Abstract
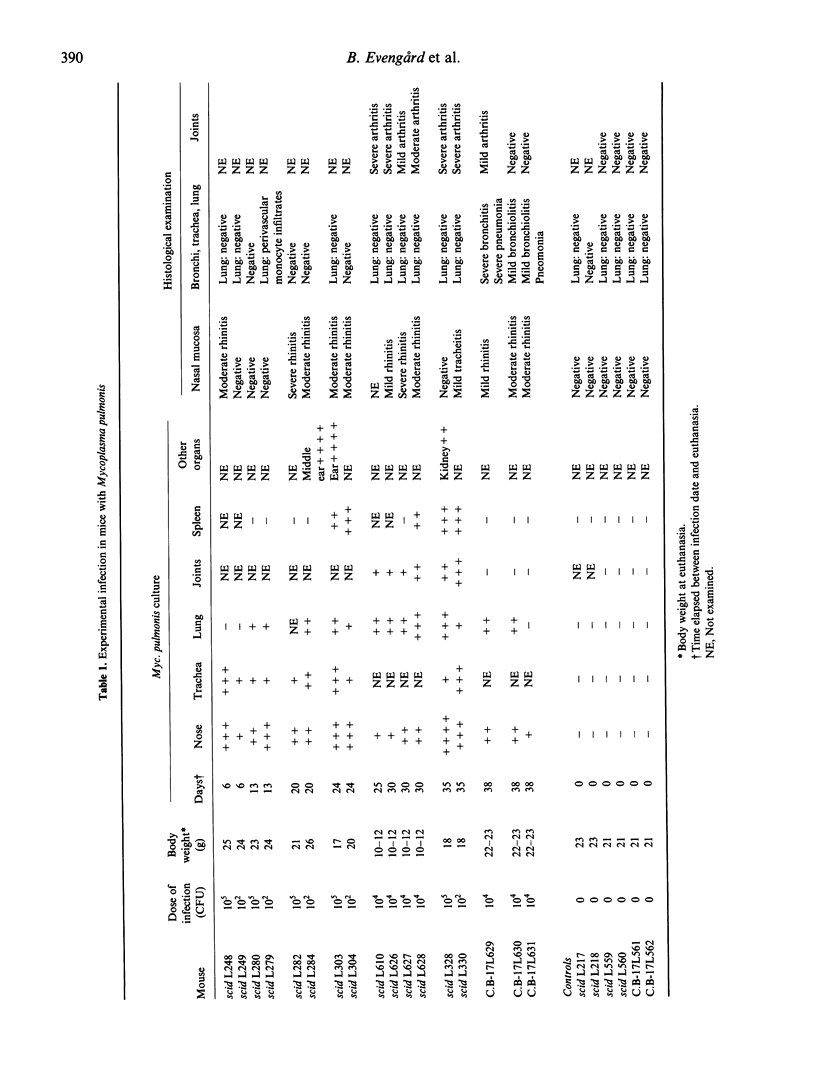
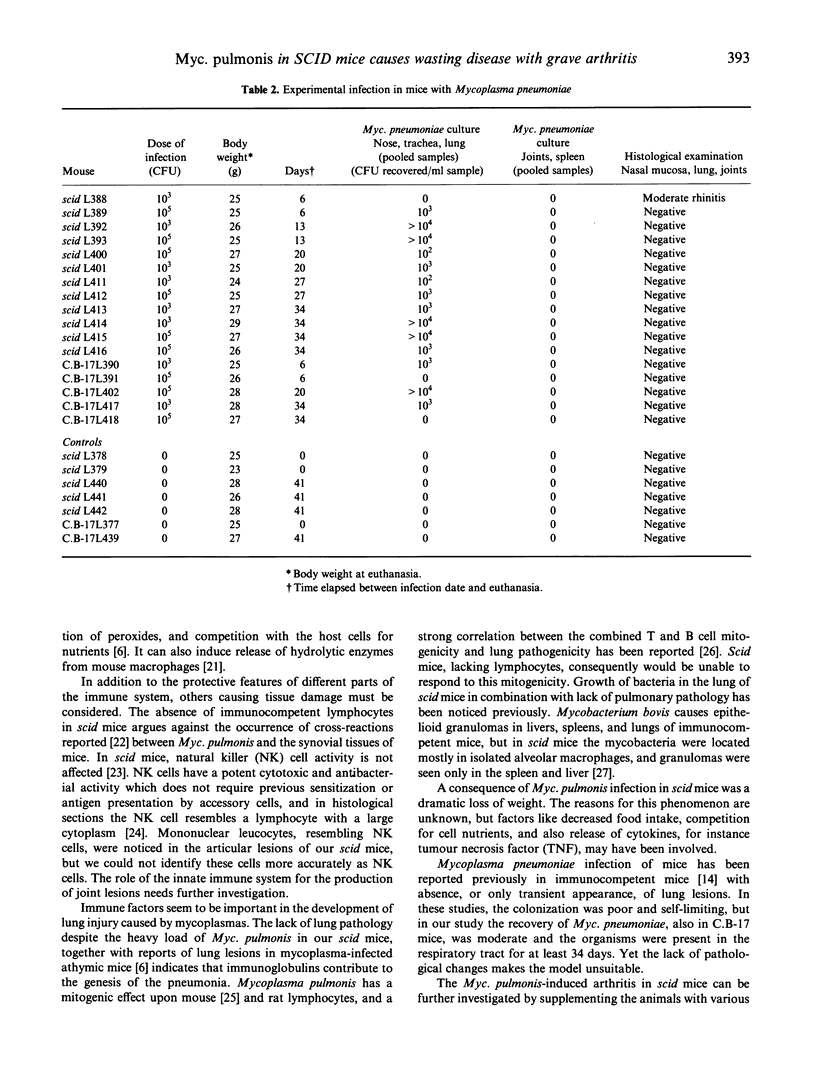
Mycoplasma pulmonis or Myc. pneumoniae were inoculated intranasally to C.B-17 scid/scid mice (severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice). Immunocompetent C.B-17 mice were inoculated as controls. During the observation period of 5 weeks the mice were killed and necropsied. Mycoplasma pulmonis was recovered from all of the inoculated mice, and dissemination to various tissues increased with time. SCID mice, unlike immunocompetent mice, did not show lung lesions but exhibited severe inflammatory changes of the joints. Mycoplasma pulmonis, however, was isolated both from the lungs and the articular lesions. In addition, SCID mice infected for more than 3 weeks suffered from a pronounced loss of weight and emaciation. In the experiment with Myc. pneumoniae the agent could be reisolated, but lesions were not found in any of the infected mice. Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in SCID mice may be useful as a model of arthritis in immunodeficient humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barden J. A., Tully J. G. Experimental arthritis in mice with Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):5–10. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.5-10.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. J., Carroll A. M. The SCID mouse mutant: definition, characterization, and potential uses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:323–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly-Rowland L., Ward J. R. Arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma pulmonis: humoral antibody and lymphocyte responses of CBA mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1083–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1083-1092.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Keller G. M., Phillips R. A., Miller R. G., Bosma G. C., O'Toole M., Bosma M. J. Functional status of cells from lymphoid and myeloid tissues in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency disease. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1804–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Pollack S. B., Bosma M. J., Phillips R. A. Natural killer (NK) cells are present in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (scid). J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3798–3801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Mahoney A. D., Kalmanson G. M., Guze L. B. Arthritis in mice due to infection with Mycoplasma pulmonis. II. Serological and histological features. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):103–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. L., Webster A. D., Taylor-Robinson D., Rapaport G., Hughes G. R. Primary late-onset hypogammaglobulinaemia associated with inflammatory polyarthritis and septic arthritis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Feb;42(1):108–110. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorup-Rönström C., Ahl T., Hammarström L., Smith C. I., Rylander M., Hallander H. Septic osteomyelitis and polyarthritis with ureaplasma in hypogammaglobulinemia. Infection. 1989 Sep-Oct;17(5):301–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01650712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Cunningham A. J., Metcalfe A., Kennedy M., Quinn P. A. Role of antibody in the protection of mice from arthritis induced by Mycoplasma pulmonis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Feb;47(2):253–259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Taylor-Robinson D., Osborn M. F., Ling L., Pope C., Fornasier V. Effect of T-cell deficiency on the chronicity of arthritis induced in mice by Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.192-196.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E., Taylor-Robinson D., Pope C., Taylor G., Furr P. Effect of inherited deficiency of the fifth component of complement on arthritis induced in mice by Mycoplasma pulmonis. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Sep-Oct;21(7):792–797. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn D. F., Chinookoswong N. Detection of Mycoplasma pulmonis in arthritic joints of rats by indirect immunoperoxidase staining. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1321–1323. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1321-1323.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn D. F., Magill L. S., Chinookoswong N. Localization of Mycoplasma pulmonis in cartilage. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):730–733. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.730-733.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsky I. I., Organick A. B. Pneumonia due to mycoplasma in gnotobiotic mice. I. Pathogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma salivarium, and Mycoplasma pulmonis for the lungs of conventional and gnotobiotic mice. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1154–1163. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1154-1163.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Davidson S., Lindenbaum E. S. Role of mitogenicity in pathogenicity of mycoplasmas for murine hosts. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135A(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Izzo A. A. Granuloma formation in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice in response to progressive BCG infection. Tendency not to form granulomas in the lung is associated with faster bacterial growth in this organ. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1959–1966. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Gumpel J. M., Hill A., Swannell A. J. Isolation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from the synovial fluid of a hypogrammaglobulinaemic patient in a survey of patients with inflammatory polyarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Apr;37(2):180–182. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.2.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Schorlemmer H. U., Furr P. M., Allison A. C. Macrophage secretion and the complement cleavage product C3a in the pathogenesis of infections by mycoplasmas and L-forms of bacteria and in immunity to these organisms. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Sep;33(3):486–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A. D., Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Asherson G. L. Mycoplasmal (ureaplasma) septic arthritis in hypogammaglobulinaemia. Br Med J. 1978 Feb 25;1(6111):478–479. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6111.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




