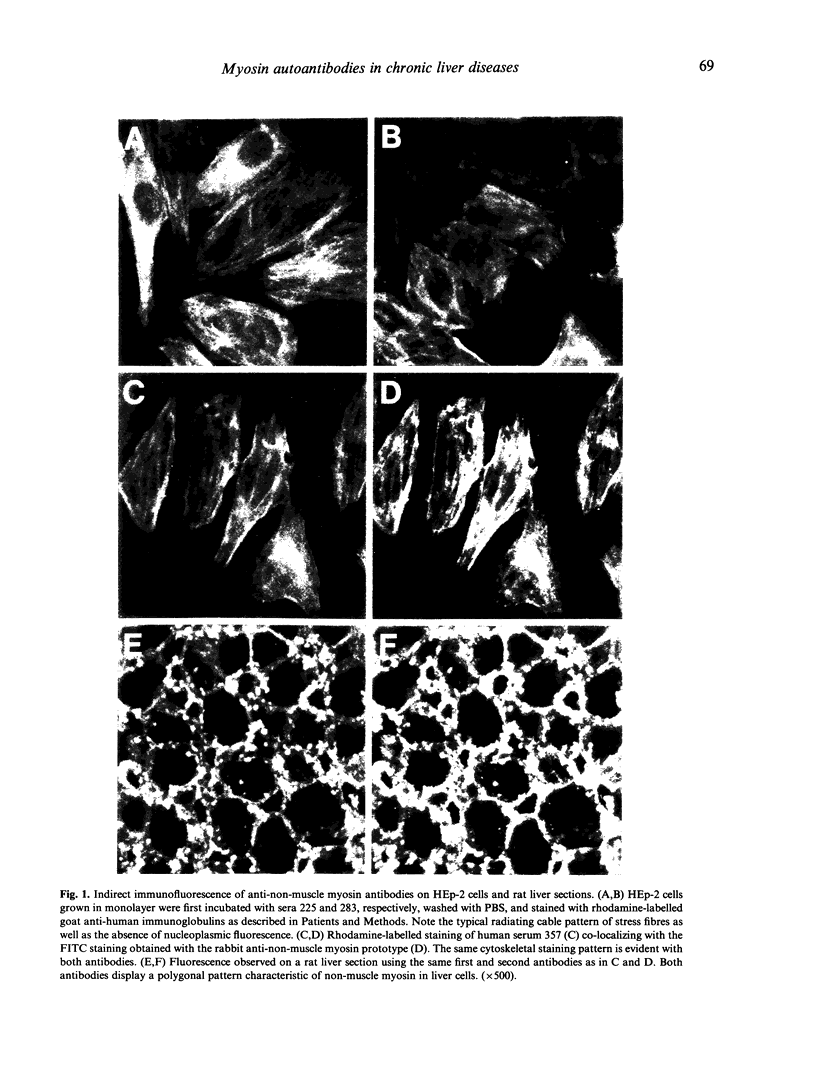
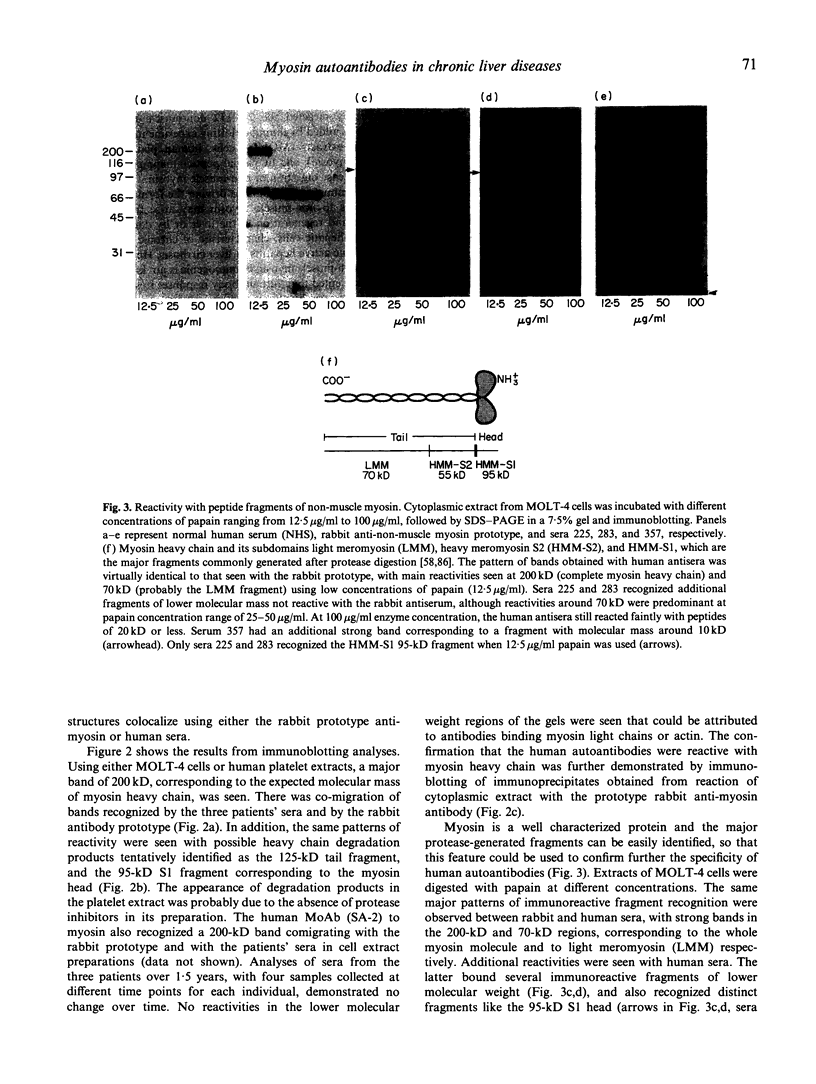
Three patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related chronic liver disease were shown to have autoantibodies strongly reacting with cytoskeletal fibres of non-muscle cells. The heavy chain of non-muscle myosin microfilament was the main target for those autoantibodies, as determined by (i) cell and tissue immunofluorescence studies showing colocalization with an anti-myosin antibody prototype; (ii) primary reactivity in immunoblotting with a 200-kD protein, using either MOLT-4 cells, human platelets, or affinity-purified non-muscle myosin as antigen extract; and (iii) immunoblotting of similar immunoreactive fragments in papain-digested MOLT-4 cell extracts, by using those human sera and antibody prototype. Autoantibodies to non-muscle myosin heavy chain were not previously reported in patients with chronic liver diseases, especially in those associated with HCV infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcover A., Molano J., Renart J., Gil-Aguado A., Nieto A., Avila J. Antibodies to vimentin intermediate filaments in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):922–928. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J. Descartes before the horse: I clone, therefore I am: the hepatitis C virus in current perspective. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Oct 15;115(8):644–649. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-8-644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Margolis H. S., Krawczynski K., Judson F. N., Mares A., Alexander W. J., Hu P. Y., Miller J. K., Gerber M. A., Sampliner R. E. The natural history of community-acquired hepatitis C in the United States. The Sentinel Counties Chronic non-A, non-B Hepatitis Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 31;327(27):1899–1905. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212313272702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacoub P., Musset L., Lunel Fabiani F., Perrin M., Leger J. M., Thi Huong Du L., Wechsler B., Bletry O., Opolon P., Huraux J. M. Hepatitis C virus and essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;32(8):689–692. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.8.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Francoeur A. M., Tan E. M. Epitopes, structural domains, and asymmetry of amino acid residues in SS-B/La nuclear protein. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3744–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citi S., Kendrick-Jones J. Localization of myosin in the cytoskeleton of brush border cells using monoclonal antibodies and confocal laser-beam scanning microscopy. Tissue Cell. 1991;23(6):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(91)90031-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citi S., Kendrick-Jones J. Regulation of non-muscle myosin structure and function. Bioessays. 1987 Oct;7(4):155–159. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEICHER H. R., HOLMAN H. R., KUNKEL H. G. Anti-cytoplasmic factors in the sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and certain other diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1960 Feb;3:1–15. doi: 10.1002/art.1780030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das K. M., Dasgupta A., Mandal A., Geng X. Autoimmunity to cytoskeletal protein tropomyosin. A clue to the pathogenetic mechanism for ulcerative colitis. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2487–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Scheerder I. K., De Buyzere M., Delanghe J., Maas A., Clement D. L., Wieme R. Humoral immune response against contractile proteins (actin and myosin) during cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 1991 Aug;12 (Suppl 500):88–94. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/12.suppl_d.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Scheerder I., Vandekerckhove J., Robbrecht J., Algoed L., De Buyzere M., De Langhe J., De Schrijver G., Clement D. Post-cardiac injury syndrome and an increased humoral immune response against the major contractile proteins (actin and myosin). Am J Cardiol. 1985 Oct 1;56(10):631–633. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(85)91024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Monot C., Abuaf N. Sera with high levels of anti-smooth muscle and anti-mitochondrial antibodies frequently bind to cytoskeleton proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Oct;82(1):52–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake S., Xu M., Piessens W. F. Myosin heavy chain is a dominant parasite antigen recognized by antibodies in sera from donors with filarial infections. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Dec;56(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90186-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairfax A. J., Gröschel-Stewart U. Myosin autoantibodies detected by immunofluorescence. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):27–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri C., Greco F., Longombardo G., Palla P., Moretti A., Marzo E., Fosella P. V., Pasero G., Bombardieri S. Antibodies to hepatitis C virus in patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Dec;34(12):1606–1610. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler V. M., Davis J. Q., Bennett V. Human erythrocyte myosin: identification and purification. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):47–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross W. L., Krüger J., Gröschel-Stewart U., Friedrich H., Kunze K. Studies on HLA antigens and cellular and humoral autoimmune phenomena in patients with myasthenia gravis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):48–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J., Deny P., Munz-Gotheil C., Ambrosini J. C., Trinchet J. C., Pateron D., Mal F., Callard P., Beaugrand M. Lymphocytic sialadenitis of Sjögren's syndrome associated with chronic hepatitis C virus liver disease. Lancet. 1992 Feb 8;339(8789):321–323. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91645-O. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsfall A. C., Rose L. M. Cross-reactive maternal autoantibodies and congenital heart block. J Autoimmun. 1992 Aug;5(4):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Gretch D. R., Yamabe H., Hart J., Bacchi C. E., Hartwell P., Couser W. G., Corey L., Wener M. H., Alpers C. E. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 18;328(7):465–470. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302183280703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P. Molecular genetic dissection of myosin heavy chain function. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90583-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosawa K., Furuta S. Clinical aspects and epidemiology of hepatitis B and C viruses in hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1992;31 (Suppl):S150–S156. doi: 10.1007/BF00687126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Helve T., Virtanen I. Antibodies to cytoplasmic intermediate filaments in rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 1983 Aug;10(4):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Miettinen A., Salaspuro M., Virtanen I., Stenman S. Cytoskeleton antibodies in chronic active hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):297–302. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson C. M., O'Donoghue H. L., Reed W. D. Mouse cytomegalovirus infection induces antibodies which cross-react with virus and cardiac myosin: a model for the study of molecular mimicry in the pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. Immunology. 1992 Mar;75(3):513–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E., Kurki P., Andersson L. C. Autoantibody to "intermediate filament" in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Dec;14(4):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariette X., Zerbib M., Jaccard A., Schenmetzler C., Danon F., Clauvel J. P. Hepatitis C virus and Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Feb;36(2):280–281. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayet W. J., Press A. G., Hermann E., Moll R., Manns M., Ewe K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Antibodies to cytoskeletal proteins in patients with Crohn's disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;20(5):516–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1990.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. M., Crossley C. A., Ayoub E. M., Harley J. B., Cunningham M. W. Poststreptococcal anti-myosin antibody idiotype associated with systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):915–921. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald B. L., Dawkins R. L., Robinson J. Myosin autoantibodies reacting with selective muscle fiber types. Muscle Nerve. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(1):37–43. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan S. A., Haire M. The specificity of IgG- and IgM-class smooth muscle antibody in the sera of patients with multiple sclerosis and active chronic hepatitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Oct;14(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel G., Ritter A., Gerken G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Decker R., Manns M. P. Anti-GOR and hepatitis C virus in autoimmune liver diseases. Lancet. 1992 Feb 1;339(8788):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels V. V., Moll P. P., Rodeheffer R. J., Miller F. A., Jr, Tajik A. J., Burnett J. C., Jr, Driscoll D. J., Thibodeau S. N., Ansari A. A., Herskowitz A. Circulating heart autoantibodies in familial as compared with nonfamilial idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994 Jan;69(1):24–27. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)61607-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishiro S., Hoshi Y., Takeda K., Yoshikawa A., Gotanda T., Takahashi K., Akahane Y., Yoshizawa H., Okamoto H., Tsuda F. Non-A, non-B hepatitis specific antibodies directed at host-derived epitope: implication for an autoimmune process. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1400–1403. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93101-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Barohn R. J., Krolick K. A. Unexpected cross-reactivity between myosin and a main immunogenic region (MIR) of the acetylcholine receptor by antisera obtained from myasthenia gravis patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Sep;64(3):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90203-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu N., Beisel K. W., Traystman M. D., Rose N. R., Craig S. W. Autoantibodies specific for the cardiac myosin isoform are found in mice susceptible to Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2488–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu N., Craig S. W., Rose N. R., Alvarez F., Beisel K. W. Coxsackievirus induced myocarditis in mice: cardiac myosin autoantibodies do not cross-react with the virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):566–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu N., Ploier B. Experimentally-induced autoimmune myocarditis: production of heart myosin-specific autoantibodies within the inflammatory infiltrate. Autoimmunity. 1991;8(4):317–322. doi: 10.3109/08916939109007639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D. A., Rose N. R., Ansari A. A., Herskowitz A. Induction of multiple heart autoantibodies in mice with coxsackievirus B3- and cardiac myosin-induced autoimmune myocarditis. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):343–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue H. L., Lawson C. M., Reed W. D. Autoantibodies to cardiac myosin in mouse cytomegalovirus myocarditis. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):20–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Turbyfill K. R. Myosin-cross-reactive epitope of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigen B. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):557–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.557-564.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A. S., Schotland D. L., Lamme S. Antimuscle and antiacetylcholine receptor antibodies in myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Jun;9(5):407–415. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A. S., Schotland D. L., Rowland L. P. Antibody to human myosin in man. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1969;94:48–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez C. G., Myers J. C., Shows T. B., Leinwand L. A. Human nonmuscle myosin heavy chain mRNA: generation of diversity through alternative polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senécal J. L., Ichiki S., Girard D., Raymond Y. Autoantibodies to nuclear lamins and to intermediate filament proteins: natural, pathologic or pathogenic? J Rheumatol. 1993 Feb;20(2):211–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senécal J. L., Oliver J. M., Rothfield N. Anticytoskeletal autoantibodies in the connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):889–898. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senécal J. L., Rauch J. Hybridoma lupus autoantibodies can bind major cytoskeletal filaments in the absence of DNA-binding activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jul;31(7):864–875. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. B., Cohn L., Nashel D. Rheumatic manifestations of hepatitis C infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;23(3):149–154. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(05)80035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Wang M., McBride O. W., Kawamoto S., Yamakawa K., Gdula D., Adelstein R. S., Weir L. Human nonmuscle myosin heavy chains are encoded by two genes located on different chromosomes. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):530–539. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. On the crawling of animal cells. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1086–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.8493552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J., Watanabe T., Nakamura N., Sobue K. Morphological and biochemical analyses of contractile proteins (actin, myosin, caldesmon and tropomyosin) in normal and transformed cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):595–606. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts R. S., McCormick T. S., Rowland E. C., Miller S. D., Engman D. M. Cardiac antigen-specific autoantibody production is associated with cardiomyopathy in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1493–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H. Anti-cytoskeletal autoantibodies: diagnostic significance for liver diseases, infections and systemic autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity. 1991;11(2):119–125. doi: 10.3109/08916939109035142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran A., Quaranta J. F., Benzaken S., Thiers V., Chau H. T., Hastier P., Regnier D., Dreyfus G., Pradier C., Sadoul J. L. High prevalence of thyroid autoantibodies in a prospective series of patients with chronic hepatitis C before interferon therapy. Hepatology. 1993 Aug;18(2):253–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Kinoshita R., Kishimoto I., Okamoto S. Polyarthritis associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Mar;33(3):289–291. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.3.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Ueno S., Hazama T., Ogasahara S., Kang J., Takahashi M., Tarui S. Radioimmunoassay for antibodies to human skeletal muscle myosin in serum from patients with polymyositis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 May;52(2):297–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., Spudich J. A. Myosin structure and function in cell motility. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:379–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. L., Lennon V. A., Momoi M. Y., Howard F. M., Jr Serum antibodies and monoclonal antibodies secreted by thymic B-cell clones from patients with myasthenia gravis define striational antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;505:168–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb51290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. L., Lennon V. A. Thymic B lymphocyte clones from patients with myasthenia gravis secrete monoclonal striational autoantibodies reacting with myosin, alpha actinin, or actin. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1043–1059. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A. M., Cresteil D., Homberg J. C., Alvarez F. Characterization of anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody (anti-LKM1) from hepatitis C virus-positive and -negative sera. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1762–1767. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuura S., Ueno T., Watanabe S., Hirose M., Namihisa T. Immunocytochemical localization of myosin in normal and phalloidin-treated rat hepatocytes. Gastroenterology. 1989 Oct;97(4):982–989. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Hsu K. C., Seegal B. C. Heart-reactive antibody associated with rheumatic fever: characterization and diagnostic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):147–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Scheerder I. K., de Buyzere M. L., Delanghe J. R., Clement D. L., Wieme R. J. Anti-myosin humoral immune response following cardiac injury. Autoimmunity. 1989;4(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.3109/08916938909034359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]