Abstract
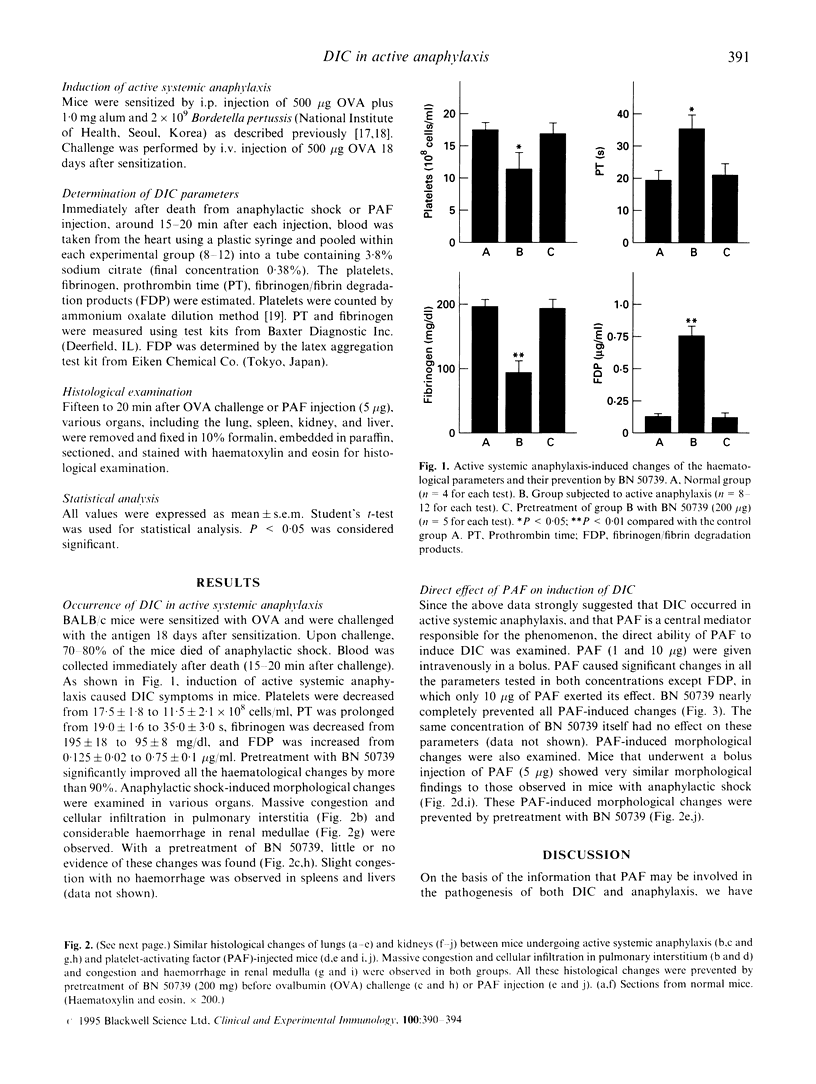
The possible occurrence of DIC in active systemic anaphylaxis was investigated in mice. Induction of active systemic anaphylaxis resulted in the development of DIC symptoms such as thrombocytopenia, prolongation of prothrombin time, hypofibrinogaemia, and elevated level of fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products. In addition, in histological examinations, massive congestion and cellular infiltration in pulmonary interstitia, and considerable haemorrhage in renal medullae were observed. All these changes were nearly completely prevented by pretreatment with platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist (BN 50739). Moreover, the same haematological and morphological changes were produced by a bolus injection of PAF. These data strongly suggest that DIC occurs in active systemic anaphylaxis and PAF plays a pivotal role in the development of DIC in anaphylaxis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arimura A., Nagata M., Watanabe A., Nakamura K., Takeuchi M., Harada M. Production of active and passive anaphylactic shock in the WBB6F1 mouse, a mast cell-deficient strain. Experientia. 1990 Jul 15;46(7):739–742. doi: 10.1007/BF01939952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., SCHNEIDERMAN M., CRONKITE E. P. The reproducibility and constancy of the platelet count. Am J Clin Pathol. 1953 Jan;23(1):15–26. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/23.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., ten Cate H., Barzegar S., Spriggs D. R., Sherman M. L., Rosenberg R. D. Tumor necrosis factor infusions have a procoagulant effect on the hemostatic mechanism of humans. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):618–623. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Fiers W., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Etienne A., Touvay C., Bourgain R. H., Lefort J., Vargaftig B. B. Involvement of platelet activating factor in respiratory anaphylaxis, demonstrated by PAF-acether inhibitor BN 52021. Lancet. 1985 Jun 29;1(8444):1501–1501. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Touqui L., Shen T. Y., Vargaftig B. B. Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):97–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Breviario F., Tetta C., Aglietta M., Mantovani A., Dejana E. Interleukin 1 stimulates platelet-activating factor production in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):2027–2033. doi: 10.1172/JCI112532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Bussolino F., Salvidio G., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin stimulates peritoneal macrophages, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, and vascular endothelial cells to synthesize and release platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1390–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Bussolino F., Baglioni C. Synthesis and release of platelet-activating factor is inhibited by plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor or alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and is stimulated by proteinases. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1293–1306. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha T. Y., Reed N. D., Crowle P. K. Immune response potential of mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;80(1):85–94. doi: 10.1159/000234031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha T. Y., Reed N. D. Systemic anaphylaxis in mast-cell-deficient mice of W/Wv and Sl/Sld genotypes. Exp Cell Biol. 1987;55(2):63–68. doi: 10.1159/000163399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. M., Lespy L., Maffrand J. P. Protective effect of SR 27417, a novel PAF antagonist, on lethal anaphylactic and endotoxin-induced shock in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 3;205(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90909-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi N., Komuro Y., Morooka S. Effect of a selective PAF antagonist SM-10661 ((+/-)-cis-3,5-dimethyl-2-(3-pyridyl)thiazolidin-4-one HCl) on experimental disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Lipids. 1991 Dec;26(12):1391–1395. doi: 10.1007/BF02536573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imura Y., Terashita Z., Nishikawa K. Possible role of platelet activating factor (PAF) in disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), evidenced by use of a PAF antagonist, CV-3988. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 14;39(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K. Biology of immunoglobulin E. Molecular basis of reaginic hypersensitivity. Prog Allergy. 1975;19:60–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura M., Terashita Z., Imura Y., Shino A., Nishikawa K. Inhibitory effect of TCV-309, a novel platelet activating factor (PAF) antagonist, on endotoxin-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in rats: possible role of PAF in tissue factor generation. Thromb Res. 1993 May 15;70(4):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90101-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi M., ten Cate H., van der Poll T., van Deventer S. J. Pathogenesis of disseminated intravascular coagulation in sepsis. JAMA. 1993 Aug 25;270(8):975–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashita Z., Imura Y., Nishikawa K. Inhibition by CV-3988 of the binding of [3H]-platelet activating factor (PAF) to the platelet. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 1;34(9):1491–1495. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90689-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Epstein L. B. Biphasic platelet-activating factor synthesis by human monocytes stimulated with IL-1-beta, tumor necrosis factor, or IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3945–3950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilain B., Lagente V., Touvay C., Desquand S., Randon J., Lefort J., Braquet P., Vargaftig B. B. Pharmacological control of the in vivo passive anaphylactic shock by the PAF-acether antagonist compound BN 52021. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1986 Aug;18 (Suppl):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0031-6989(86)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




