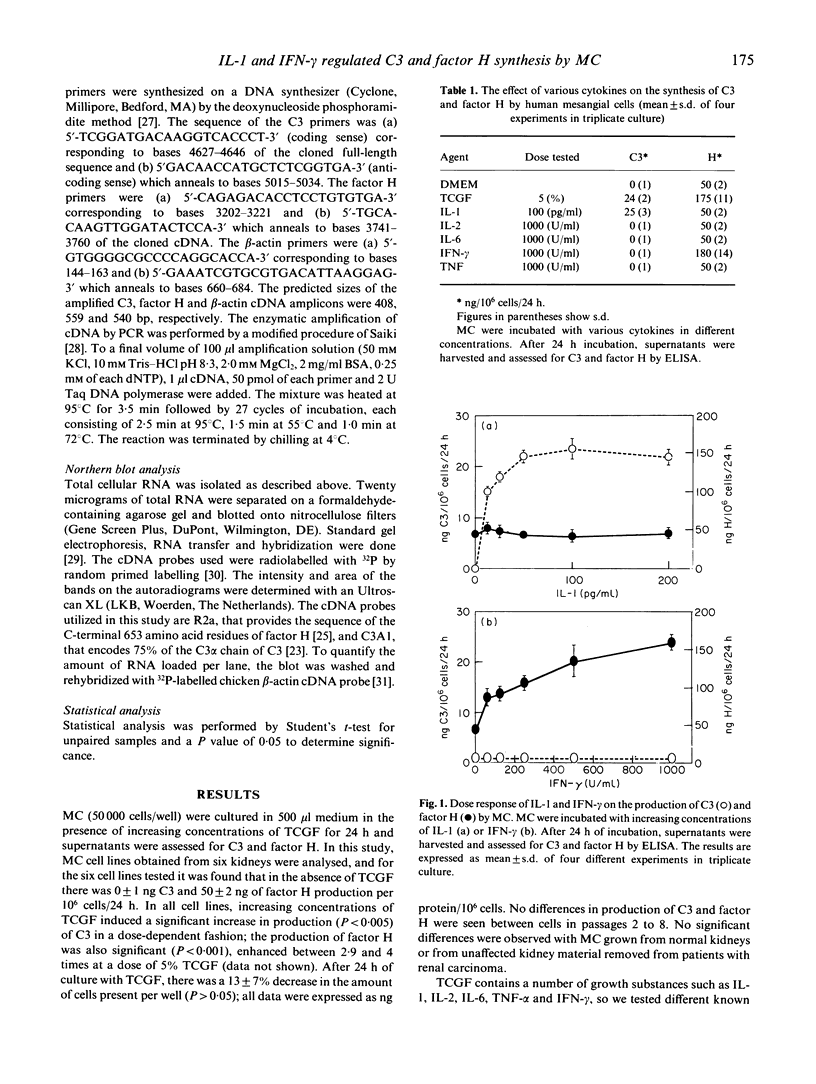
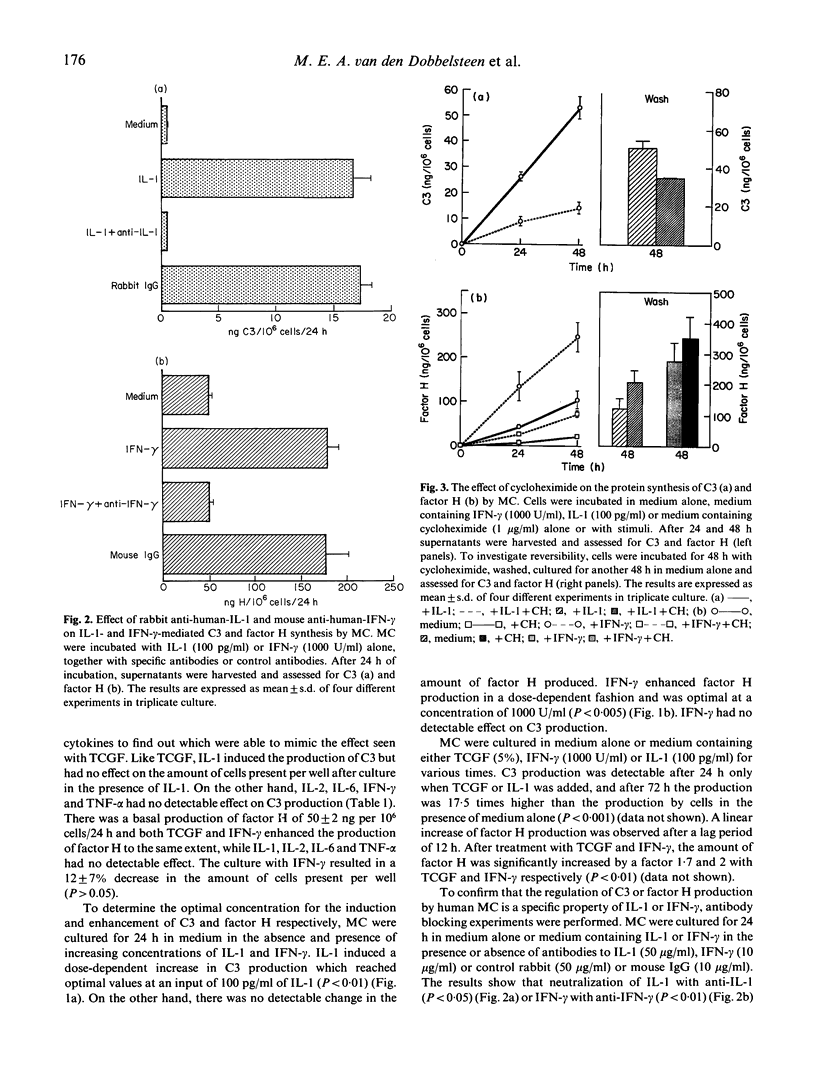
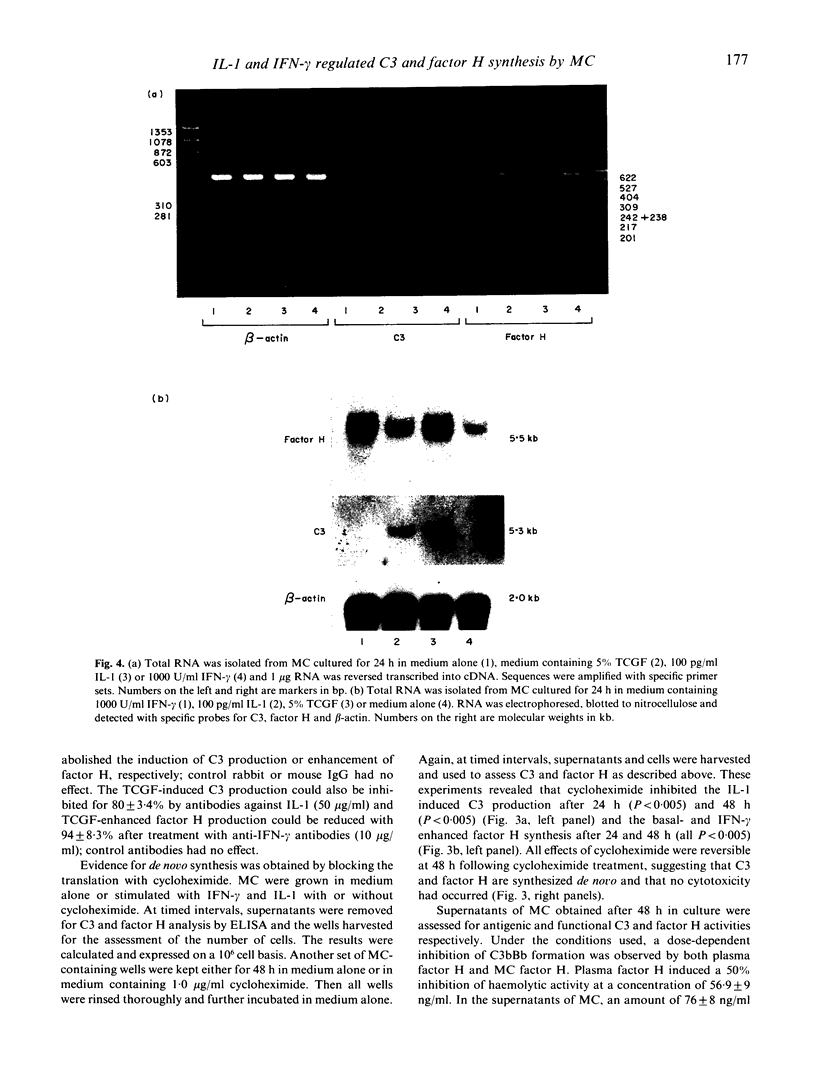
Abstract
Previous reports have shown production of complement components C4, C2 and factor B by renal tissue. We have shown recently that human proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTEC) synthesize C3 in vitro, and that IL-2 enhances this production. In the present study we demonstrate that human mesangial cells (MC) in culture produce factor H and that supernatants of activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (T cell growth factor (TCGF)) induce C3 production and enhance factor H synthesis in both a time- and dose-dependent manner. To investigate whether certain defined cytokines from TCGF were responsible for the observed effect, we tested various cytokines for their effect on complement production by MC. It is shown that IL-1 induces C3 synthesis whereas factor H production is up-regulated by IFN-gamma, in both a dose- and time-dependent manner. Antibody blocking experiments revealed that C3 synthesis induced by both TCGF and IL-1 could be blocked with antibodies specific for IL-1, and also that TCGF and IFN-gamma enhanced factor H synthesis could both be blocked with antibodies specific for IFN-gamma. Cycloheximide was able to inhibit C3 and factor H production, suggesting de novo synthesis of the proteins. mRNA-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis revealed mRNA encoding for C3 after stimulation with TCGF and IL-1. Factor H genes are constitutively expressed in cultured mesangial cells and its expression is up-regulated by TCGF and IFN-gamma. Northern blot analysis with specific probes for C3 and factor H revealed bands which support the results obtained by PCR analysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnum S. R., Amiguet P., Amiguet-Barras F., Fey G., Tack B. F. Complete intron/exon organization of DNA encoding the alpha' chain of human C3. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8471–8474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bene M. C., Faure G. C. Composition of mesangial deposits in IgA nephropathy: complement factors. Nephron. 1987;46(2):219–219. doi: 10.1159/000184350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooimans R. A., Hiemstra P. S., van der Ark A. A., Sim R. B., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Biosynthesis of complement factor H by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Regulation by T cell growth factor and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2024–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooimans R. A., Stegmann A. P., van Dorp W. T., van der Ark A. A., van der Woude F. J., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Interleukin 2 mediates stimulation of complement C3 biosynthesis in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):379–384. doi: 10.1172/JCI115314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooimans R. A., van der Ark A. A., Buurman W. A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Differential regulation of complement factor H and C3 production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by IFN-gamma and IL-1. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3835–3840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Baker P. J., Adler S. Complement and the direct mediation of immune glomerular injury: a new perspective. Kidney Int. 1985 Dec;28(6):879–890. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Bloem A. C., Ballieux R. E. Immunoglobulin production by human peripheral lymphocytes induced by anti-C3 receptor antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1197–1201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feucht H. E., Zwirner J., Bevec D., Lang M., Felber E., Riethmüller G., Weiss E. H. Biosynthesis of complement C4 messenger RNA in normal human kidney. Nephron. 1989;53(4):338–342. doi: 10.1159/000185778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Chromic chloride: a coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E., Hetland G. Mononuclear phagocytes have the potential to synthesize the complete functional complement system. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):489–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Strunk R. C. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Similarities and differences in stimulation of expression of alternative pathway of complement and IFN-beta 2/IL-6 genes in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3862–3867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Strunk R. C. Synovial fibroblast-like cells synthesize seven proteins of the complement system. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D. The multifunctional role of C3, the third component of complement. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenburg A. M., Meijer-Paape M. E., Daha M. R., Paul L. C. Inhibition of T cell cytolytic potential by concanavalin A: a result of activation? Scand J Immunol. 1987 Nov;26(5):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller E. W., Kim Y., Michael A. F., Vernier R. L., van der Hem G. K., van der Woude F. J. Explantation of mesangial cell 'hillocks': a method for obtaining human mesangial cells in culture. Int J Exp Pathol. 1992 Feb;73(1):9–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J., Schreiner G. F., Nonaka M., Beuscher H. U., Colten H. R. Local extrahepatic expression of complement genes C3, factor B, C2, and C4 is increased in murine lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1676–1684. doi: 10.1172/JCI113780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Ng S. Y., Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Evolutionary conservation in the untranslated regions of actin mRNAs: DNA sequence of a human beta-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1687–1696. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoche J., Day A. J., Harris T. J., Sim R. B. The complete amino acid sequence of human complement factor H. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):593–602. doi: 10.1042/bj2490593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoche J., Day A. J., Willis A. C., Belt K. T., Campbell R. D., Sim R. B. Partial characterization of human complement factor H by protein and cDNA sequencing: homology with other complement and non-complement proteins. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jan;6(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01145180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother K., Hänsch G. M., Rauterberg E. W. Complement in inflammation: induction of nephritides and progress to chronicity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;94(1-4):23–37. doi: 10.1159/000235320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks S. H., Zhou W., Pani A., Campbell R. D., Martin J. Complement C3 gene expression and regulation in human glomerular epithelial cells. Immunology. 1993 Jul;79(3):348–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelen M. A., Brooimans R. A., van der Woude F. J., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. IFN-gamma mediates stimulation of complement C4 biosynthesis in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1993 Jul;44(1):50–57. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Cosio F. G., Birmingham D. J. Complement activation induces the expression of decay-accelerating factor on human mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3901–3908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Glomerular cell culture. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Eidlen D. M., Mason R. J. Pulmonary alveolar type II epithelial cells synthesize and secrete proteins of the classical and alternative complement pathways. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1172/JCI113472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Morris S. C., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: structural analysis of the polypeptide chains of C3 and C3b. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1497–1503. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. B., Pantazis P., Davies P. F. The third component of complement is transcribed and secreted by cultured human endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):9–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler J. M., Daha M. R., Austen K. F., Fearon D. T. Control of the amplification convertase of complement by the plasma protein beta1H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of C3b hemolytic activity by a plasma protein distinct from C3b inactivator. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1011–1013. doi: 10.1126/science.948757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte D. P., Welch T. R., Beischel L. S. Detection and cellular localization of human C4 gene expression in the renal tubular epithelial cells and other extrahepatic epithelial sources. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):717–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Fey G. H. Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]