Abstract
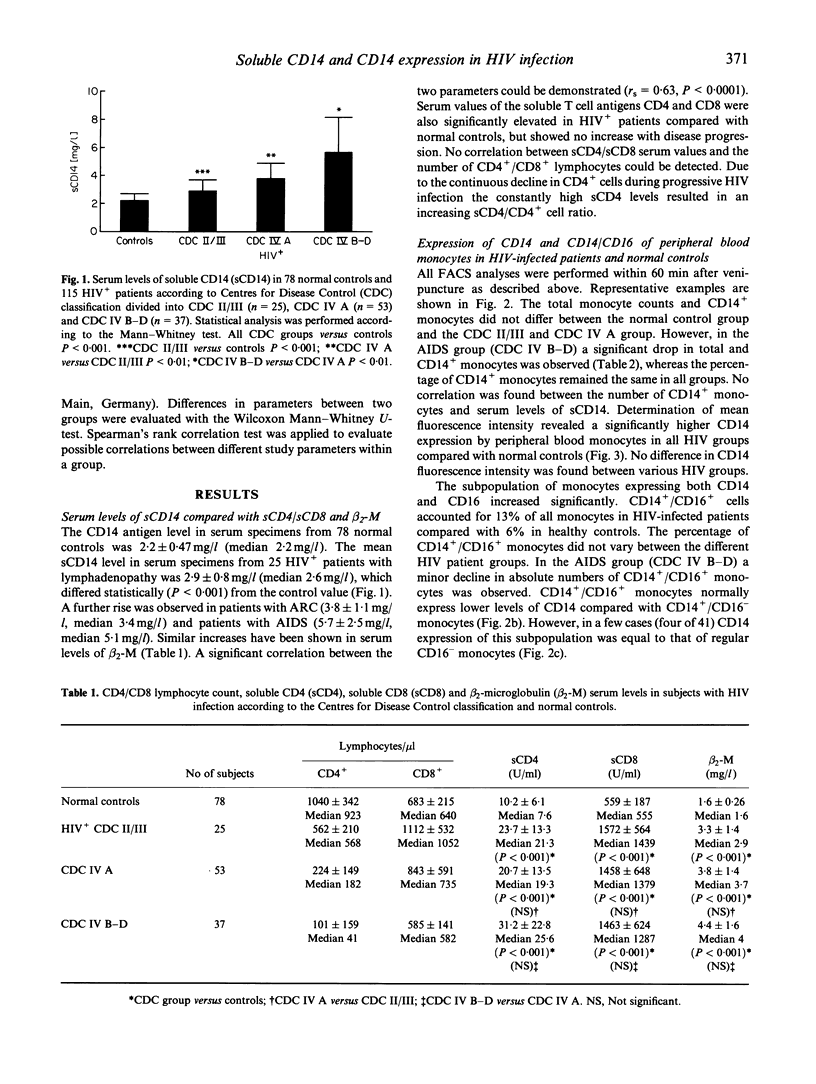
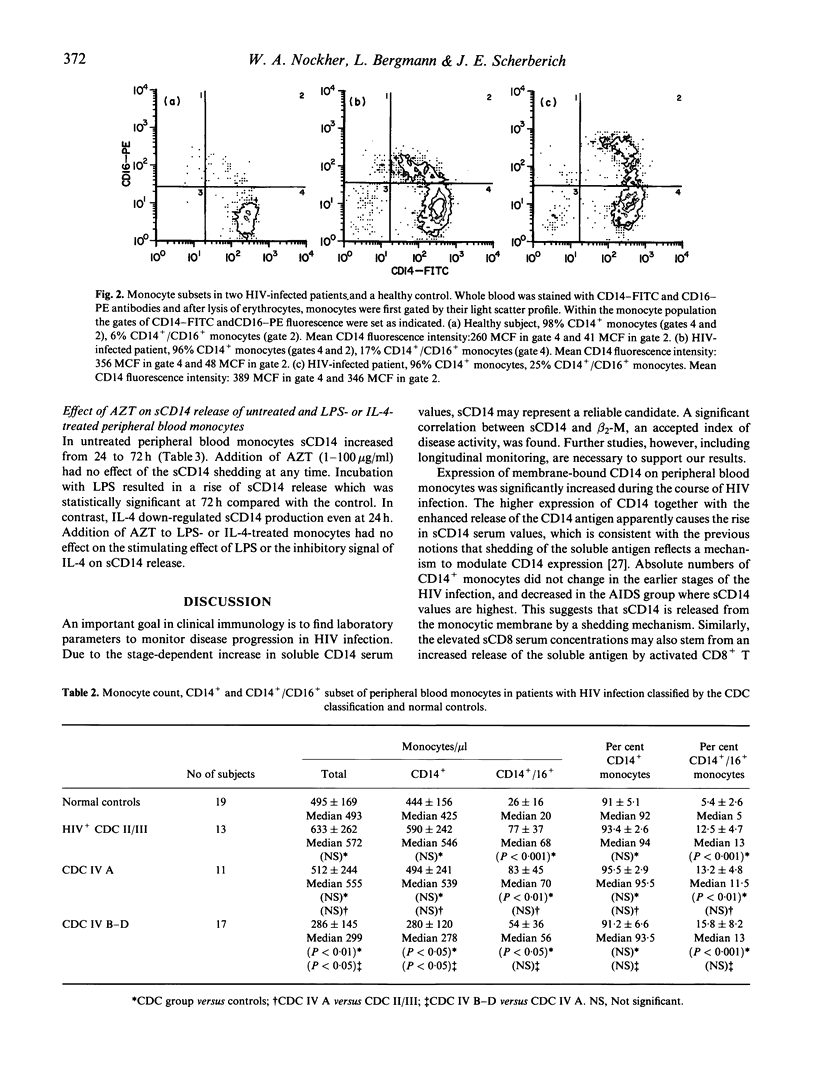
Serum levels of soluble CD14 were elevated in HIV-infected asymptomatic patients or those with lymphadenopathy (CDC II/III) 2.9 +/- 0.8 mg/l compared with normal controls with 2.2 +/- 0.47 mg/l, P < 0.001. A further rise was seen in patients with ARC (CDC IVA) 3.8 +/- 1.1 mg/l, P < 0.01 and patients with AIDS (CDC IVB-D) 5.7 +/- 2.5 mg/l, P < 0.01. Although absolute numbers of CD14+ cells decrease in the AIDS group, the percentage of CD14+ monocytes did not change. In contrast, levels of soluble T cell antigens sCD4 and sCD8, which are higher in HIV-infected patients compared with normal subjects, showed no increase with disease progression. Serum levels of sCD14 were correlated positively with beta 2-microglobulin levels (rs = 0.63, P < 0.0001). Whereas the percentage of CD14+ monocytes did not change, an increase in monocytic CD14 expression in HIV-infected patients was observed (P < 0.01). The percentage of a monocyte subset expressing both CD14 and CD16 increased from 6% in normal healthy persons to 13% in HIV-infected patients (P < 0.001), and did not vary between the HIV patient groups. Incubation of cultured peripheral blood monocytes with azidothymidine had no effect on either normal or LPS-induced or IL-4-inhibited sCD14 release in vitro. Therefore, an effect of AZT on sCD14 serum values in vivo is considered to be unlikely. Our data further provide evidence that monocytes/macrophages are engaged in HIV infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostini C., Pizzolo G., Zambello R., Trentin L., Siviero F., Vinante F., Morosato L., Francavilla E., Cadrobbi P., Semenzato G. Shedding of the soluble form of the CD8 complex by CD8+/HLA-DR+ cells in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):813–819. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199107000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Wright S. D., Seshamma T., Oakes J. W., Pomerantz R. J. CD14 is involved in control of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression in latently infected cells by lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6285–6289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Baudys M., Hilgert I., Stefanová I., Low M. G., Zbrozek J., Horejsí V. Structural relationship between the soluble and membrane-bound forms of human monocyte surface glycoprotein CD14. Mol Immunol. 1989 Jul;26(7):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Horejsí V., Baudys M., Kristofová H., Strominger J. L., Kostka W., Hilgert I. Biochemical characterization of a soluble form of the 53-kDa monocyte surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Strominger J. L. Shedding as a mechanism of down-modulation of CD14 on stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1567–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekhuizen H., Blokland I., Corsèl-van Tilburg A. J., Koning F., van Furth R. CD14 contributes to the adherence of human monocytes to cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3761–3767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. J., Berger M. F., Tschuchnigg M., Valentine J. E., Kennedy B. G., Divjak M., Cooper D. A., Turner J. J., Penny R., Sewell W. A. Increased expression of interferon-gamma in hyperplastic lymph nodes from HIV-infected patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Apr;92(1):100–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05954.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of human blood monocytes with Nycodenz, a new non-ionic iodinated gradient medium. Scand J Immunol. 1983 May;17(5):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capsoni F., Minonzio F., Ongari A. M., Colombo G., Rizzardi G. P., Bonara P., D'Arminio-Monforte A., Zanussi C. Increased expression of IgG Fc receptor type I on neutrophils and monocytes from HIV-infected subjects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(2):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb07924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capsoni F., Minonzio F., Ongari A. M., Rizzardi G. P., Lazzarin A., Zanussi C. Monocyte-derived macrophage function in HIV-infected subjects: in vitro modulation by rIFN-gamma and rGM-CSF. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Feb;62(2):176–182. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayota A., Vuillier F., Scott-Algara D., Feuillie V., Dighiero G. Impaired proliferative capacity and abnormal cytokine profile of naive and memory CD4 T cells from HIV-seropositive patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):478–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Shearer G. M. A TH1-->TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J., Bass H. Z., Fahey J. L. Elevated IFN-gamma and decreased IL-2 gene expression are associated with HIV infection. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):5031–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingerle G., Pforte A., Passlick B., Blumenstein M., Ströbel M., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. The novel subset of CD14+/CD16+ blood monocytes is expanded in sepsis patients. Blood. 1993 Nov 15;82(10):3170–3176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey E. A., Miller D. S., Jahr T. G., Sundan A., Bazil V., Espevik T., Finlay B. B., Wright S. D. Soluble CD14 participates in the response of cells to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1665–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyert S. M., Ferrero E., Rettig W. J., Yenamandra A. K., Obata F., Le Beau M. M. The CD14 monocyte differentiation antigen maps to a region encoding growth factors and receptors. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.2448876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hailman E., Lichenstein H. S., Wurfel M. M., Miller D. S., Johnson D. A., Kelley M., Busse L. A., Zukowski M. M., Wright S. D. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein accelerates the binding of LPS to CD14. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):269–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haziot A., Chen S., Ferrero E., Low M. G., Silber R., Goyert S. M. The monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14, is anchored to the cell membrane by a phosphatidylinositol linkage. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):547–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haziot A., Rong G. W., Silver J., Goyert S. M. Recombinant soluble CD14 mediates the activation of endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1500–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haziot A., Tsuberi B. Z., Goyert S. M. Neutrophil CD14: biochemical properties and role in the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in response to lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 15;150(12):5556–5565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Finley F., Leturcq D., Moriarty A., Lee J. D., Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S. Analysis of lipopolysaccharide binding by CD14. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24818–24823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger C., Schütt C., Obertacke U., Joka T., Müller F. E., Knöller J., Köller M., König W., Schönfeld W. Serum CD14 levels in polytraumatized and severely burned patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):297–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeta M. O., Durieux J. J., Fernandez N., Herrmann R., Ferrara P. Release from a human monocyte-like cell line of two different soluble forms of the lipopolysaccharide receptor, CD14. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2144–2151. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmann R., Fisscher A. E., Obrecht J. P. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 down-regulate soluble CD14 release in human monocytes and macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Sep;52(3):323–330. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauener R. P., Goyert S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Interleukin 4 down-regulates the expression of CD14 in normal human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2375–2381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Crowe S., Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Gardner K. D., Jr, McGrath M. S., Mills J. Release of interleukin 1 inhibitory activity (contra-IL-1) by human monocyte-derived macrophages infected with human immunodeficiency virus in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2097–2105. doi: 10.1172/JCI113831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue K. H., Lauener R. P., Winchester R. J., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Engagement of CD14 on human monocytes terminates T cell proliferation by delivering a negative signal to T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackensen A., Galanos C., Wehr U., Engelhardt R. Endotoxin tolerance: regulation of cytokine production and cellular changes in response to endotoxin application in cancer patients. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1992 Nov-Dec;3(6):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R., Ball E. D., Graziano R. F., Fanger M. W. Isolation and characterization of My23, a myeloid cell-derived antigen reactive with the monoclonal antibody AML-2-23. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1929–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melendez-Guerrero L. M., Nicholson J. K., McDougal J. S. In vitro infection of monocytes with HIVBa-L. Effect on cell surface expression of CD4, CD14, HLA-DR, and HLA-DQ. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):731–741. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nockher W. A., Wigand R., Schoeppe W., Scherberich J. E. Elevated levels of soluble CD14 in serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Apr;96(1):15–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugin J., Schürer-Maly C. C., Leturcq D., Moriarty A., Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S. Lipopolysaccharide activation of human endothelial and epithelial cells is mediated by lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and soluble CD14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2744–2748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Tan S., Tenen D. G., Nicholson-Weller A., Seed B. Monocyte antigen CD14 is a phospholipid anchored membrane protein. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B. E., Brown M. C., Ip S. H., Carrabis S., Sullivan J. L. Soluble CD8 during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2230–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushijima H., Kunisada T., Ami Y., Tsuchie H., Takahashi I., Klöcking H. P., Müller W. E. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected cells of myeloid-monocytic lineage (ML-1, HL-60, THP-1, U-937). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992 Oct;5(10):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Gilquin J., Kazatchkine M. D. Zidovudine inhibits functional extracellular monocytic interleukin-1. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):255–257. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199003000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Laude M., Gilquin J., Kazatchkine M. D. HIV infection is associated with the spontaneous production of interleukin-1 (IL-1) in vivo and with an abnormal release of IL-1 alpha in vitro. AIDS. 1989 Nov;3(11):695–699. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198911000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Fingerle G., Ströbel M., Schraut W., Stelter F., Schütt C., Passlick B., Pforte A. The novel subset of CD14+/CD16+ blood monocytes exhibits features of tissue macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2053–2058. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


