Abstract
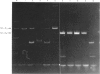
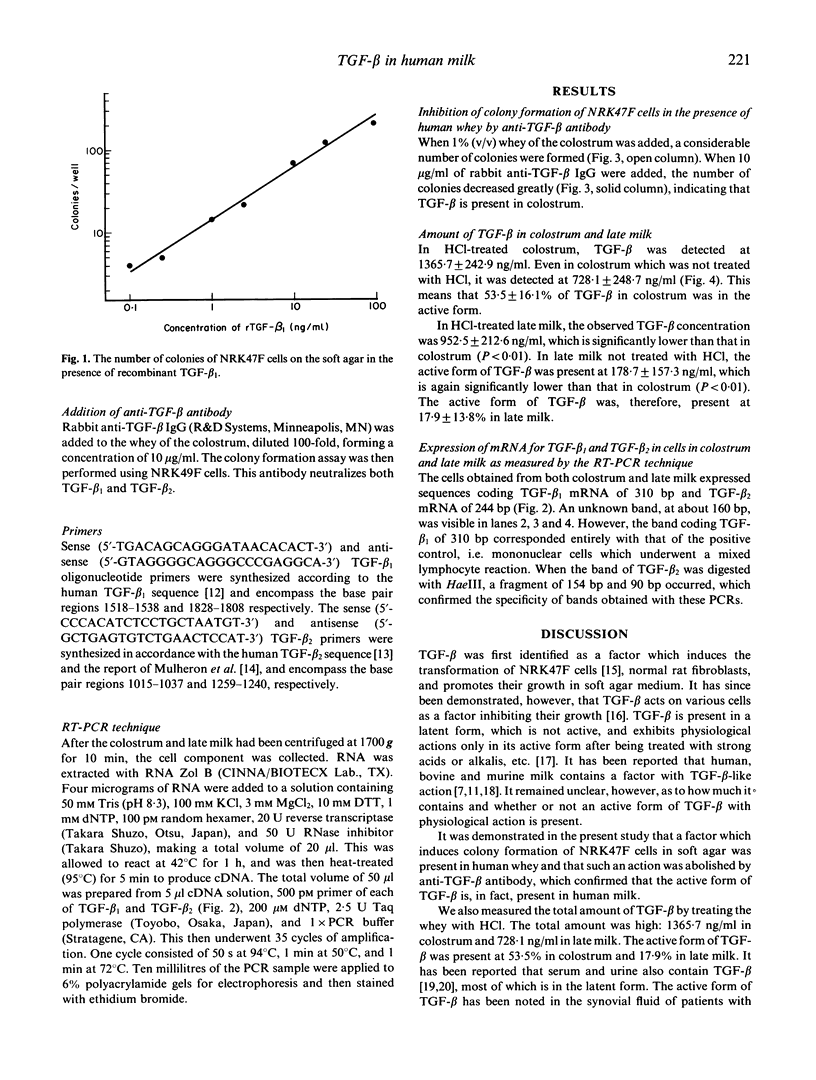
The amount of TGF-beta contained in human whey was studied by the colony formation of NRK47F cells. It was noted that a factor inducing colony formation did exist in human whey, and its action was neutralized when anti-TGF-beta antibodies were introduced. This suggests that TGF-beta does exist in human whey. In colostrum, the total amount of TGF-beta was 1365.7 +/- 242.9 ng/ml, of which the active form comprised 728.1 +/- 248.7 ng/ml (n = 21). In late milk, the total TGF-beta was 952.5 +/- 212.6 ng/ml, with an active form of 178.7 +/- 157.3 ng/ml. Thus human milk contains a large amount of active TGF-beta. Furthermore, it was revealed by the reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction that mRNAs coding TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 exist in human milk cells. These results suggest that both TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 exist in human milk.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brennan F. M., Chantry D., Turner M., Foxwell B., Maini R., Feldmann M. Detection of transforming growth factor-beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue: lack of effect on spontaneous cytokine production in joint cell cultures. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):278–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor is a major growth-promoting agent in human milk. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):198–199. doi: 10.1126/science.6968093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K., Puri S., Cheema P. S. Predictive value of cord blood IgE in the development of atopic disease and role of breast-feeding in its prevention. Clin Allergy. 1985 Nov;15(6):517–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb02304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs C. B., Proper J. A., Tucker R. F., Moses H. L. Serum contains a platelet-derived transforming growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5312–5316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. A., Bürk R. R. Isolation and characterisation of milk growth factor, a transforming-growth-factor-beta 2-related polypeptide, from bovine milk. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):353–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel C. W., Robinson S. D. Regulation of mammary growth and function by TGF-beta. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992 Jun;32(2):145–151. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080320210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Flanders K. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Immunodetection and quantitation of the two forms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2) secreted by cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):79–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y., Cox D. A., Knecht R., Raschdorf F., Cerletti N. Separation, purification, and sequence identification of TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 from bovine milk. J Protein Chem. 1991 Oct;10(5):565–575. doi: 10.1007/BF01025484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki T., Olofsson A., Morén A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Miyazono K., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. TGF-beta 1 binding protein: a component of the large latent complex of TGF-beta 1 with multiple repeat sequences. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90069-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. H., Kagnoff M. F. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 is a costimulator for IgA production. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L. Proteolytic activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta from fibroblast-conditioned medium. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1659–1665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Role for carbohydrate structures in TGF-beta 1 latency. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):158–160. doi: 10.1038/338158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulheron G. W., Bossert N. L., Lapp J. A., Walmer D. K., Schomberg D. W. Human granulosa-luteal and cumulus cells express transforming growth factors-beta type 1 and type 2 mRNA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Feb;74(2):458–460. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.2.1370508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness J. C., Morgan L., Outzen H. C., Tapper D. Specific growth factor activity identifies and predicts murine mammary tumor. J Surg Res. 1991 Jan;50(1):6–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda K., Umeda M., Ono T. Transforming growth factor activity in human colostrum. Gan. 1984 Feb;75(2):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrides P. E., Hosang M., Shooter E., Esch F. S., Böhlen P. Isolation and characterization of epidermal growth factor from human milk. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:107–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito S., Maruyama M., Kato Y., Moriyama I., Ichijo M. Detection of IL-6 in human milk and its involvement in IgA production. J Reprod Immunol. 1991 Sep;20(3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(91)90051-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein G. B., Strickland P., Coleman S., Daniel C. W. Epithelium-dependent extracellular matrix synthesis in transforming growth factor-beta 1-growth-inhibited mouse mammary gland. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2209–2219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha S. K., Yunis A. A. Isolation of colony stimulating factor from human milk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):797–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90852-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeck M., Ruegg C., Miescher S., Carrel S., Cox D., Von Fliedner V., Alkan S. Comparison of the immunosuppressive properties of milk growth factor and transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3258–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söder O. Isolation of interleukin-1 from human milk. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;83(1):19–23. doi: 10.1159/000234325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyama H., Tokuyama Y. Bovine colostric transforming growth factor-beta-like peptide that induces growth inhibition and changes in morphology of human osteogenic sarcoma cells (MG-63). Cell Biol Int Rep. 1989 Mar;13(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(89)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Sherwin S. A., Ranchalis J., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors in the urine of normal, pregnant, and tumor-bearing humans. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Oct;69(4):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi H., Suzuki S., Noji T., Nagashima K., Kuroume T. Epidermal growth factor in cow's milk and milk formulas. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Mar;75(2):233–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zugmaier G., Lippman M. E. Effects of TGF beta on normal and malignant mammary epithelium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;593:272–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwiebel J. A., Bano M., Nexo E., Salomon D. S., Kidwell W. R. Partial purification of transforming growth factors from human milk. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):933–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4001–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martin R., Haendler B., Hofer-Warbinek R., Gaugitsch H., Wrann M., Schlüsener H., Seifert J. M., Bodmer S., Fontana A., Hofer E. Complementary DNA for human glioblastoma-derived T cell suppressor factor, a novel member of the transforming growth factor-beta gene family. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3673–3677. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vlasselaer P., Punnonen J., de Vries J. E. Transforming growth factor-beta directs IgA switching in human B cells. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2062–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]