Abstract
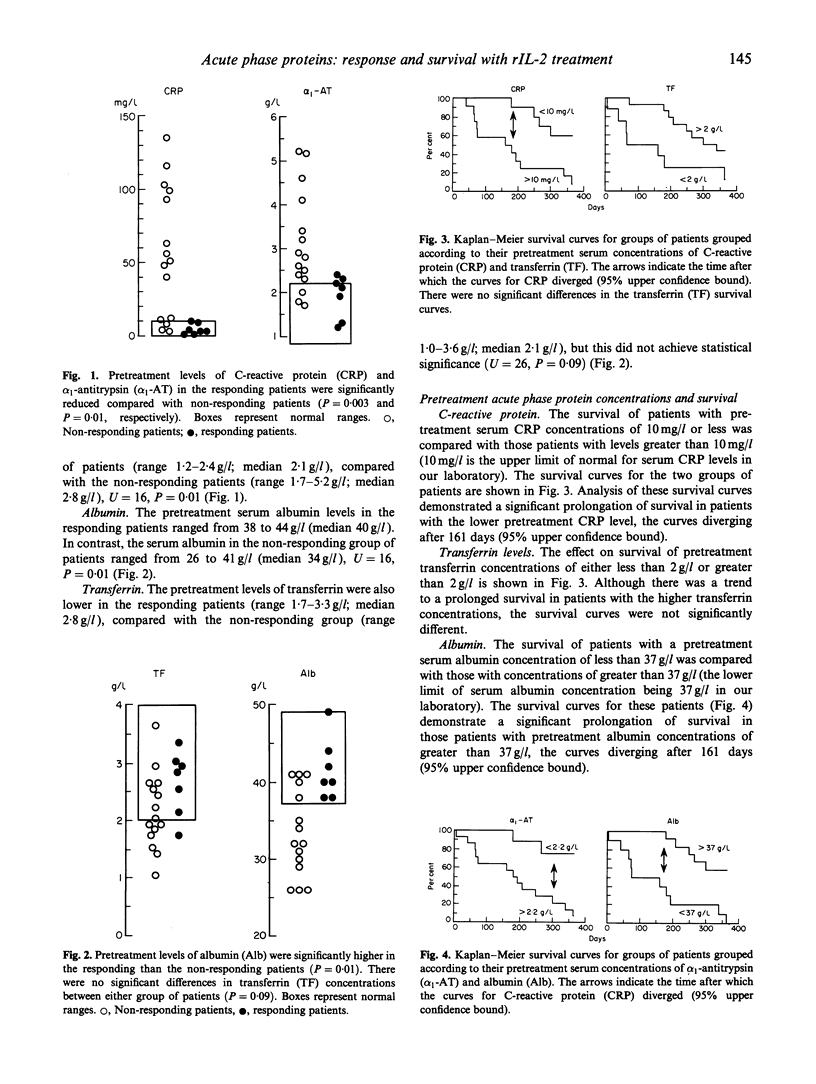
Twenty-four patients with metastatic colorectal cancer were treated with recombinant IL-2 (rIL-2) by continuous intravenous infusion for 5 days (18 x 10(6) U/m2 per 24 h), followed by three injections of 5-fluorouracil (600 mg/m2) and folinic acid (25 mg/m2) at weekly intervals. The response to treatment was assessed using standard UICC criteria (partial or complete response, stasis or progression of disease). The serum concentrations of the acute phase proteins; C-reactive protein (CRP), retinol binding protein (RBP), alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha 1-AT), transferrin (TF) and albumin were measured. A response to therapy occurred in the tumours of seven (29%) of the 24 patients (two complete and five partial responses). All patients who demonstrated a response to treatment had a serum albumin level of > 37 g/l and a CRP level of < or = 10 mg/l. In contrast, of the 17 patients who did not respond to therapy, 12 (71%) had a serum albumin of less than 37 g/dl and a CRP of greater than 10 mg/l. Examination of the survival times of the 12 patients who had a pretreatment serum albumin level of less than 37 g/l revealed that all had died within 12 months of cessation of therapy. However, 58% of patients with pretreatment serum albumin levels of greater than 37 g/l survived for longer than 12 months. These results have shown that (i) patients who respond to rIL-2-based therapy and (ii) those patients who have prolonged survival times, can be identified by pretreatment measurement of serum levels of acute phase proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou S. P., Kushner I. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. Adv Intern Med. 1992;37:313–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr L. C., Skene A. I., Thomas J. M. Metastasectomy. Br J Surg. 1992 Dec;79(12):1268–1274. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800791207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry W. R., Laszlo J., Cox E., Walker A., Paulson D. Prognostic factors in metastatic and hormonally unresponsive carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer. 1979 Aug;44(2):763–775. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197908)44:2<763::aid-cncr2820440251>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J. Y., Negrier S., Combaret V., Attali S., Goillot E., Merrouche Y., Mercatello A., Ravault A., Tourani J. M., Moskovtchenko J. F. Serum level of interleukin 6 as a prognosis factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 15;52(12):3317–3322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J. Y., Négrier S., Philip T., Favrot M., Mercatello A. Pretreatment serum CRP and response to interleukin 2. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jan;69(1):200–201. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broom J., Heys S. D., Whiting P. H., Park K. G., Strachan A., Rothnie I., Franks C. R., Eremin O. Interleukin 2 therapy in cancer: identification of responders. Br J Cancer. 1992 Dec;66(6):1185–1187. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner H. W., Motwani B. T. Chemotherapy of advanced cancer of the colon and rectum. Semin Oncol. 1991 Oct;18(5):443–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper E. H. Acute phase reactant proteins as prognostic indicators in cancer. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1988 Dec;13(6):361–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deehan D. J., Heys S. D., Simpson W. G., Broom J., Franks C., Eremin O. In vivo cytokine production and recombinant interleukin 2 immunotherapy: an insight into the possible mechanisms underlying clinical responses. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jun;69(6):1130–1135. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Hasselgren P. O. Cytokines and glucocorticoids in the regulation of the "hepato-skeletal muscle axis" in sepsis. Am J Surg. 1991 Feb;161(2):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(91)91143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A. Clinical and nutritional aspects of changes in acute-phase proteins during inflammation. Proc Nutr Soc. 1989 Sep;48(3):347–354. doi: 10.1079/pns19890050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Colley C. M., Myers M. A. Liver export proteins and trauma. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jul;41(3):265–273. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Mold C., Siegel J., Fiedel B. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. Adv Intern Med. 1982;27:345–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Robb R. J., Roth J. A., Neckers L. M., Lachman L. B., Wilson D. J., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. III. Evidence that IL-2 is sufficient for direct activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes into lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1356–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heys S. D., Franks C. R., Eremin O. Interleukin 2 therapy: current role in surgical oncological practice. Br J Surg. 1993 Feb;80(2):155–162. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The phenomenon of the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafreniere R., Rosenberg S. A. Successful immunotherapy of murine experimental hepatic metastases with lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3735–3741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic S., Jahreis G. P., Wong G. G., Baumann H. IL-6 modulates the synthesis of a specific set of acute phase plasma proteins in vivo. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):808–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki S., Iwano M., Miki Y., Yamamoto M., Tang B., Yokokawa K., Sonoda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) functions as an in vitro autocrine growth factor in renal cell carcinomas. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80805-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. B., Hoogstraten B., Staquet M., Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981 Jan 1;47(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<207::aid-cncr2820470134>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Shu S., Schwarz S. L., Rosenberg S. A. Adoptive immunotherapy of established pulmonary metastases with LAK cells and recombinant interleukin-2. Science. 1984 Sep 28;225(4669):1487–1489. doi: 10.1126/science.6332379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Quigley J., Haworth S., Cooper E. H., Haije W., van der Werf-Messing B., Richards B., Robinson M. R. Prognostic significance of serum proteins in invasive bladder cancer. A preliminary report of the E.O.R.T.C. Urological Group. Eur J Cancer. 1981 Feb;17(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(81)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A. T., Gerard J. P., Henderson L. E., Farrar W., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Herberman R. B., Rabin H. Effects of natural and recombinant IL 2 on regulation of IFN gamma production and natural killer activity: lack of involvement of the Tac antigen for these immunoregulatory effects. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):779–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirott M. N., Bajorin D. F., Wong G. Y., Tao Y., Chapman P. B., Templeton M. A., Houghton A. N. Prognostic factors in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma. A multivariate analysis. Cancer. 1993 Nov 15;72(10):3091–3098. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931115)72:10<3091::aid-cncr2820721034>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg J. C. A rate nephelometer for measuring specific proteins by immunoprecipitin reactions. Clin Chem. 1977 Aug;23(8):1456–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J., Tosato G. Impairment of natural killer functions by interleukin 6 increases lymphoblastoid cell tumorigenicity in athymic mice. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):239–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI115283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umpleby H. C., Bristol J. B., Rainey J. B., Williamson R. C. Survival of 727 patients with single carcinomas of the large bowel. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984 Dec;27(12):803–810. doi: 10.1007/BF02553944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Gewurz H., Hansen B., James K., Baum L. L. Effects of C-reactive protein on human lymphocyte responsiveness. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. S. Changing patterns in the treatment of rectal cancer. Br J Surg. 1989 Jan;76(1):5–6. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lowenthal J. W., Erard F., Hashimoto N., Devos R., MacDonald H. R. Activated B cells express receptors for, and proliferate in response to, pure interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1170–1183. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mello J., Struthers L., Turner R., Cooper E. H., Giles G. R. Multivariate analyses as aids to diagnosis and assessment of prognosis in gastrointestinal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1983 Sep;48(3):341–348. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1983.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


