Abstract
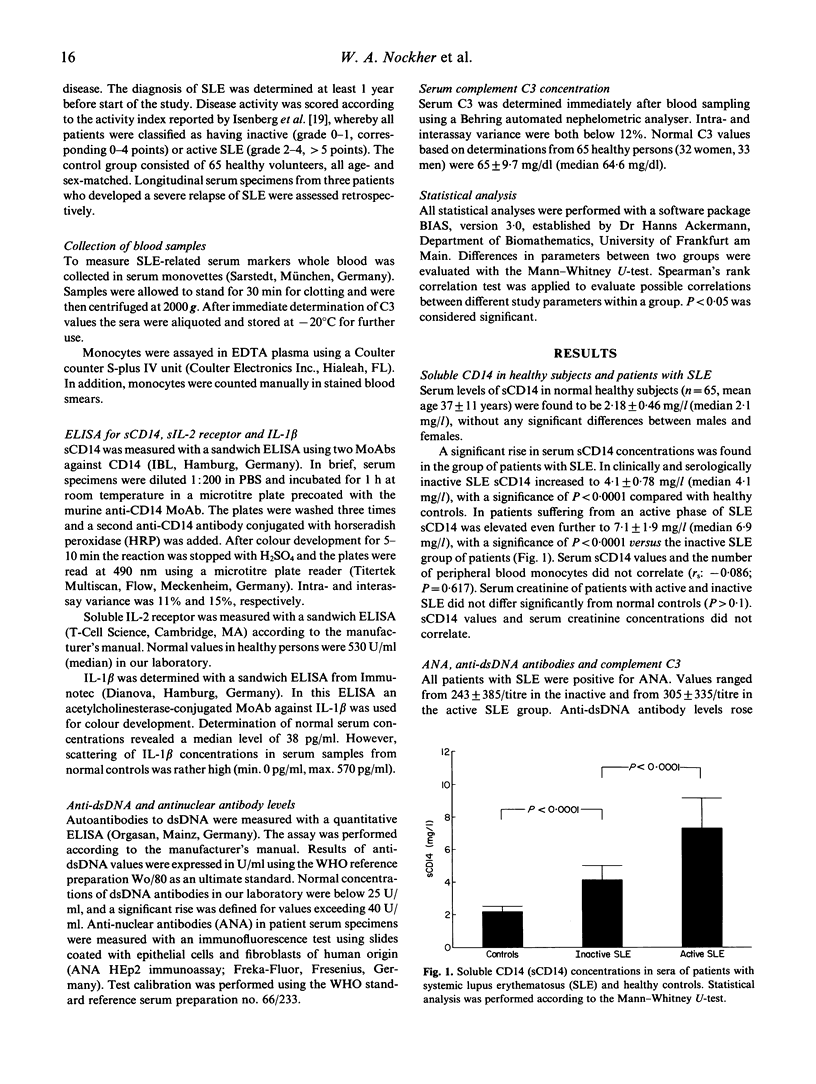
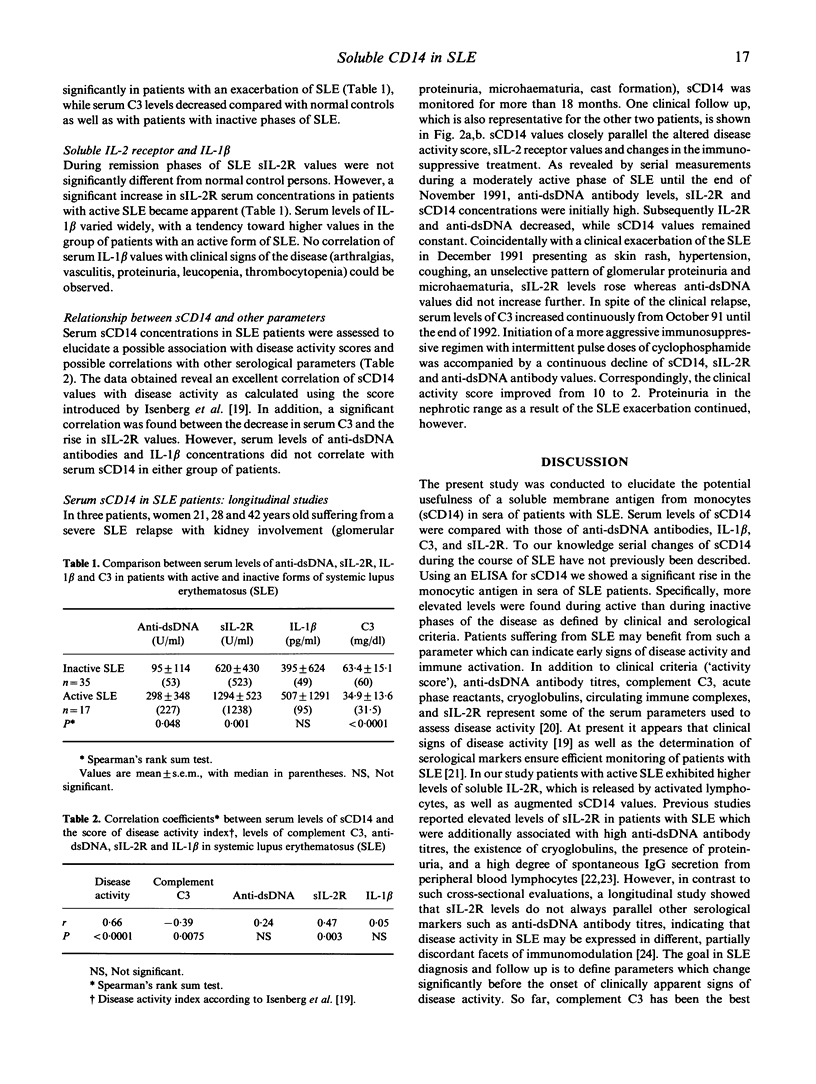
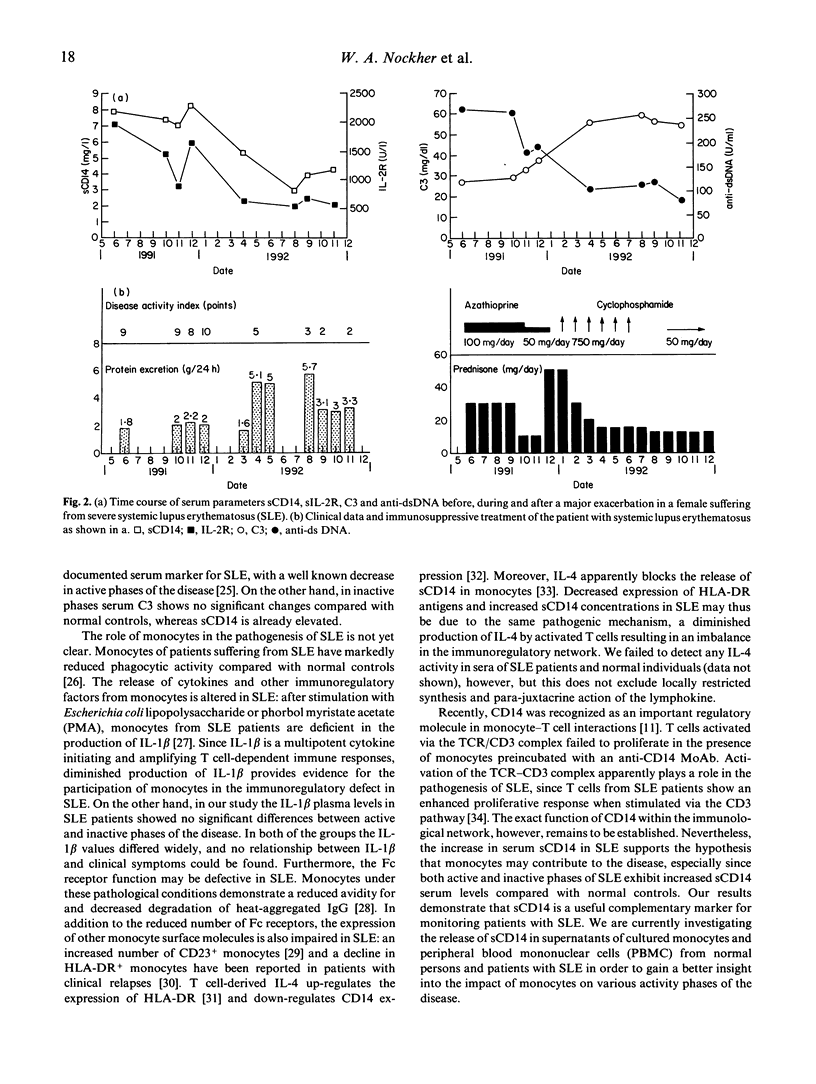
A soluble form of CD14 (sCD14) was assessed with an ELISA assay in the serum of the following three clinical groups: 35 patients with an inactive phase of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 17 patients with SLE relapses, and 65 normal healthy volunteers. Increased levels of sCD14 were observed in all patients suffering from SLE compared with normal controls. In addition, patients with active SLE revealed higher serum concentrations of sCD14 (median 6.9 mg/l) than patients under remission (4.1 mg/l; P < 0.0001). Serum values of sCD14 correlated neither with the number of peripheral blood monocytes bearing the CD14 membrane antigen, nor with serum concentrations of IL-1 beta. Serum sCD14 was compared with other clinical parameters used to monitor the clinical course of patients with SLE, among them complement C3, anti-dsDNA antibodies and soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R). A good correlation emerged between sCD14 and C3 as well as sIL-2R concentrations, but sCD14 and anti-dsDNA titres disclosed no significant correlation in both groups of patients with SLE. Serial studies in patients with severe SLE showed that serum sCD14 closely parallels the clinical course as defined by an activity score. Our data suggest that serum sCD14 represents a promising parameter to monitor disease activity in patients with SLE.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airo P., Braga S., Prati E., Brugnoni D., Bettinzioli M., Gorla R., Cattaneo R. Evaluation of serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor as an indicator of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;11(1):97–100. doi: 10.1007/BF02207093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcocer-Varela J., Laffon A., Alarcón-Segovia D. Defective monocyte production of, and T lymphocyte response to, interleukin-1 in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):125–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen R., Gadd S., Brugger W., Löhr G. W., Atkins R. C. Activation of human monocyte-derived macrophages cultured on Teflon: response to interferon-gamma during terminal maturation in vitro. Immunobiology. 1988 May;177(2):186–198. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(88)80038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Horejsí V., Baudys M., Kristofová H., Strominger J. L., Kostka W., Hilgert I. Biochemical characterization of a soluble form of the 53-kDa monocyte surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Strominger J. L. Shedding as a mechanism of down-modulation of CD14 on stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1567–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker H., Potyka P., Weber C., Federlin K. Detection of circulating Fc epsilon R2/CD23+ monocytes in patients with rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):61–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero E., Goyert S. M. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4173–4173. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Dawisha S., Steinberg A. D. Assessment of in vivo frequency of mutated T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):297–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyert S. M., Ferrero E., Rettig W. J., Yenamandra A. K., Obata F., Le Beau M. M. The CD14 monocyte differentiation antigen maps to a region encoding growth factors and receptors. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.2448876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haziot A., Chen S., Ferrero E., Low M. G., Silber R., Goyert S. M. The monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14, is anchored to the cell membrane by a phosphatidylinositol linkage. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):547–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. P., Perrin L. H., Miescher P. A., Zubler R. H. Correlation of T and B cell activities in vitro and serum IL-2 levels in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):827–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghirami G., Simon J., Balow J. E., Tsokos G. C. Activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induce B cells to produce immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1988 Jul-Sep;6(3):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Dudeney C., Williams W., Addison I., Charles S., Clarke J., Todd-Pokropek A. Measurement of anti-DNA antibodies: a reappraisal using five different methods. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jun;46(6):448–456. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.6.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama S., Chia D., Knutson D. W., Barnett E. V. Decreased Fc receptor avidity and degradative function of monocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger C., Schütt C., Obertacke U., Joka T., Müller F. E., Knöller J., Köller M., König W., Schönfeld W. Serum CD14 levels in polytraumatized and severely burned patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):297–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmann R., Fisscher A. E., Obrecht J. P. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 down-regulate soluble CD14 release in human monocytes and macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Sep;52(3):323–330. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauener R. P., Goyert S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Interleukin 4 down-regulates the expression of CD14 in normal human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2375–2381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue K. H., Lauener R. P., Winchester R. J., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Engagement of CD14 on human monocytes terminates T cell proliferation by delivering a negative signal to T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R., Lomnitzer R., Wadee A. A., Rabson A. R. Defective monocyte function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jan;34(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoguchi M., Nasu N., Yoshida S., Higuchi Y., Akizuki S., Yamamoto S. Mouse and human CD14 (myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein) primary structure deduced from cDNA clones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Yamashita U., Suzuki H. Decrease in HLA-DR-positive monocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3560–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Tan S., Tenen D. G., Nicholson-Weller A., Seed B. Monocyte antigen CD14 is a phospholipid anchored membrane protein. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stekman I. L., Blasini A. M., Leon-Ponte M., Baroja M. L., Abadi I., Rodriguez M. A. Enhanced CD3-mediated T lymphocyte proliferation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Apr;34(4):459–467. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart P. M., Zlotnik A., Woodward J. G. Induction of class I and class II MHC antigen expression on murine bone marrow-derived macrophages by IL-4 (B cell stimulatory factor 1). J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1542–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. M., Dooley M. A., Christenson V. D., Pisetsky D. S. The relationship between soluble interleukin 2 receptor levels and antidouble stranded DNA antibody levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1991 Feb;18(2):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. D. Relative value of serum C3 and C4 levels in predicting relapse in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991 Dec;18(6):686–688. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80610-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Brelsford W. G. Soluble interleukin-2 receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Borg E. J., Horst G., Hummel E. J., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):634–643. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Borg E. J., Horst G., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Changes in plasma levels of interleukin-2 receptor in relation to disease exacerbations and levels of anti-dsDNA and complement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Oct;82(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


