Abstract
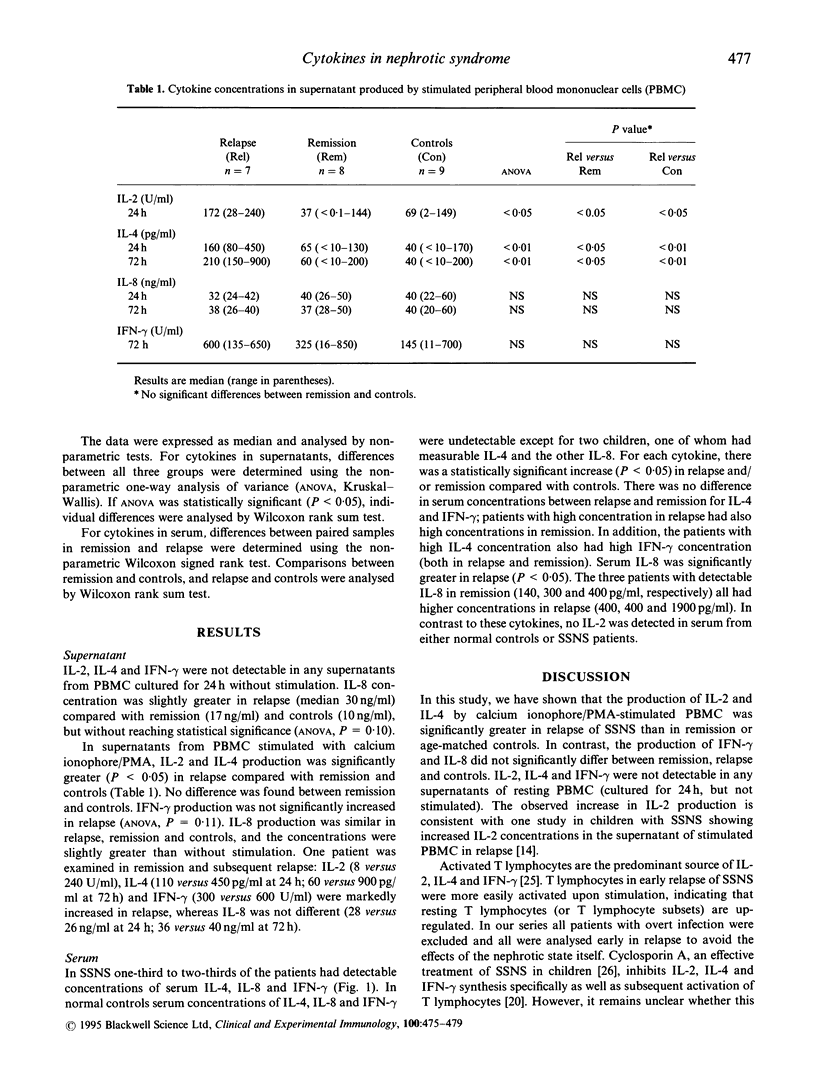
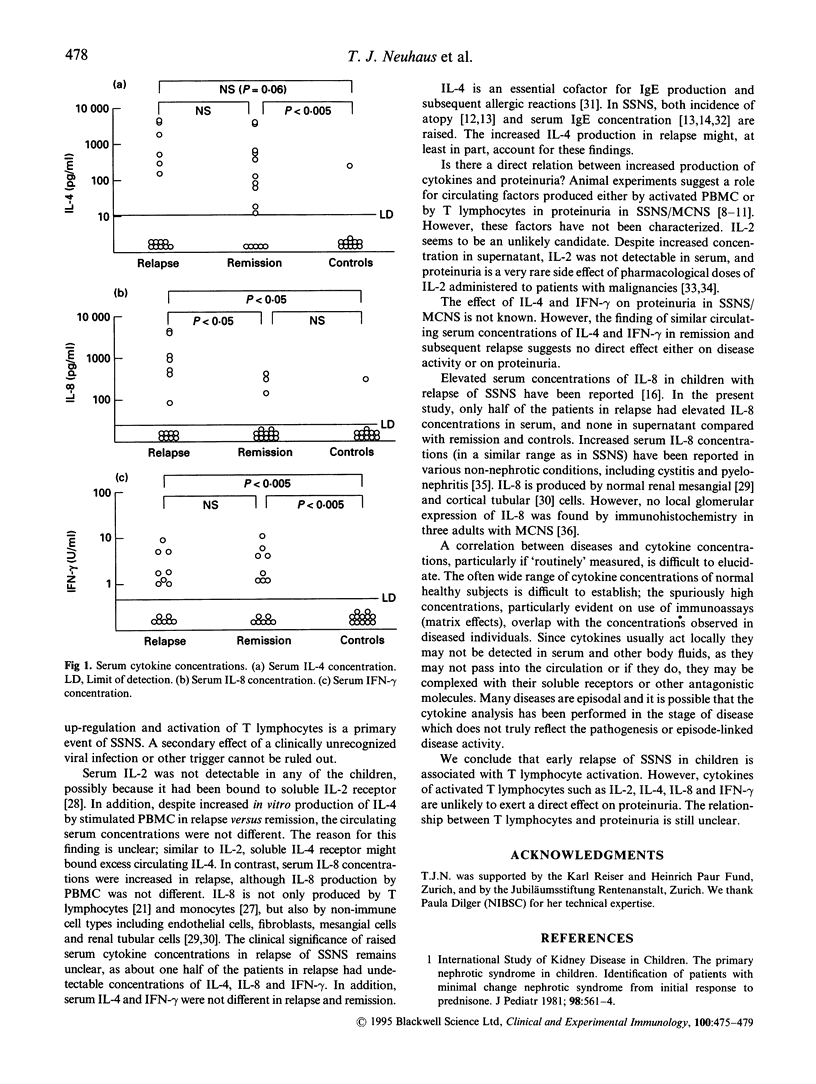
We investigated the production of cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and serum cytokine concentrations in children with steroid-sensitive idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (SSNS). PBMC from patients off treatment were collected during remission and relapse and cultured in medium alone or stimulated with calcium ionophore plus phorbol myristate acetate. Control PBMC were taken from healthy age-matched children. IL-2 was measured by bioassay, IL-4 by immunoradiometric assay, and IL-8 and IFN-gamma by ELISA. After 24 h culture without stimulation, IL-2, IL-4 and IFN-gamma were not detectable in the supernatant in any of the children. After stimulation, the supernatant concentrations of IL-2 (median 172 U/ml at 24 h) and IL-4 (160 pg/ml at 24 h; 210 pg/ml at 72 h) were significantly increased in relapse compared with remission (IL-2 37 U/ml; IL-4 65 pg/ml and 60 pg/ml) and controls (IL-2 69 U/ml; IL-4 40 pg/ml and 40 pg/ml) (P < 0.05). The concentration of IFN-gamma was not significantly increased in relapse compared with remission and controls (600, 325, and 145 U/ml, respectively, at 72 h). IL-8 concentrations were similar in relapse, remission and controls with stimulation (median 32, 40 and 40 ng/ml, respectively) and without (30, 17 and 10 ng/ml). IL-2 was not detectable in serum, but IL-4, IL-8 and IFN-gamma were measurable in about half the patients, both in relapse and remission, though were virtually undetectable in controls. We conclude that relapse of SSNS in children is associated with T lymphocyte activation with release of IL-2, IL-4 and IFN-gamma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Alm G., Perlmann P. Monoclonal antibody two-site ELISA for human IFN-gamma. Adaptation for determinations in human serum or plasma. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird C., Wadhwa M., Thorpe R. Development of immunoassays for human interleukin 3 and interleukin 4, some of which discriminate between different recombinant DNA-derived molecules. Cytokine. 1991 Nov;3(6):562–567. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90482-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumpas D. T., Anastassiou E. D., Older S. A., Tsokos G. C., Nelson D. L., Balow J. E. Dexamethasone inhibits human interleukin 2 but not interleukin 2 receptor gene expression in vitro at the level of nuclear transcription. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1739–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI115192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho B. S., Lee C. E., Pyun K. H. Studies on the role of interleukin-4 and Fc epsilon RII in the pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 1992 Dec;7(4):343–348. doi: 10.3346/jkms.1992.7.4.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmel E. A., Verweij C. L., Durand D. B., Higgins K. M., Lacy E., Crabtree G. R. Cyclosporin A specifically inhibits function of nuclear proteins involved in T cell activation. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1617–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.2595372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiser R. T., Arnold W. C., Charlton R. K., Steele R. W., Childress S. H., Shirkey B. T-lymphocyte subsets in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1991 Nov;40(5):913–916. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garin E. H., Blanchard D. K., Matsushima K., Djeu J. Y. IL-8 production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in nephrotic patients. Kidney Int. 1994 May;45(5):1311–1317. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groshong T., Mendelson L., Mendoza S., Bazaral M., Hamburger R., Tune B. Serum IgE in patients with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Nov;83(5):767–771. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Kawagoe H., Yamamoto Y., Kuroki N., Fujimoto S., Tanaka K., Kurokawa M. Nephrotic syndrome associated with recombinant interleukin-2. Nephron. 1990;54(3):277–278. doi: 10.1159/000185875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton S. A., Shah V., Byrne M. R., Morgan G., Barratt T. M., Dillon M. J. Lymphocyte subpopulations, interleukin-2 and interleukin-2 receptor expression in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 1994 Apr;8(2):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00865458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S. H., Hylander B., Wretlind B., Brauner A. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in serum and urine in patients with acute pyelonephritis in relation to bacterial-virulence-associated traits and renal function. Nephron. 1994;67(2):172–179. doi: 10.1159/000187923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joffe M. I., Rabson A. R. Dissociation of lymphokine production and blastogenesis in children with measles infections. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jul;10(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Yoshikawa N., Nakamura H. T-cell subpopulations in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol. 1994 May;41(5):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama A., Fujisaki M., Kobayashi M., Igarashi M., Narita M. A glomerular permeability factor produced by human T cell hybridomas. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):453–460. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusner D. J., Luebbers E. L., Nowinski R. J., Konieczkowski M., King C. H., Sedor J. R. Cytokine- and LPS-induced synthesis of interleukin-8 from human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1991 Jun;39(6):1240–1248. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Tomizawa S., Shimabukuro N., Fukuda T., Johshita T., Kuroume T. Effect of supernatants derived from T lymphocyte culture in minimal change nephrotic syndrome on rat kidney capillaries. Nephron. 1989;51(1):73–76. doi: 10.1159/000185246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow S. R., Sarsfield J. K., Scott D. G., Rajah S. M. Steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome and allergy: immunological studies. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jul;56(7):517–524. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.7.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow S. R., Sarsfield J. K. Steroid-responsive and nephrotic syndrome and allergy: clinical studies. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jul;56(7):509–516. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.7.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori A., Yamamoto K., Dohi M., Suko M., Okudaira H. Interleukin-4 gene expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;95(2-3):282–284. doi: 10.1159/000235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozen S., Saatci U., Tinaztepe K., Bakkaloglu A., Barut A. Urinary tumor necrosis factor levels in primary glomerulopathies. Nephron. 1994;66(3):291–294. doi: 10.1159/000187825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Chang A. E., Avis F. P., Leitman S., Linehan W. M., Robertson C. N., Lee R. E., Rubin J. T. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):889–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Nelson D. L. The soluble interleukin-2 receptor: biology, function, and clinical application. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Oct 15;113(8):619–627. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-8-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S., Mittal A., Andal A. Pattern of interleukins in minimal-change nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Nephron. 1993;65(1):56–61. doi: 10.1159/000187441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmouder R. L., Strieter R. M., Wiggins R. C., Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L. In vitro and in vivo interleukin-8 production in human renal cortical epithelia. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):191–198. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaper H. W. The immune system in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 1989 Jan;3(1):101–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00859637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Morita E., Christophers E. Purification and partial biochemical characterization of a human monocyte-derived, neutrophil-activating peptide that lacks interleukin 1 activity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3474–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R., Yoshikawa N., Nakamura H., Ito H. Infusion of peripheral blood mononuclear cell products from nephrotic children increases albuminuria in rats. Nephron. 1992;60(1):35–41. doi: 10.1159/000186702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Geha R. S. Regulation of IgE synthesis in humans. J Clin Immunol. 1989 Mar;9(2):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00916934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Yokoyama H., Tomosugi N., Hisada Y., Ohta S., Naito T., Kobayashi K., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Detection of urinary interleukin-8 in glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 1994 Aug;46(2):455–460. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa N., Kusumi Y., Matsumoto K., Oshima S., Takeuchi A., Kawamura O., Kubota T., Kondo S., Niwa H. Studies of a glomerular permeability factor in patients with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Nephron. 1989;51(3):370–376. doi: 10.1159/000185325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipfel P. F., Bialonski A., Skerka C. Induction of members of the IL-8/NAP-1 gene family in human T lymphocytes is suppressed by cyclosporin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 27;181(1):179–183. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


