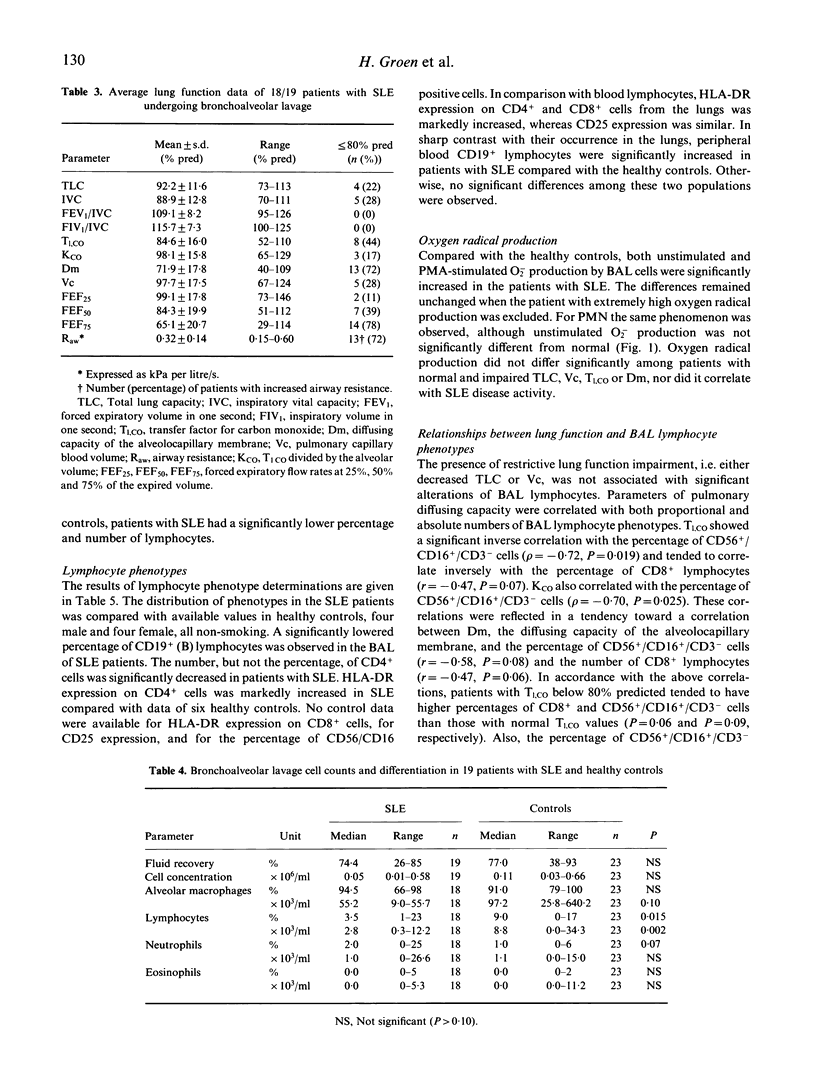
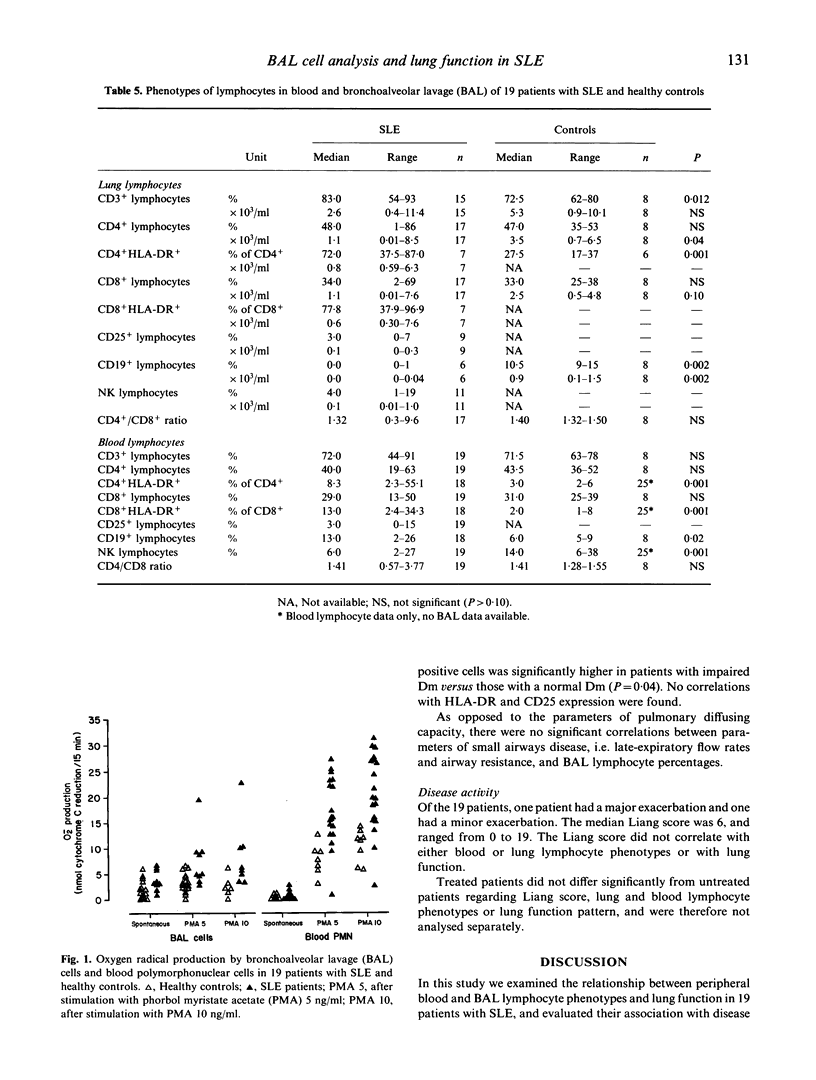
Abstract
We examined the relationship between peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) lymphocyte phenotypes and lung function in 19 patients with SLE, and evaluated their association with disease activity. Lung function assessment showed a mildly restrictive pattern with frequent impairment of transfer factor for carbon monoxide (T1,co) and diffusing capacity of the alveolocapillary membrane (Dm), of late-expiratory airflow rates and with a high prevalence of increased airway resistance. T1,co, Kco and Dm correlated inversely with the numbers of CD8+ cells and CD56+/CD16+/CD3- (NK) cells in BAL. Oxygen radical production, both by stimulated and unstimulated BAL cells and blood polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) was significantly increased in SLE. In comparison with healthy controls, patients with SLE had a lower percentage of CD19+ B cells in the BAL versus an increased percentage of these cells in peripheral blood. HLA-DR expression on CD4+ and CD8+ lung lymphocytes was markedly increased in SLE. Current SLE disease activity was not associated with changes in BAL or peripheral blood lymphocyte phenotypes. Our data suggest that an ongoing cell-mediated immune response is present in the lungs in SLE, particularly involving activated CD8+ T cells and CD56+/CD16+/CD3- NK cells. It is associated with up-regulated local production of oxygen radicals and with impaired pulmonary diffusing capacity. This inflammatory process seems to be independent of general SLE disease activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andonopoulos A. P., Constantopoulos S. H., Galanopoulou V., Drosos A. A., Acritidis N. C., Moutsopoulos H. M. Pulmonary function of nonsmoking patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chest. 1988 Aug;94(2):312–315. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos G., Majoor G., Slaaf D., Reneman R., van Breda Vriesman P. In vivo demonstration of microvascular pathology by intravital microscopy in experimental chronic graft-versus-host disease: analogy with scleroderma. J Rheumatol. 1988 Sep;15(9):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., Andres G. A. The pathogenesis of extrarenal lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):880–886. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., O'Connell D. W., Pawlowski I. B., Hsu K. C., Andres G. A. Experimental immune complex disease of the lung. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling certain human interstitial lung diseases. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):105–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Berton G., Agostini C., Zambello R., Trentin L., Cipriani A., Semenzato G. Generation of superoxide anion by alveolar macrophages in sarcoidosis: evidence for the activation of the oxygen metabolism in patients with high-intensity alveolitis. Immunology. 1989 Mar;66(3):451–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick T. W., DeHoratius R. J., Skipper B. E., Messner R. P. Pulmonary dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus without pulmonary symptoms. J Rheumatol. 1976 Sep;3(3):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker J. L., Steinberg A. D., Reinertsen J. L., Plotz P. H., Balow J. E., Klippel J. H. NIH conference. Systemic lupus erythematosus: evolving concepts. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):587–604. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H., Dubois E. L., Sherwin R. P., Balchum O. J. Diffuse interstitial lung disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jul;79(1):37–45. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Howie A. D., Moran F., Buchanan W. W. Pulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Dec;37(6):536–539. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.6.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groen H., Wichers G., ter Borg E. J., van der Mark T. W., Wouda A. A., Kallenberg C. G. Pulmonary diffusing capacity disturbances are related to nailfold capillary changes in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon with and without an underlying connective tissue disease. Am J Med. 1990 Jul;89(1):34–41. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90095-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groen H., ter Borg E. J., Postma D. S., Wouda A. A., van der Mark T. W., Kallenberg C. G. Pulmonary function in systemic lupus erythematosus is related to distinct clinical, serologic, and nailfold capillary patterns. Am J Med. 1992 Dec;93(6):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90194-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Kanayama Y., Ohe A., Kato N., Horiguchi T., Ishii M., Shiota K. Immunopathologic studies of pneumonitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jul;91(1):30–34. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B. Soluble immunologic products in scleroderma sera. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jan;58(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen O., Salorinne V., Poppius H. Respiratory function in systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Nov;32(6):531–535. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.6.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley T. J., Peck G. L., Moutsopoulos H. M., Gratwohl A. A., Deisseroth A. B. Scleroderma, Sjögren-like syndrome, and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Dec;87(6):707–709. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-6-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang M. H., Socher S. A., Larson M. G., Schur P. H. Reliability and validity of six systems for the clinical assessment of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Sep;32(9):1107–1118. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L., Hurd E. R., Lewis D. C., Ziff M. Evidence of microvascular injury in scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus: quantitative study of the microvascular bed. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jun;71(6):919–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. R., Paradis I. L., Gryzan S., Medsger T. A., Jr, Follansbee W. P., Klein H. A., Dauber J. H. Role of inflammation in the lung disease of systemic sclerosis: comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Mar;107(3):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertschuk L. P., Moccia L. F., Rosen Y., Lyons H., Marino C. M., Rashford A. A., Wollschlager C. M. Acute pulmonary complications in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunofluorescence and light microscopic study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Nov;68(5):553–557. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma D. S., Renkema T. E., Noordhoek J. A., Faber H., Sluiter H. J., Kauffman H. Association between nonspecific bronchial hyperreactivity and superoxide anion production by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in chronic air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jan;137(1):57–61. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUGHTON F. J., FORSTER R. E. Relative importance of diffusion and chemical reaction rates in determining rate of exchange of gases in the human lung, with special reference to true diffusing capacity of pulmonary membrane and volume of blood in the lung capillaries. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Sep;11(2):290–302. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman H. M., Sullivan K. M., Weiden P. L., McDonald G. B., Striker G. E., Sale G. E., Hackman R., Tsoi M. S., Storb R., Thomas E. D. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):204–217. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Stokes L., Turner-Warwick M. Intrathoracic manifestations of SLE. Clin Rheum Dis. 1982 Apr;8(1):229–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallaert B., Dugas M., Dansin E., Perez T., Marquette C. H., Ramon P., Tonnel A. B., Voisin C. Subclinical alveolitis in immunological systemic disorders. Transition between health and disease? Eur Respir J. 1990 Nov;3(10):1206–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H. P., Matthay R. A. Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Thorac Imaging. 1992 Mar;7(2):1–18. doi: 10.1097/00005382-199203000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- du Bois R. M. Recent advances in the immunology of interstitial lung disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Jan;21(1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb00798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Borg E. J., Horst G., Hummel E. J., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):634–643. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


