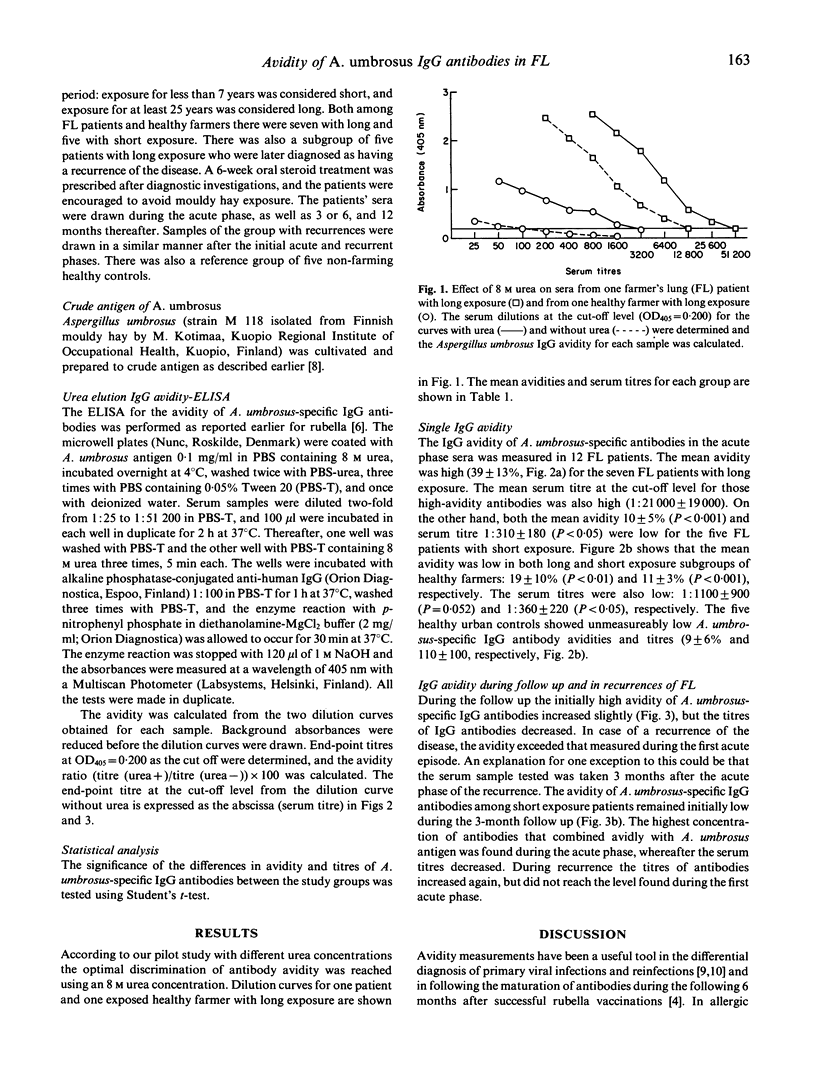
Abstract
Farmer's lung disease (FL), the commonest form of allergic alveolitis caused by repeated inhalation of mouldy hay, is associated with exposure to the fungus Aspergillus umbrosus among Finnish farmers. The antigen-binding avidity of A. umbrosus-specific IgG antibodies was measured in 12 FL patients in acute phases of initial and recurrent attacks and during 1 year follow up as well as in 12 healthy farmers and five healthy urban controls. The farmers' groups were further divided into two subgroups: subjects with short exposure (< 7 years) and subjects with long exposure (> 25 years). During the first acute phase FL patients with long exposure exhibited a high avidity of A. umbrosus-specific IgG antibodies that remained high during the 1 year follow up, although the A. umbrosus-specific IgG antibody titre decreased. A re-exposure to mouldy hay leading to a recurrence further enhanced the maturation of the antibody avidity, so that an even higher A. umbrosus-specific IgG avidity with a less significant increase of antibody titre occurred than during the first acute attack. Notably higher IgG antibody avidity was observed in FL patients with long exposure than in healthy farmers or in healthy controls.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berek C., Berger A., Apel M. Maturation of the immune response in germinal centers. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1121–1129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90289-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Hietala J., Tiilikainen A., Hartikainen-Sorri A. L., Räihä K., Suni J., Vänänen P., Pietiläinen M. Maturation of immunoglobulin G avidity after rubella vaccination studied by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (avidity-ELISA) and by haemolysis typing. J Med Virol. 1989 Apr;27(4):293–298. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890270407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Lappalainen M., Seppäiä I., Mäkelä O. Recent primary toxoplasma infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):736–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Seppälä I. Recent rubella virus infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J Clin Immunol. 1988 May;8(3):214–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00917569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Vaheri A., Brummer-Korvenkontio M. Rapid diagnosis of hantavirus disease with an IgG-avidity assay. Lancet. 1991 Nov 30;338(8779):1353–1356. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92235-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun P. P. Denaturation of globular proteins by urea: breakdown of hydrogen or hydrophobic bonds? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):424–425. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaukonen K., Savolainen J., Viander M., Terho E. O. Characterization of Aspergillus umbrosus carbohydrate antigens by biotinylated lectins and IgG response to mannan/mannoprotein antigens in patients with farmer's lung. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 Jan;23(1):21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb02479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen O. P., Meurman O. H. An ELISA for the estimation of high-avidity and total specific IgG and IgM antibodies to rubella virus. J Virol Methods. 1982 Sep;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangeney M., Fischer A., Le Deist F., Latgé J. P., Durandy A. Direct activation of human B lymphocytes by Candida albicans-derived mannan antigen. Cell Immunol. 1989 Sep;122(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHeyzer-Williams M. G., Nossal G. J., Lalor P. A. Molecular characterization of single memory B cells. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):502–505. doi: 10.1038/350502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: correlation of cellular and immunologic changes with clinical phases of disease. Lung. 1988;166(4):189–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02714049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Human TH1 and TH2 subsets: regulation of differentiation and role in protection and immunopathology. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;98(4):279–285. doi: 10.1159/000236199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau S., Hedman K. Rubella infection and reinfection distinguished by avidity of IgG. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1108–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91926-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Kocks C., Rajewsky K., Dildrop R. Analysis of somatic mutation and class switching in naive and memory B cells generating adoptive primary and secondary responses. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):757–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L. A., Eisen H. N. The relative affinity of antibodies synthesized in the secondary response. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1185–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W. Chronic immune complex disease in mice: the role of antibody affinity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):414–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Lew A. M. The importance of antibody affinity in the performance of immunoassays for antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 22;78(2):173–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terho E. O., Lacey J. Microbiological and serological studies of farmers' lung in Finland. Clin Allergy. 1979 Jan;9(1):43–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1979.tb01521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M. G., Cesari I. M., Yonkovich S. J., Cohn M. Variability in the lambda light chain sequences of mouse antibody. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1045–1047. doi: 10.1038/2281045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Kim Y. T., Quagliata F., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. 3. Changes in heterogeneity of antibody affinity during the course of the immune response. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):477–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Siskind G. W. Distribution of antibody affinities: technique of measurement. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):987–1011. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


