Abstract
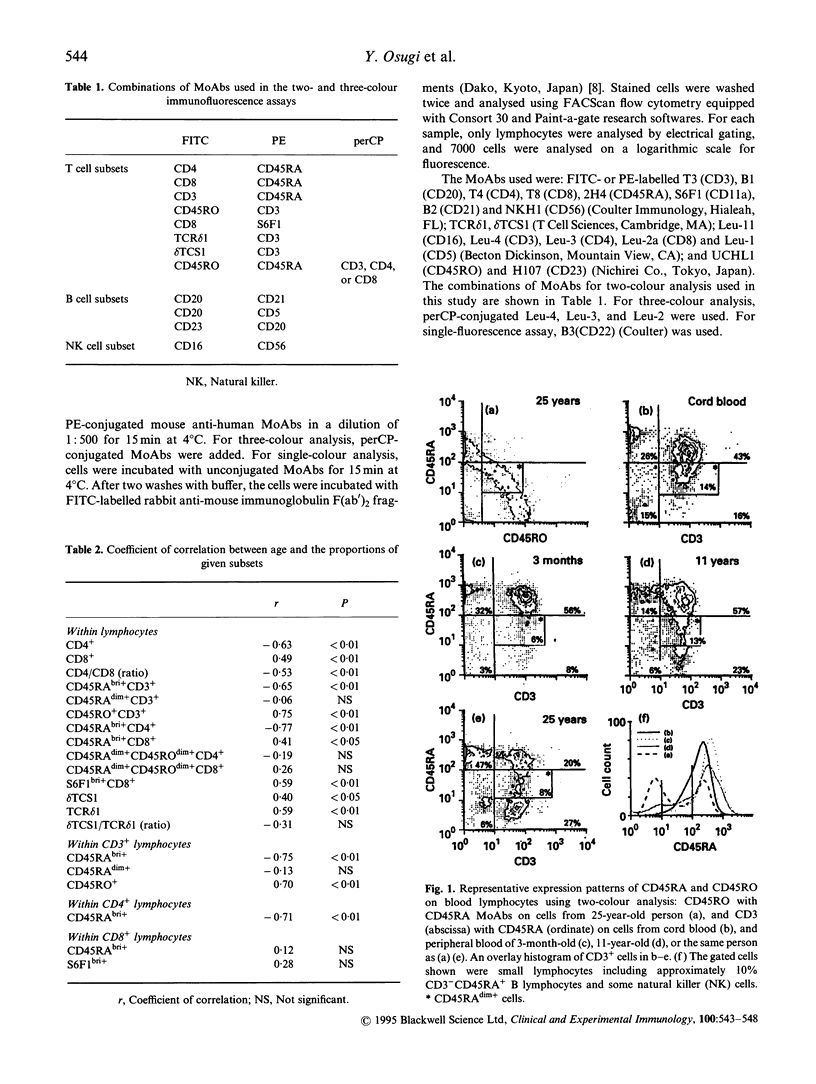
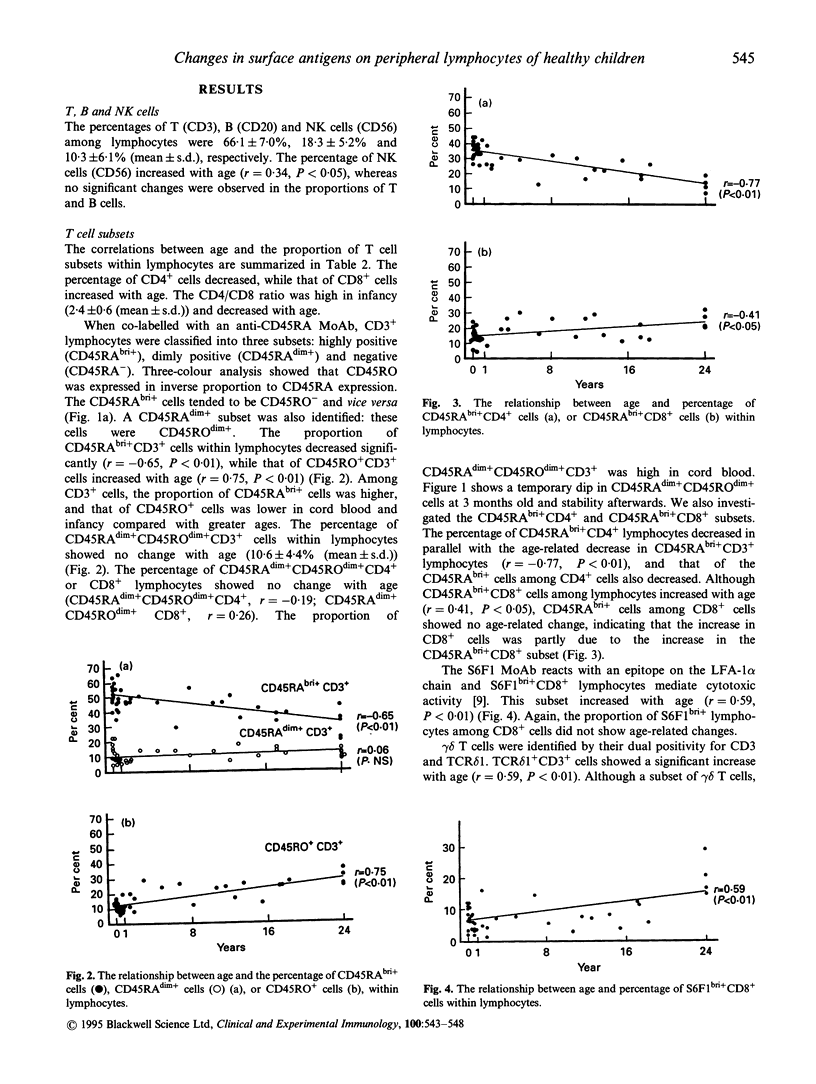
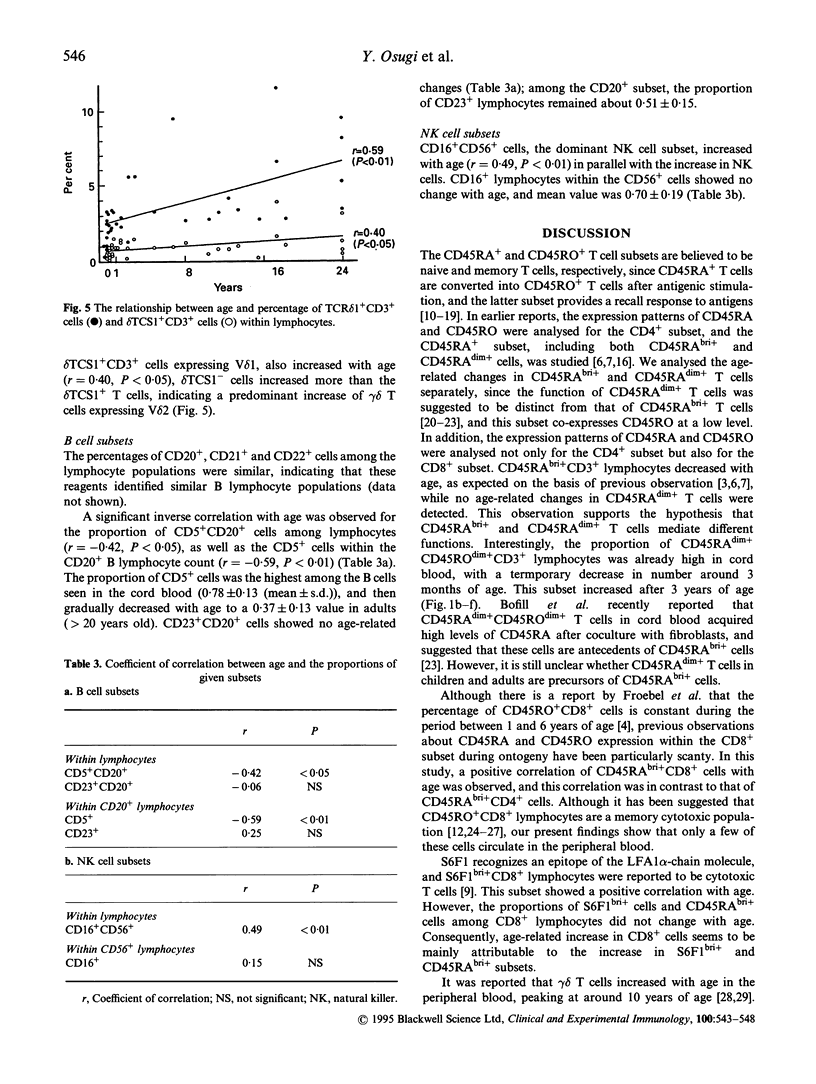
The age-related changes in proportion of various subsets within lymphocytes were investigated in cord blood and peripheral blood from healthy children and adults. The percentages of T and B cells did not show age-related changes, whereas natural killer (NK) cells increased significantly with age. Within lymphocytes or the CD3+ T cell population the proportion of CD45RAbright+ lymphocytes decreased and that of CD45RO+ cells increased, while that of CD45RAdim+ cells showed no age-related change. Within lymphocytes, the percentage of CD45RAbright+ CD4+ cells decreased, together with a decline of that of CD4+ cells. The proportions of CD45RAbright+ CD8+ cells and S6F1bright+ CD8+ cells increased with age, and the age-dependent increase of the proportion of CD8+ cells seems to be mainly attributable to the increases in these subsets. The CD45RAdim+ CD4+ and CD45RAdim+ CD8+ cells co-expressing CD45RO at a low level nevertheless showed no age-related changes. In gamma delta T cells, both delta TCS1+ and delta TCS1- T cells increased with age, but the delta TCS1- gamma delta T cells increased more than the delta TCS1+ subset. Among lymphocytes, the percentages of CD20+, CD21+ and CD22+ cells remained similar, with no age-related changes, but the proportion of CD5+ cells within lymphocytes or B cells decreased. The proportions of CD16+ NK cells among lymphocytes increased with age, and this change was attributable to the increase of CD56+ cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Salmon M., Janossy G. The synergy between naive and memory T cells during activation. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. C., Boyd A. W., Fisher D. C., Slaughenhoupt B., Groopman J. E., O'Hara C. J., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Isolation and functional analysis of human B cell populations. I. Characterization of the B1+B2+ and B1+B2- subsets. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):820–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreu-Sánchez J. L., Moreno de Alborán I. M., Marcos M. A., Sánchez-Movilla A., Martínez-A C., Kroemer G. Interleukin 2 abrogates the nonresponsive state of T cells expressing a forbidden T cell receptor repertoire and induces autoimmune disease in neonatally thymectomized mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1323–1329. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandeira A., Itohara S., Bonneville M., Burlen-Defranoux O., Mota-Santos T., Coutinho A., Tonegawa S. Extrathymic origin of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bearing T-cell antigen receptor gamma delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bofill M., Akbar A. N., Salmon M., Robinson M., Burford G., Janossy G. Immature CD45RA(low)RO(low) T cells in the human cord blood. I. Antecedents of CD45RA+ unprimed T cells. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5613–5623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. CD5+ B lymphocytes, polyreactive antibodies and the human B-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Battistin S., Santini G. F. Age-related changes in human lymphocyte subsets: progressive reduction of the CD4 CD45R (suppressor inducer) population. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Sep;48(3):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörken B., Moldenhauer G., Pezzutto A., Schwartz R., Feller A., Kiesel S., Nadler L. M. HD39 (B3), a B lineage-restricted antigen whose cell surface expression is limited to resting and activated human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4470–4479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erkeller-Yuksel F. M., Deneys V., Yuksel B., Hannet I., Hulstaert F., Hamilton C., Mackinnon H., Stokes L. T., Munhyeshuli V., Vanlangendonck F. Age-related changes in human blood lymphocyte subpopulations. J Pediatr. 1992 Feb;120(2 Pt 1):216–222. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froebel K. S., Doherty K. V., Whitelaw J. A., Hague R. A., Mok J. Y., Bird A. G. Increased expression of the CD45RO (memory) antigen on T cells in HIV-infected children. AIDS. 1991 Jan;5(1):97–99. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel H., Schmitt B., Kindermann W. Age-related increase of CD45RO+ lymphocytes in physically active adults. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Oct;23(10):2704–2706. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. Immunological memory. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:49–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Cerf-Bensussan N., Malissen B., Malassis-Seris M., Briottet C., Vassalli P. Two gut intraepithelial CD8+ lymphocyte populations with different T cell receptors: a role for the gut epithelium in T cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannet I., Erkeller-Yuksel F., Lydyard P., Deneys V., DeBruyère M. Developmental and maturational changes in human blood lymphocyte subpopulations. Immunol Today. 1992 Jun;13(6):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara J., Kawa-Ha K., Yumura-Yagi K., Kurahashi H., Tawa A., Ishihara S., Inoue M., Murayama N., Okada S. In vivo and in vitro expression of myeloid antigens on B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 1991 Jan;5(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Lee J., Beverley P. C. Ontogeny of expression of UCHL1 antigen on TcR-1+ (CD4/8) and TcR delta+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):771–773. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J. The CD5 B cell. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:117–185. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Vitetta E. S. Limiting dilution analysis of CD45Rhi and CD45Rlo T cells: further evidence that CD45Rlo cells are memory cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;130(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R. T-cell memory: the connection between function, phenotype and migration pathways. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90051-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Rudd C. E., Hagan M., Takeuchi T., Schlossman S. F. The role of the 2H4 molecule in the generation of suppressor function in Con A-activated T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3247–3253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Rudd C. E., Letvin N. L., Schlossman S. F. A novel epitope of the LFA-1 antigen which can distinguish killer effector and suppressor cells in human CD8 cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):479–482. doi: 10.1038/330479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., van Agthoven A., Terhorst C., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B cell-specific antigen (B2) distinct from B1. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura M., Fujii Y., Inada K., Nakahara K., Matsuda H. Both CD45RA+ and CD45RA- subpopulations of CD8+ T cells contain cells with high levels of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 expression, a phenotype of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura M., Fujii Y., Takeuchi Y., Inada K., Nakahara K., Matsuda H. Age-related accumulation of LFA-1high cells in a CD8+CD45RAhigh T cell population. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1057–1063. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. M., Groh V., Band H., Porcelli S. A., Morita C., Fabbi M., Glass D., Strominger J. L., Brenner M. B. Evidence for extrathymic changes in the T cell receptor gamma/delta repertoire. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1597–1612. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha B., Vassalli P., Guy-Grand D. The V beta repertoire of mouse gut homodimeric alpha CD8+ intraepithelial T cell receptor alpha/beta + lymphocytes reveals a major extrathymic pathway of T cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):483–486. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer U., Jung T., Heymanns J., Rieger C. H. Imbalance of CD4+CD45R+ and CD4+CD29+ T helper cell subsets in patients with atopic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):25–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki S., Abo T., Masuda T., Ohteki T., Kanno A., Takeda K., Rikiishi H., Nagura H., Kumagai K. Identification of activated T cell receptor gamma delta lymphocytes in the liver of tumor-bearing hosts. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):409–415. doi: 10.1172/JCI114726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. H., Brown M. H., Rowe D., Callard R. E., Beverley P. C. Functional subsets of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody, UCHL1. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):63–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stashenko P., Nadler L. M., Hardy R., Schlossman S. F. Expression of cell surface markers after human B lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3848–3852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Hall L. R., Saga Y., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. Differential usage of three exons generates at least five different mRNAs encoding human leukocyte common antigens. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1548–1566. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Morimoto C., Schrieber M., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. Characterization of CD45 and CD45R monoclonal antibodies using transfected mouse cell lines that express individual human leukocyte common antigens. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3910–3914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L. The leukocyte common antigen family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:339–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Berton M. T., Burger C., Kepron M., Lee W. T., Yin X. M. Memory B and T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:193–217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yachie A., Ueno Y., Takano N., Miyawaki T., Taniguchi N. Developmental changes of double-negative (CD3+ 4-8-) T cells in human peripheral blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):258–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Clement L. T. Phenotypic characterization of the post-thymic differentiation of human alloantigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1518–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Takeda Y., Ohga S., Kishihara K., Yuuki H., Nomoto K. Functional T cell receptor delta chain gene messages in athymic nude mice. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1039–1043. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Reis M. D., Mak T. W. Athymic mice express a high level of functional gamma-chain but greatly reduced levels of alpha- and beta-chain T-cell receptor messages. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):482–485. doi: 10.1038/324482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



