Abstract
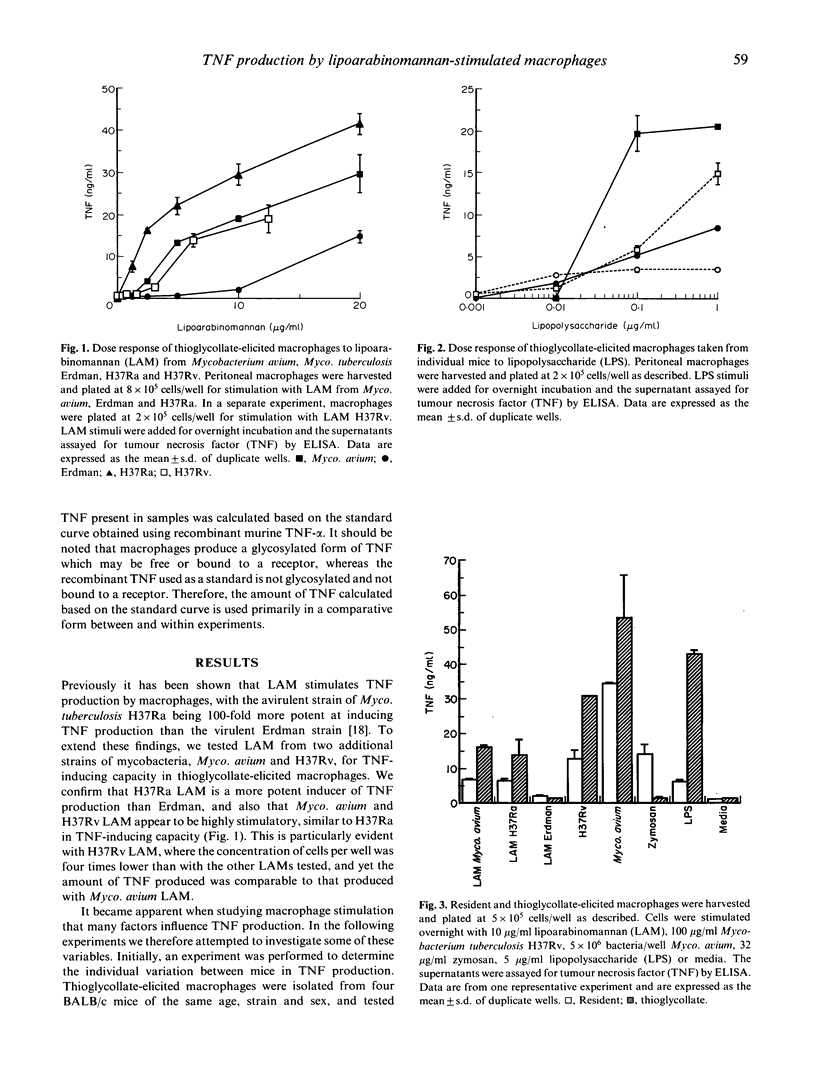
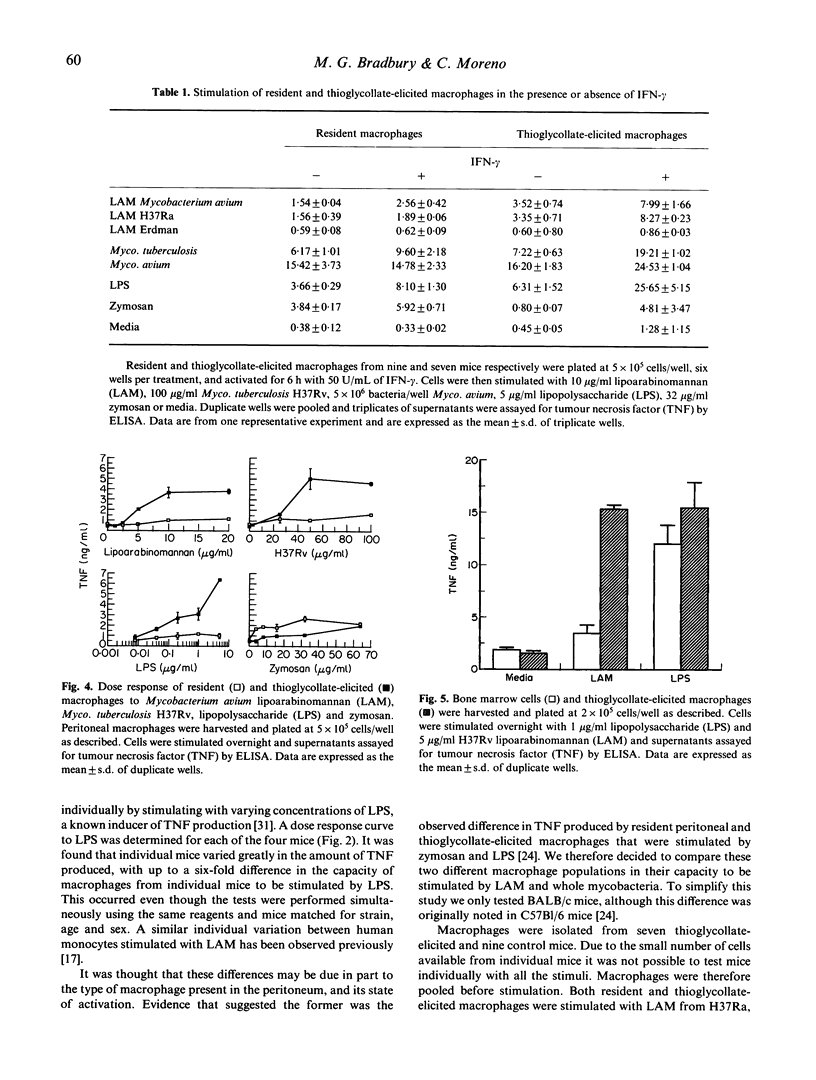
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) production is an important pathological mediator in mycobacterial infections, and yet little is known of the factors which influence its production. We have studied the influence of murine macrophage heterogeneity and activation state on TNF production following mycobacterial stimulation in vitro. Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) from strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Myco. avium differentially stimulated TNF production in thioglycollate-elicited macrophages in a dose-dependent manner. In comparison, resident peritoneal macrophages produced much less TNF when stimulated with LAM, dead mycobacteria or lipopolysaccharide (LPS). In contrast, zymosan stimulated resident macrophages to a higher degree than thioglycollate-elicited cells. Another comparison between bone marrow and thioglycollate-elicited macrophages showed that both responded to LPS, but only the latter was stimulated significantly by H37Rv LAM. This may indicate that LAM stimulation of macrophages takes place through a different pathway than both zymosan- and LPS-stimulated TNF production. Also, in vitro activation of peritoneal macrophages with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), increased TNF response to several stimuli. Our studies indicate that the pathology of mycobacterial infections through TNF production may be influenced by the type and activation state of the macrophage which responds to that infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin P. E., McCulloch E. A., Till J. E. Characterization of the factor in L-cell conditioned medium capable of stimulating colony formation by mouse marrow cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):121–134. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Chatterjee D., Abrams J. S., Lu S., Wang E., Yamamura M., Brennan P. J., Modlin R. L. Cytokine production induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan. Relationship to chemical structure. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Fong S. J., Brennan P. J., Twomey P. E., Mazumder A., Modlin R. L. Local production of tumor necrosis factor and IFN-gamma in tuberculous pleuritis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugger W., Reinhardt D., Galanos C., Andreesen R. Inhibition of in vitro differentiation of human monocytes to macrophages by lipopolysaccharides (LPS): phenotypic and functional analysis. Int Immunol. 1991 Mar;3(3):221–227. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Gray P. W., Rinderknecht E., Schreiber R. D. Evidence for a gamma-interferon receptor that regulates macrophage tumoricidal activity. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):55–74. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Beutler B. The role of cachectin/TNF in endotoxic shock and cachexia. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Bozic C. M., McNeil M., Brennan P. J. Structural features of the arabinan component of the lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9652–9660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Lowell K., Rivoire B., McNeil M. R., Brennan P. J. Lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Capping with mannosyl residues in some strains. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6234–6239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Roberts A. D., Lowell K., Brennan P. J., Orme I. M. Structural basis of capacity of lipoarabinomannan to induce secretion of tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1249-1253.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor stimulate human macrophages to restrict growth of virulent Mycobacterium avium and to kill avirulent M. avium: killing effector mechanism depends on the generation of reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Apr;49(4):380–387. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Gordon S. Alterations of surface properties by macrophage activation: expression of receptors for Fc and mannose-terminal glycoproteins and differentiation antigens. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;13:33–56. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-1445-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Sastry K., Bailly P., Warner A. Molecular characterization of the human macrophage mannose receptor: demonstration of multiple carbohydrate recognition-like domains and phagocytosis of yeasts in Cos-1 cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1785–1794. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Activation of tuberculostatic macrophage functions by gamma interferon, interleukin-4, and tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2675–2677. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2675-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Keshav S., Chung L. P. Mononuclear phagocytes: tissue distribution and functional heterogeneity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1988 Sep-Oct;1(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(88)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann D., Gallay P., Barras C., Zaech P., Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S., Glauser M. P., Baumgartner J. D. Control of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding and LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor secretion in human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3505–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N. Production of an anti-tumour cytotoxin by human monocytes. Immunology. 1981 Sep;44(1):135–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestan J., Digel W., Mittnacht S., Hillen H., Blohm D., Möller A., Jacobsen H., Kirchner H. Antiviral effects of recombinant tumour necrosis factor in vitro. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):816–819. doi: 10.1038/323816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Mehlert A., Lamb J. The inhibitory effects of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan and polysaccharides upon polyclonal and monoclonal human T cell proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):206–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Taverne J., Mehlert A., Bate C. A., Brealey R. J., Meager A., Rook G. A., Playfair J. H. Lipoarabinomannan from Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the production of tumour necrosis factor from human and murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):240–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Taverne J., Leveton C., Steele J. The role of gamma-interferon, vitamin D3 metabolites and tumour necrosis factor in the pathogenesis of tuberculosis. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):229–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguedolce M. V., Capo C., Bongrand P., Mege J. L. Zymosan-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by human monocytes. Down-modulation by phorbol ester. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2229–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarih M., Souvannavong V., Adam A. Differential stimulation of macrophages for tumor cytostasis and monokine production. Cancer Lett. 1992 Jul 10;64(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90042-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd V. L., Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., Stahl P. D. Characterization of the mannose/fucose receptor on human mononuclear phagocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Dec;32(6):423–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Silverstein S. C. Phagocytosis of unopsonized zymosan by human monocyte-derived macrophages: maturation and inhibition by mannan. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Nov;38(5):655–658. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.5.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M., Gordon S. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) release by murine peritoneal macrophages: role of cell stimulation and specific phagocytic plasma membrane receptors. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):431–437. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M., Keshav S., Harris N., Gordon S. Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor activity: a marker of alternative immunologic macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):287–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima T., Ueta C., Tsuyuguchi I., Kishimoto S. Production of tumor necrosis factor alpha by monocytes from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3286–3292. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3286-3292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Bezouska K., Drickamer K. Contribution to ligand binding by multiple carbohydrate-recognition domains in the macrophage mannose receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1719–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone S. E., Rich E. A., Wallis R. S., Ellner J. J. Expression of tumor necrosis factor in vitro by human mononuclear phagocytes stimulated with whole Mycobacterium bovis BCG and mycobacterial antigens. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3313–3315. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3313-3315.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. S., Amir-Tahmasseb M., Ellner J. J. Induction of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor by mycobacterial proteins: the monocyte western blot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3348–3352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. S., Paranjape R., Phillips M. Identification by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of a 58-kilodalton tumor necrosis factor-inducing protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):627–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.627-632.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witsell A. L., Schook L. B. Macrophage heterogeneity occurs through a developmental mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1963–1967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


