Abstract
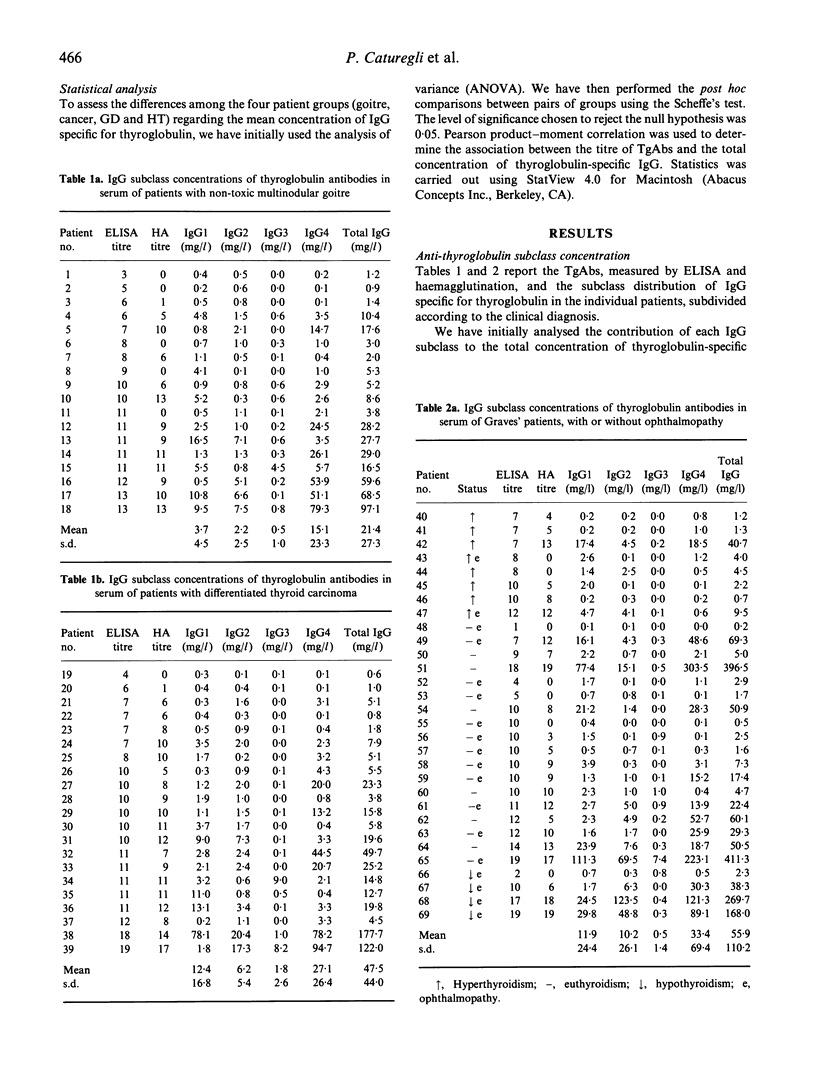
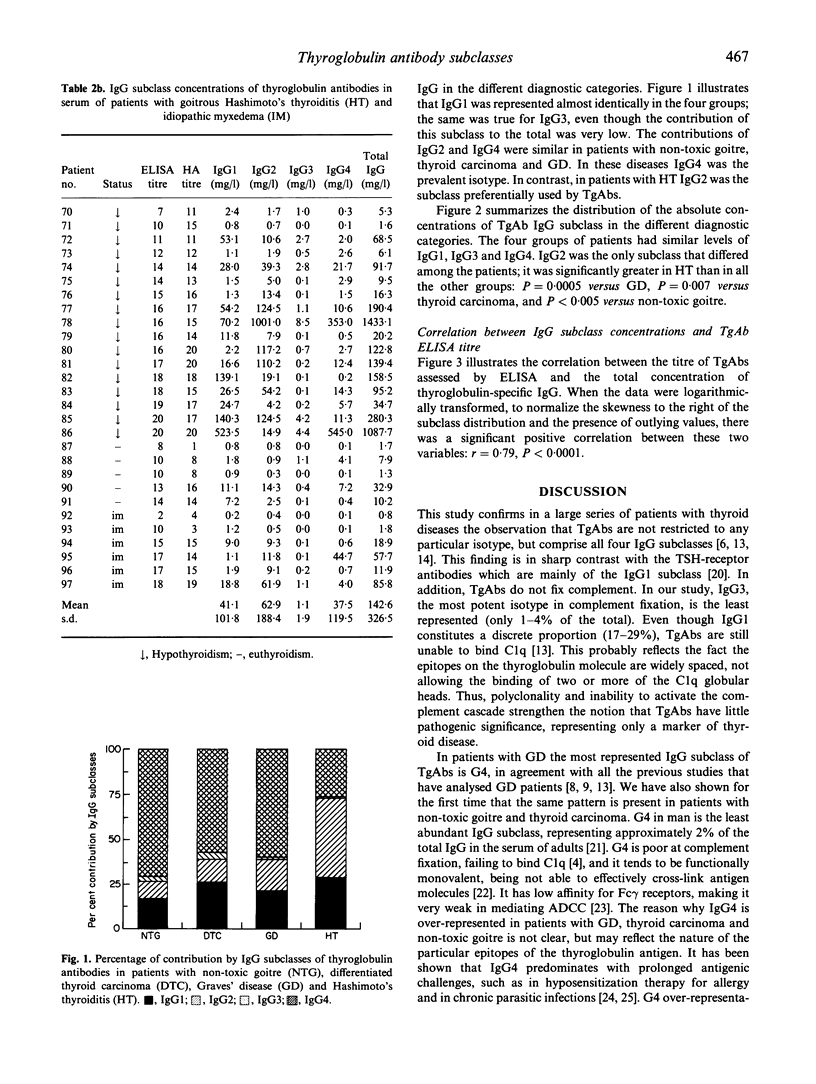
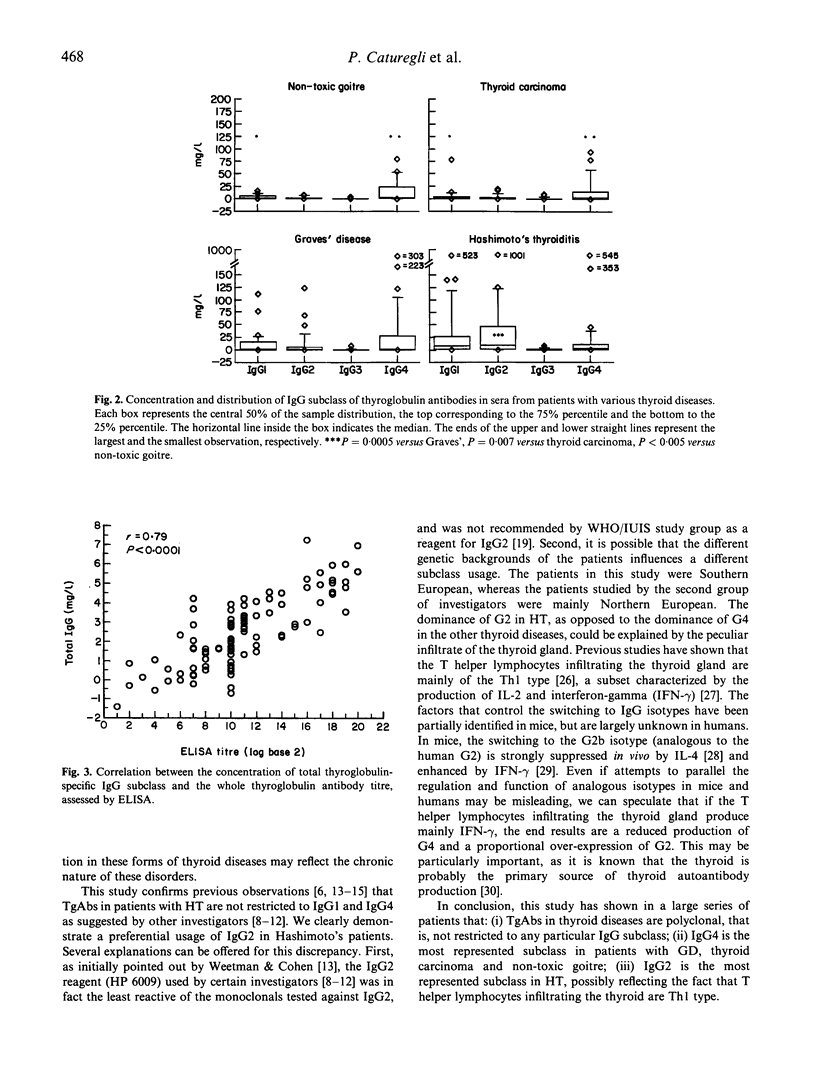
The IgG subclass distribution of thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb) has been studied in Hashimoto and Graves' patients by several investigators with conflicting results, in part explainable by methodological problems. We have recently developed a quantitative ELISA to measure in absolute terms the serum concentration of TgAb subclasses. The aim of the present study was to apply this method in a large series of patients with autoimmune as well as, for the first time, non-autoimmune thyroid diseases. We examined 28 patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, 30 with Graves' disease, 21 with thyroid carcinoma and 18 with non-toxic goitre, all selected for the presence of TgAbs. The results indicated that TgAbs in thyroid diseases were not restricted to any particular isotype, but comprised all four IgG subclasses. IgG1 was represented similarly in the four groups. The same was true for IgG3, even though its contribution to the total antibody content was very small. IgG4 was the dominant subclass in patients with Graves' disease, thyroid carcinoma and non-toxic goitre, probably reflecting a prolonged antigenic challenge. In Hashimoto's thyroiditis IgG2 was dominant, possibly because T helper lymphocytes infiltrating the thyroid are typically Th1 type.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Bindon C. I., Clark M. R., Walker M. R., Jefferis R., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1351–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R. Immunoglobulin G: functional sites. Mol Immunol. 1985 Mar;22(3):161–206. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. F., Weber C. M., Wallack P., Platzer M. Restricted heterogeneity and T cell dependence of human thyroid autoantibody immunoglobulin G subclasses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 May;62(5):945–949. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-5-945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djurup R. The subclass nature and clinical significance of the IgG antibody response in patients undergoing allergen-specific immunotherapy. Allergy. 1985 Oct;40(7):469–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan A. R., Winter G. The binding site for C1q on IgG. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):738–740. doi: 10.1038/332738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. Serum IgG subclasses in normal adults. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Torrigiani G. The distribution of anti-thyroglobulin antibodies in the immunoglobulin G subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):517–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppers R. C., Outschoorn I. M., Hamilton R. G., Burek C. L., Rose N. R. Quantitative measurement of human thyroglobulin-specific antibodies by use of a sensitive enzyme-linked immunoassay. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Apr;67(1):68–77. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Rajewsky K., Müller W. Generation and analysis of interleukin-4 deficient mice. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.1948049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariotti S., del Prete G. F., Mastromauro C., de Carli M., Romagnani S., Ricci M., Pinchera A. The autoimmune infiltrate of Basedow's disease: analysis of clonal level and comparison with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1991 May;97(2-3):139–146. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Bahn R., Rapoport B. Endocrine ophthalmopathy: a re-evaluation of the association with thyroid autoantibodies. Autoimmunity. 1992;14(2):143–148. doi: 10.3109/08916939209083133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Feldt-Rasmussen U., Young E. T., Middleton S. L., Dlichert-Toft M., Siersboek-Nielsen K., Date J., Carr D., Clark F., Rees Smith B. IgG subclass distribution of thyroid autoantibodies: a 'fingerprint' of an individual's response to thyroglobulin and thyroid microsomal antigen. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1987 Mar;26(3):335–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1987.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Aase A., Norderhaug L., Sandlie I. Antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity induced by chimeric mouse-human IgG subclasses and IgG3 antibodies with altered hinge region. Mol Immunol. 1992 Mar;29(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90018-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourits M. P., Koornneef L., Wiersinga W. M., Prummel M. F., Berghout A., van der Gaag R. Clinical criteria for the assessment of disease activity in Graves' ophthalmopathy: a novel approach. Br J Ophthalmol. 1989 Aug;73(8):639–644. doi: 10.1136/bjo.73.8.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottesen E. A., Skvaril F., Tripathy S. P., Poindexter R. W., Hussain R. Prominence of IgG4 in the IgG antibody response to human filariasis. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2707–2712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes A. B., McLachlan S. M., Bird P., Rees Smith B. The distribution of microsomal and thyroglobulin antibody activity among the IgG subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):239–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. M., McLachlan S. M., Parkes A., Clark F., Howel D., Rees Smith B. The IgG subclass distribution of thyroglobulin antibody synthesized in culture. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Aug;18(2):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M., Doniach D. Quantitative distribution of human thyroglobulin autoantibodies in different immunoglobulin classes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Sep;3(7):621–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Burek C. L. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies to thyroglobulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Mar;163(3):402–405. doi: 10.3181/00379727-163-40786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Black C. M., Cohen S. B., Tomlinson R., Banga J. P., Reimer C. B. Affinity purification of IgG subclasses and the distribution of thyroid auto-antibody reactivity in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jul;30(1):73–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Cohen S. The IgG subclass distribution of thyroid autoantibodies. Immunol Lett. 1986 Nov 3;13(6):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., McGregor A. M., Wheeler M. H., Hall R. Extrathyroidal sites of autoantibody synthesis in Graves' disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 May;56(2):330–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Yateman M. E., Ealey P. A., Black C. M., Reimer C. B., Williams R. C., Jr, Shine B., Marshall N. J. Thyroid-stimulating antibody activity between different immunoglobulin G subclasses. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):723–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI114768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zee J. S., van Swieten P., Aalberse R. C. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. II. IgG4 antibodies form small, nonprecipitating immune complexes due to functional monovalency. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3566–3571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


