Abstract
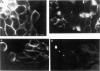
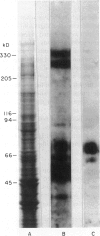
Heymann nephritis of the rat has several similarities to human idiopathic membranous glomerulo-nephropathy, and therefore serves as an animal model for study of the human disease. The disease process in the rat is initiated by autoantibodies forming in situ immune deposits on the surface of the glomerular epithelial cell in the lamina rara externa region of the glomerular basement membrane. It is now understood that multispecific antibodies (like anti-gp600) form the nephritogenic deposits which cause proteinuria, while MoAb (like anti-gp330, anti-90 kD and anti-gp70) form only transient deposits which do not give rise to proteinuria. The reasons for differences between pathologic effects of mono- and multispecific antibodies are not known. Following characterization of putative antigens of Heymann nephritis by immunofluorescence, immunogold and immunoblot techniques, we have investigated the metabolic handling of a multispecific (anti-600), monospecific antibody (anti-gp70) and a MoAb (anti-gp330) by the cultured glomerular epithelial cell to gain an insight into the mechanism of nephritogenicity of multispecific antibody. Anti-gp600 reacted to multiple antigens in the 330-kD and 70-kD regions; anti-gp70 reacted to only the 70-kD region. Ultrastructurally, all three types of antigens were present on the plasma membrane, concentrated in the microvillar region. The cells were incubated with the antibodies, and clearance of the antibodies from the cells was evaluated. Following binding, all three antibodies were internalized by the cells. However, it was found that monoclonal anti-gp330 MoAb was cleared most rapidly from the cell (t1/2 5 min), followed by anti-gp70 (t1/2 30 min). Anti-gp600 was cleared at four times slower rate than anti-gp70 (t1/2 2h) by the cell. While anti-gp330 MoAb and monospecific anti-gp70 antibody were expelled from the cell in 25-32% digested form, the multispecific anti-gp600 was digested to the extent of only 5-8%. No immune complexes were detected in the medium with any of the three antibodies. The shed label was in intact IgG form. It is concluded that multispecific antibodies of Heymann nephritis are nephritogenic because of their slower clearance and digestion and therefore, higher accretion rate on the surface of the glomerular epithelial cell. The differential handling of the antibodies by the glomerular epithelial cell offers an explanation for the in vivo differences in the nephritogenicity of these antibodies observed earlier.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrass C. K. Evaluation of sequential glomerular eluates from rats with Heymann nephritis. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):530–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Biologically active water-insoluble protein polymers. I. Their use for isolation of antigens and antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Noble B., Kerjaschki D., Malavasi F., Roholt O. A., Farquhar M. G., Andres G. Antibody-induced redistribution of Heymann antigen on the surface of cultured glomerular visceral epithelial cells: possible role in the pathogenesis of Heymann glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2409–2416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Kerjaschki D., Gonda M., Nevins T., Rielle J. C., Brentjens J., Andres G. Expression and modulation of surface antigens in cultured rat glomerular visceral epithelial cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Nov;37(11):1675–1687. doi: 10.1177/37.11.2809176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Steinmuller D. R., Stilmant M. M., Salant D. J., Lowenstein L. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1275–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Baird L. G., Erikson M. E., Collins A. B., McCluskey R. T. Characterization of antigens and antibody specificities involved in Heymann nephritis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2400–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan E. A., Wang C. Y., Wang L. C., Evans R. L. Noncovalently bonded subunits of 22 and 28 kd are rapidly internalized by T cells reacted with anti-Leu-4 antibody. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):536–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasinath B. S., Singh A. K., Kanwar Y. S., Lewis E. J. Effect of puromycin aminonucleoside on HSPG core protein content of glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F590–F596. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J. Isolation and characterization of rat glomerular epithelial cells in vitro. Kidney Int. 1978 Jul;14(1):21–30. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makker S. P., Singh A. K. Characterization of the antigen (gp600) of Heymann nephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Plutner H. Internalization and degradation of macrophage Fc receptors bound to polyvalent immune complexes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Plutner H., Ukkonen P. Internalization and rapid recycling of macrophage Fc receptors tagged with monovalent antireceptor antibody: possible role of a prelysosomal compartment. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1163–1169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesando J. M., Ritz J., Lazarus H., Tomaselli K. J., Schlossman S. F. Fate of a common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen during modulation by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):540–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Allegri L., Melcion C., Pirotsky E., Appay M. D., Bariety J., Pontillon F., Verroust P. A monoclonal antibody to brush border and passive Heymann nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):319–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B., Galceran M., Verroust P. An immunopathologic study of a 330-kD protein defined by monoclonal antibodies and reactive with anti-RTE alpha 5 antibodies and kidney eluates from active Heymann nephritis. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Belok S., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G. A new role for complement in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1339–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI109987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D., Unanue E. R. Redistribution of myosin accompanying capping of surface Ig. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1393–1398. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Makker S. P. Circulatory antigens of Heymann nephritis. I. Identification and partial characterization. Immunology. 1986 Mar;57(3):467–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Schwartz M. M. Circulatory antigen of Heymann nephritis. II. Isolation of a 70,000 MW antigen from normal rat serum which cross-reacts with Heymann nephritis antigen. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):451–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Schwartz M. M. Nephritogenicity and immunocytochemical localization of the 70-kilodalton glycoprotein subunit (gp70) of Heymann antigen. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jul;48(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackpole C. W., Jacobson J. B., Lardis M. P. Antigenic modulation in vitro. I. Fate of thymus-leukemia (TL) antigen-antibody complexes following modulation of TL antigenicity from the surfaces of mouse leukemia cells and thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):939–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Thompson J., Sariban-Sohraby S., Handler J. S. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of epithelial membrane polarization. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2173–2180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Karnovsky M. J., Engers H. D. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. 3. Relationship between the formation and fate of anti-Ig-surface Ig complexes and cell metabolism. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):675–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A., Cohen E. P. Studies on the effect of specific antisera on the metabolism of cellular antigens. II. The synthesis and degradation of TL antigens of mouse cells in the presence of TL antiserum. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1296–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]