Abstract
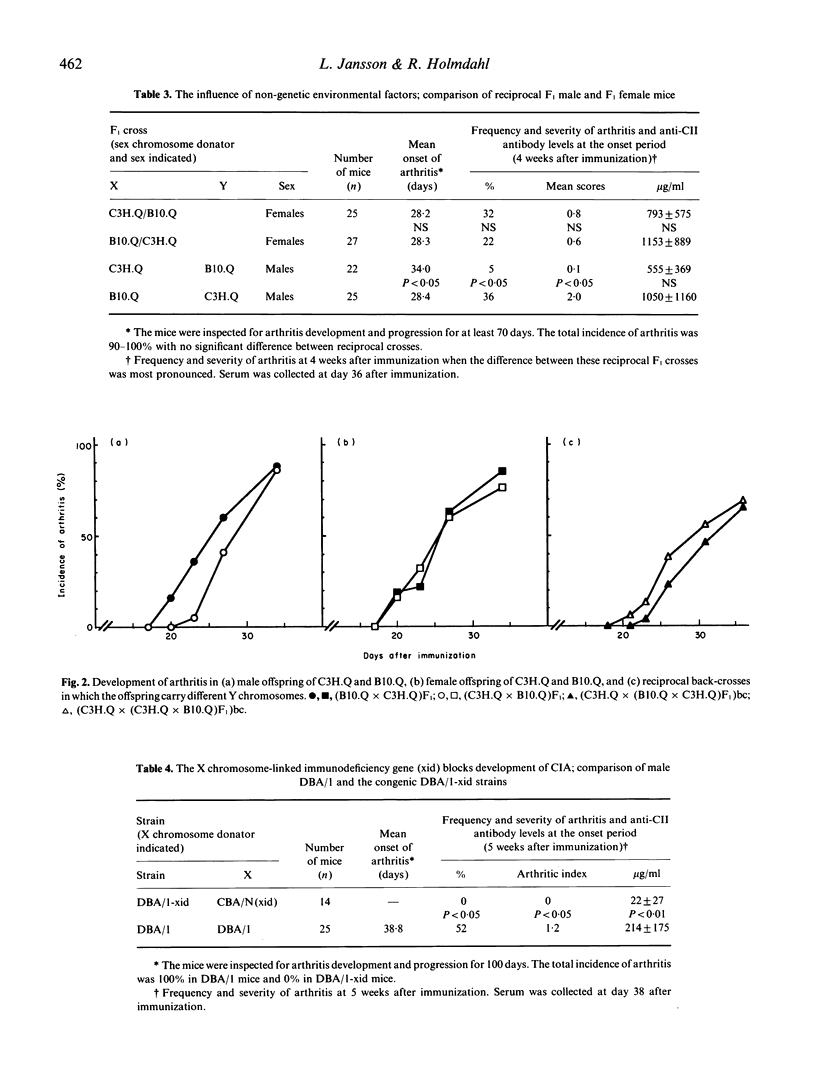
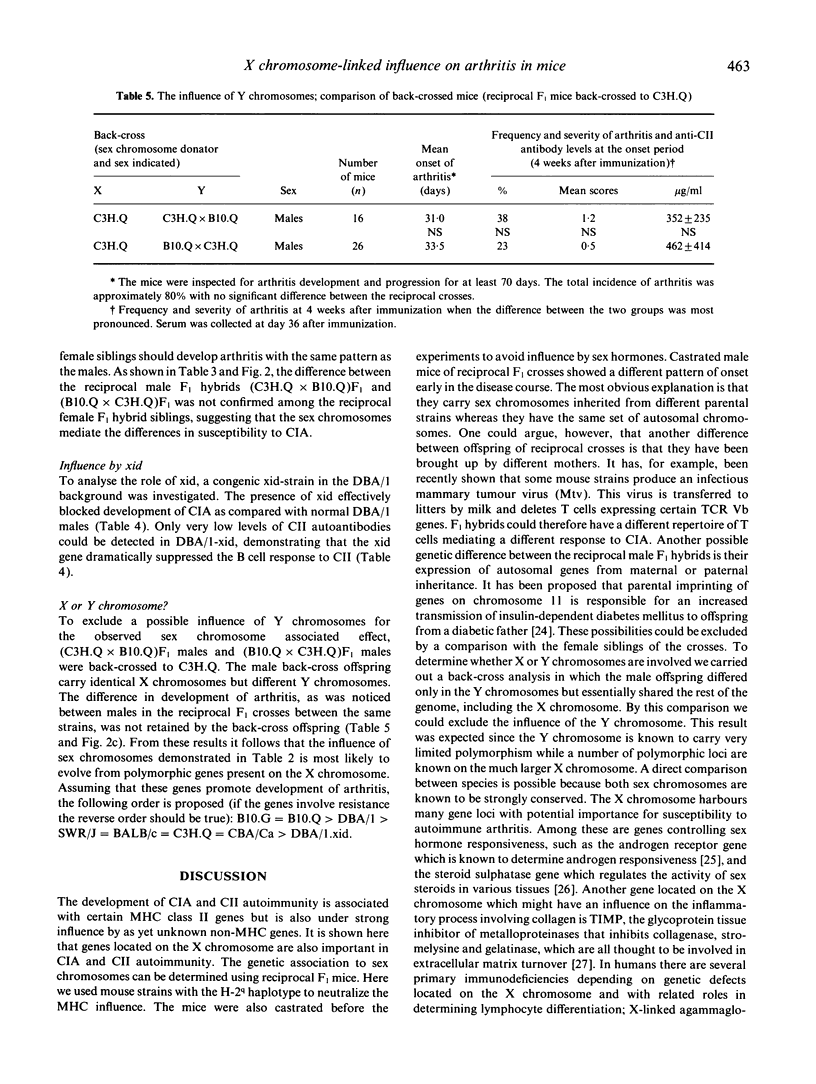
Susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice is associated with a class II gene in MHC (Aq) but also with unknown genes outside MHC. Investigated here is the influence of genes on the X chromosome as well as the role of the X-linked immunodeficiency (xid) mutation. Reciprocal male F1 hybrids, bred to be heterozygous or homozygous for Aq, showed a genetic influence in their susceptibility to develop CIA. Crosses were made between B10.G, B10.Q, DBA/1, SWR/J, C3H.Q and CBA/Ca, and all F1 mice were castrated to avoid sex hormone modulation of the susceptibility. A differential timing of arthritis onset and severity were seen in the reciprocal F1 males. An exception was the reciprocal F1 male offspring from SWR/J and DBA/1 crosses which differed only in disease severity late in the course of the disease. The female F1 crosses did not show the same pattern of differential susceptibility to CIA as the F1 males. To exclude the possible influence of the Y chromosome, F1 males of reciprocal crosses were back-crossed to the parental strains creating offspring with equal X chromosomes but divergent Y chromosomes. No difference in development of arthritis was observed in these. The influence of the xid mutation was investigated next. The xid loci from the CBA/N mouse was bred into DBA/1 strain which is highly susceptible to CIA. The resulting congenic DBA/1-xid strain was resistant to induction of CIA and did not develop an antibody response to type II collagen. We conclude that polymorphic genes on the X chromosome modulate susceptibility to CIA. The results from the experiments with mice carrying xid mutations confirm that such immune modulating genes exist on the sex chromosomes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., Goldschmidt T. J., Michaelsson E., Larsson A., Holmdahl R. T-cell receptor V beta haplotype and complement component C5 play no significant role for the resistance to collagen-induced arthritis in the SWR mouse. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):191–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. I., Hedrick S. M., Nielsen E. A., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E., Davis M. M. Isolation of a cDNA clone corresponding to an X-linked gene family (XLR) closely linked to the murine immunodeficiency disorder xid. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):369–372. doi: 10.1038/314369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. I., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E., Davis M. M. Expression of an X-linked gene family (XLR) in late-stage B cells and its alteration by the xid mutation. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):372–374. doi: 10.1038/314372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. A. High sensitivity to androgen as a contributing factor in sex differences in the immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Nov;22(11):1218–1233. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E. Molecular approaches to analysis of X-linked immunodeficiencies. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:215–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtenay J. S., Dallman M. J., Dayan A. D., Martin A., Mosedale B. Immunisation against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):666–668. doi: 10.1038/283666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutolo M., Balleari E., Giusti M., Intra E., Accardo S. Androgen replacement therapy in male patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jan;34(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton C. M., Watson M. J., Walker D. J. Sex hormones in postmenopausal HLA-identical rheumatoid arthritis discordant sibling pairs. J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):1663–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding B., Golding H., Foiles P. G., Morton J. I. CBA/N X-linked defect delays expression of the Y-linked accelerated autoimmune disease in BXSB mice. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1043–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazes J. M., Dijkmans B. A., Vandenbroucke J. P., de Vries R. R., Cats A. Pregnancy and the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;33(12):1770–1775. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfgott S. M., Bazin H., Dessein A., Trentham D. E. Suppressive effects of anti-mu serum on the development of collagen arthritis in rats. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Jun;31(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Andersson M. Female sex hormones suppress development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Dec;29(12):1501–1509. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Andersson M., Jonsson R. Genetic, hormonal and behavioural influence on spontaneously developing arthritis in normal mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):467–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Karlsson M., Andersson M. E., Rask L., Andersson L. Localization of a critical restriction site on the I-A beta chain that determines susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9475–9479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Klareskog L., Andersson M., Hansen C. High antibody response to autologous type II collagen is restricted to H-2q. Immunogenetics. 1986;24(2):84–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00373114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson L., Holmdahl R. Oestrogen-induced suppression of collagen arthritis; 17 beta-oestradiol is therapeutically active in normal and castrated F1 hybrid mice of both sexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):446–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julier C., Hyer R. N., Davies J., Merlin F., Soularue P., Briant L., Cathelineau G., Deschamps I., Rotter J. I., Froguel P. Insulin-IGF2 region on chromosome 11p encodes a gene implicated in HLA-DR4-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):155–159. doi: 10.1038/354155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. B., Quintáns J. Phosphorylcholine-specific helper T cells in mice with an X-linked defect of antibody production to the same hapten. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):267–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E. A., Schorderet D. F., Gartler S. M. Linkage of the steroid sulfatase gene to the sex-reversed mutation in the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):465–468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. J., Guelde G., Hansen C., Mond J. J. Synergistic effects of the xid gene in X chromosome congenic mice. I. Inability of C3.CBA/N mice to respond to thymus-dependent antigens in adoptive transfer assays. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1363–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. J., Stall A. M., Sieckmann D. G., Lamers M. C., Finkelman F. D., Finch L., Longo D. L. Receptor-mediated elimination of phosphocholine-specific B cells in x-linked immune-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2568–2577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Klein D. Mouse inbred and congenic strains. Methods Enzymol. 1987;150:163–196. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)50076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahita R. G. Sex steroids and the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Feb;28(2):121–126. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P., Holmdahl R. Oestrogen-induced suppression of collagen arthritis. II. Treatment of rats suppresses development of arthritis but does not affect the anti-type II collagen humoral response. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Nov;26(5):579–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Shapiro L. J., Norum R. A., Mohandas T., Axelman J., Dabora R. L. Differential expression of steroid sulphatase locus on active and inactive human X chromosome. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):838–840. doi: 10.1038/299838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahm M. H., Paslay J. W., Davie J. M. Unbalanced X chromosome mosaicism in B cells of mice with X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):920–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Sriram S., Cooper S. M. Prevention of type II collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo treatment with anti-L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings D. J., Saffran D. C., Tsukada S., Largaespada D. A., Grimaldi J. C., Cohen L., Mohr R. N., Bazan J. F., Howard M., Copeland N. G. Mutation of unique region of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.8332901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Y. J., Steinberg A. D. Influence of Y and X chromosomes on B cell responses in autoimmune prone mice. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1261–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I. CBA/N immune defective mice; evidence for the failure of a B cell subpopulation to be expressed. Immunol Rev. 1982;64:117–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinella D. G., Jeffers J. R., Reife R. A., Stuart J. M. The role of C5 and T-cell receptor Vb genes in susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis. Immunogenetics. 1991;34(1):23–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00212308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ball E. J., Dry P. J., Nunez G. The human immune response region (HLA-D) and disease susceptibility. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:113–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Dixon F. J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):378–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Sideras P., Smith C. I., Vorechovský I., Chapman V., Paul W. E. Colocalization of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and X-linked immunodeficiency genes. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.8332900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):688–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wordsworth P., Bell J. Polygenic susceptibility in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Jun;50(6):343–346. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.6.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeicher M., Mozes E., Lonai P. Lymphocytes alloantigens associated with X-chromosome-linked immune response genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):721–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



