Abstract
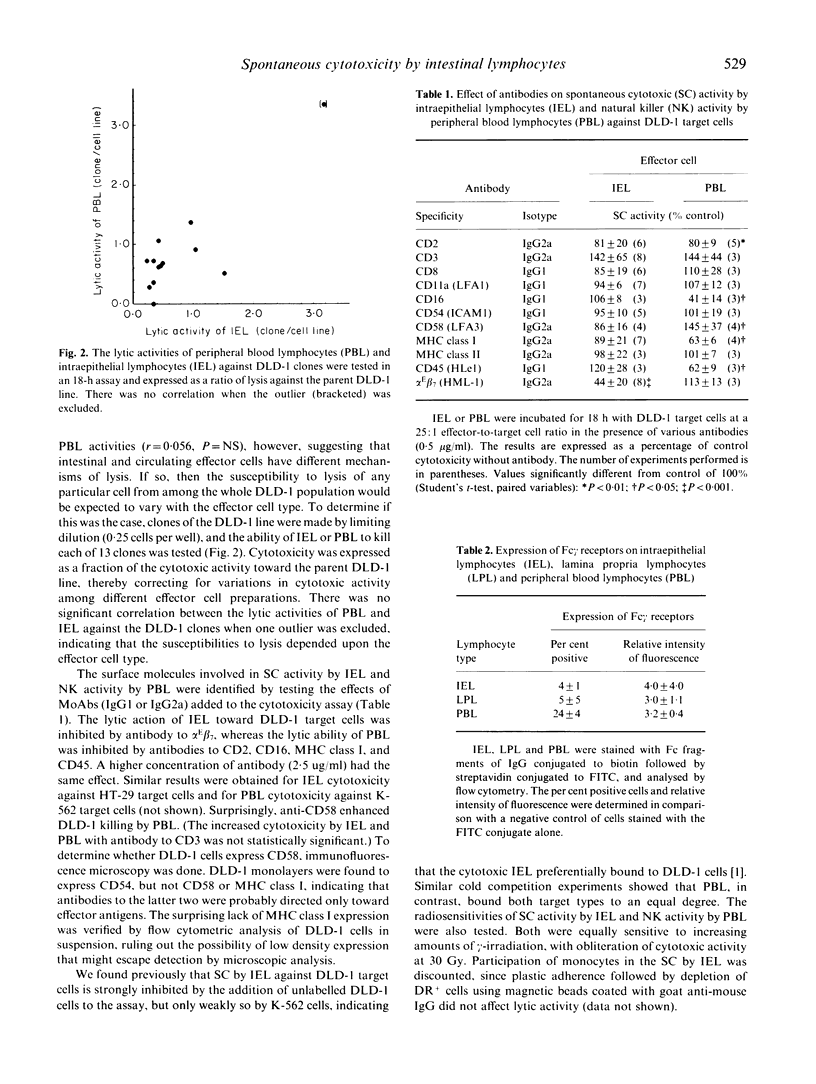
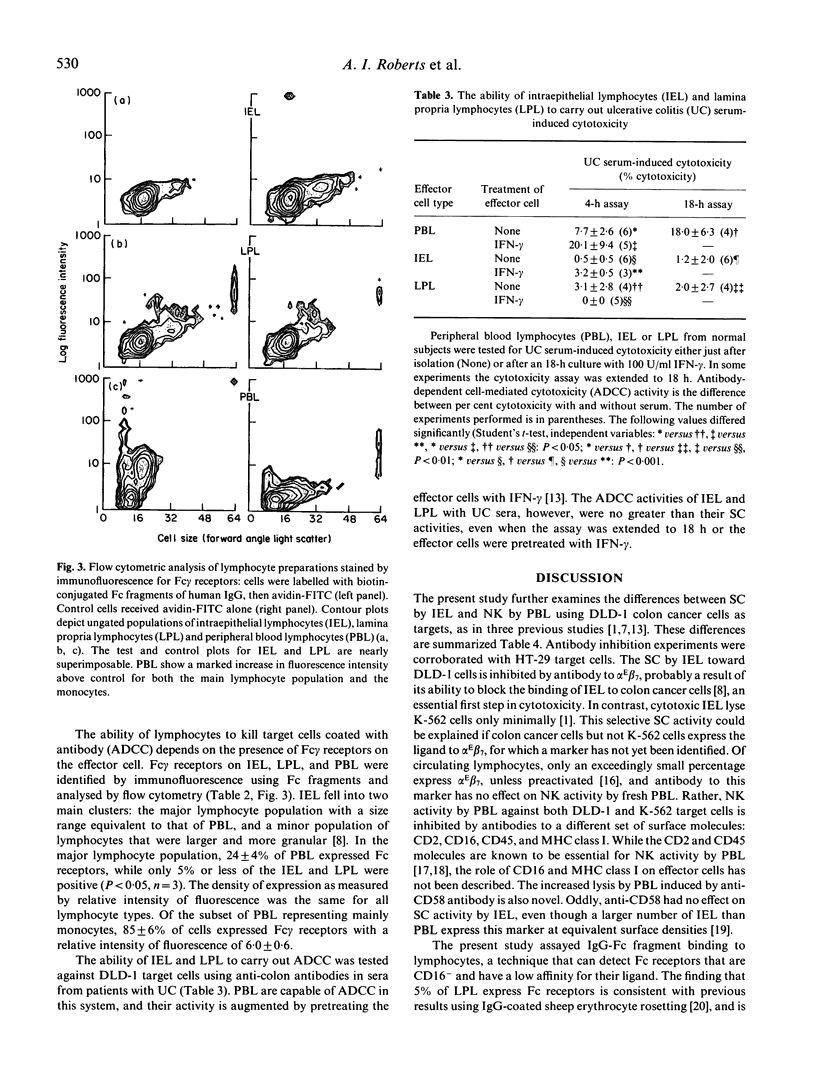
Human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL) demonstrate target cell-restricted spontaneous cytotoxic (SC) activity that is due to CD2+CD3+CD8+CD16-CD56- effector cells; they kill epithelial cell (EC) tumours (such as DLD-1 colon cancer cells), but not natural killer (NK)-sensitive K-562 cells. The present study shows that the measured levels of SC activities by IEL correlated with those of autologous lamina propria lymphocytes (LPL), but not with those of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL). Also, the susceptibilities of DLD-1 cell clones to lysis by IEL and PBL effector cells did not correlate, suggesting different mechanisms of lysis. Antibody blocking experiments showed that the main surface molecules involved in lysis depended on the effector cell type: alpha E beta 7 (HML-1) on IEL and CD16 on PBL. No antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) was demonstrated by IEL, even after stimulation with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Few IEL expressed Fc receptors for IgG. This study describes further differences between the SC activities of IEL and PBL.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer I. O., Grosch L., Hardörfer C., Röder A. Ulcerative colitis specific cytotoxic IgG-autoantibodies against colonic epithelial cancer cells. Gut. 1988 Dec;29(12):1639–1647. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.12.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Sollid L. M., Thrane P. S., Kvale D., Bjerke K., Scott H., Kett K., Rognum T. O. Lymphoepithelial interactions in the mucosal immune system. Gut. 1988 Aug;29(8):1116–1130. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.8.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba M., Bartnik W., ReMine S. G., Thayer W. R., Shorter R. G. Human colonic intraepithelial and lamina proprial lymphocytes: cytotoxicity in vitro and the potential effects of the isolation method on their functional properties. Gut. 1981 Mar;22(3):177–186. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.3.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R., Pucci A. Absence of K cells in human gut mucosa. Gut. 1978 Apr;19(4):273–276. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.4.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C., Brolin R. E., Roberts A. I. Characterization of activated lymphocytes in colon cancer. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jan;50(1 Pt 1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C. Do the CD45RO+CD8+ intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes have the characteristics of memory cells? Cell Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;147(2):331–340. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C. Proliferative responses of human intraepithelial lymphocytes to various T-cell stimuli. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1372–1381. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C., Roberts A. I. Lymphokine-activated killing by human intestinal lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1993 Jan;146(1):107–116. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C., Roberts A. I., O'Connell S. M., Robertson F. M., Nagase H. Characterization of an immunosuppressive factor derived from colon cancer cells. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2161–2168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocchi C., Battisto J. R., Farmer R. G. Gut mucosal lymphocytes in inflammatory bowel disease: isolation and preliminary functional characterization. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Sep;24(9):705–717. doi: 10.1007/BF01314469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey K. Simple linear regression in medical research. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 26;313(26):1629–1636. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512263132604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang P., Crotty B., Dalton H. R., Jewell D. P. Epithelial cells bearing class II molecules stimulate allogeneic human colonic intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gut. 1992 Aug;33(8):1089–1093. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.8.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarry A., Cerf-Bensussan N., Brousse N., Guy-Grand D., Muzeau F., Potet F. Same peculiar subset of HML1 + lymphocytes present within normal intestinal epithelium is associated with tumoral epithelium of gastrointestinal carcinomas. Gut. 1988 Dec;29(12):1632–1638. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.12.1632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Franklin G. O., Jenkins K. M., Kodner I. J., Nash G. S., Weinrieb I. J. Human intestinal mononuclear cells. I. Investigation of antibody-dependent, lectin-induced, and spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxic capabilities. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jan;78(1):47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. I., O'Connell S. M., Ebert E. C. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bind to colon cancer cells by HML-1 and CD11a. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1608–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieferdecker H. L., Ullrich R., Weiss-Breckwoldt A. N., Schwarting R., Stein H., Riecken E. O., Zeitz M. The HML-1 antigen of intestinal lymphocytes is an activation antigen. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2541–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Caulfield J. P., Michon J., Hein A., Kamada M. M., MacDermott R. P., Stevens R. L., Ritz J. T11/CD2 activation of cloned human natural killer cells results in increased conjugate formation and exocytosis of cytolytic granules. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):991–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Newman W. Definition of a "trigger" stage in the NK cytolytic reaction sequence by a monoclonal antibody to the glycoprotein T-200. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1149–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taunk J., Roberts A. I., Ebert E. C. Spontaneous cytotoxicity of human intraepithelial lymphocytes against epithelial cell tumors. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91785-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejdosiewicz L. K., Badr-el-Din S., Smart C. J., Malizia G., Oakes D. J., Heatley R. V., Losowsky M. S. Colonic mucosal T lymphocytes in ulcerative colitis: expression of CD7 antigen in relation to MHC class II (HLA-D) antigens. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Sep;34(9):1449–1456. doi: 10.1007/BF01538084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M. Quantitation of proliferative and cytotoxic precursor cells directed against human tumours: limiting dilution analysis in peripheral blood and at the tumour site. Int J Cancer. 1982 Aug 15;30(2):135–142. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo Y. K., Heo D. S., Hata K., Van Thiel D. H., Whiteside T. L. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from human colon carcinomas. Functional and phenotypic characteristics after long-term culture in recombinant interleukin 2. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):259–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


