Abstract
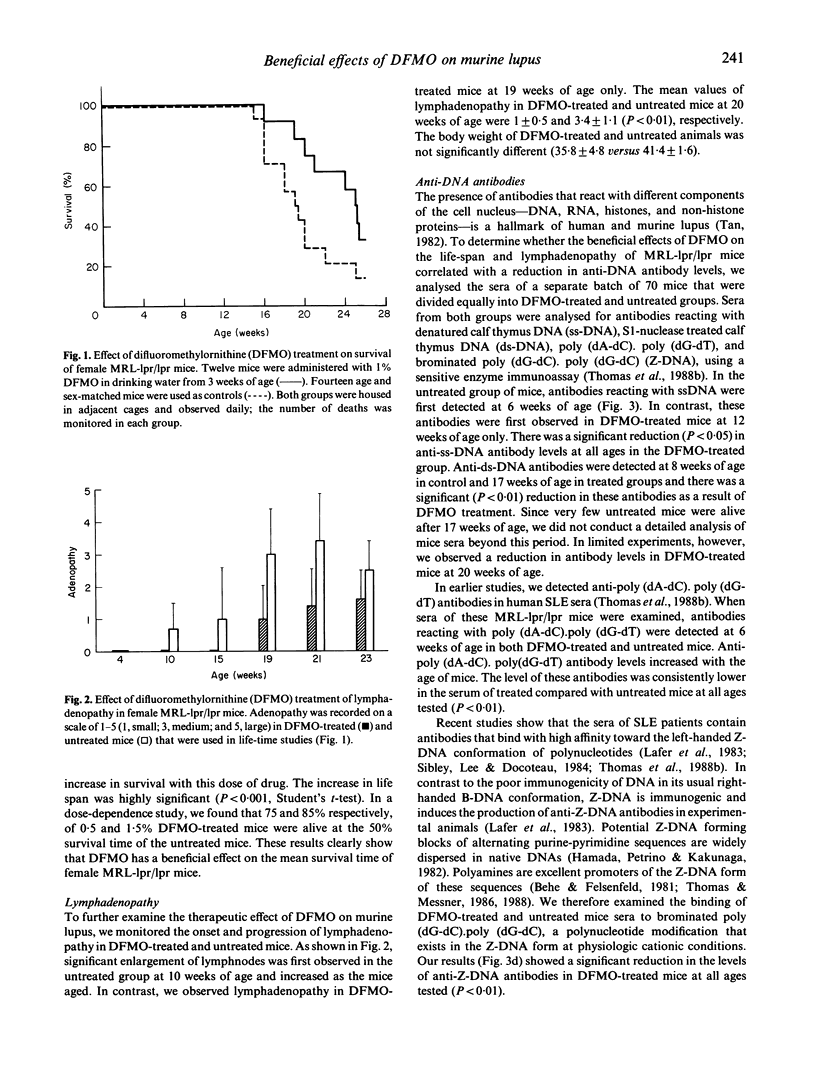
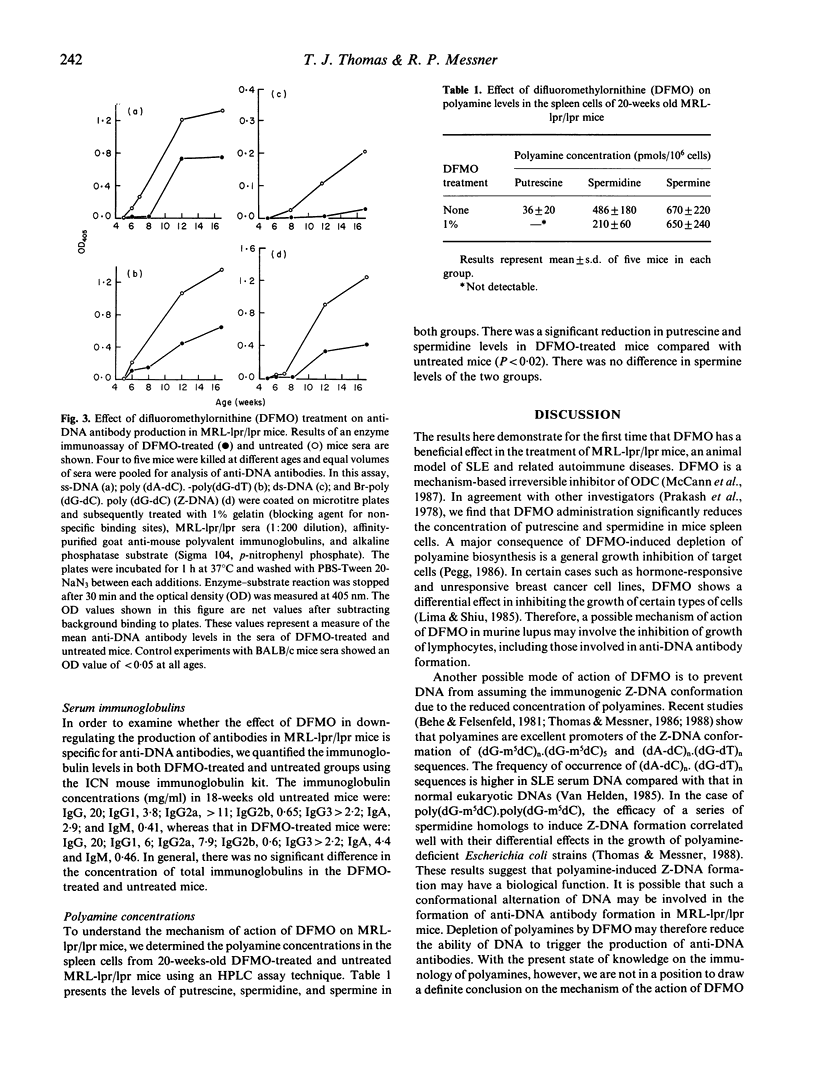
Difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), an experimental drug that inactivates ornithine decarboxylase and thus reduces the production of polyamines has a beneficial effect on the mean survival time and the clinical and laboratory manifestations of murine lupus in female MRL-lpr/lpr mice. DFMO-treated mice showed a 29% increase in the mean survival time compared with age- and sex-matched control mice of the same strain. Lymphadenopathy was evident in untreated mice at 14 weeks of age, but was delayed until 19 weeks of age in DFMO-treated mice. In addition, the sera of DFMO-treated mice contained a significantly lower concentration of anti-DNA antibodies compared with untreated mice. These results open the possibility of development of a new class of therapeutic agents based on polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors for the treatment of human autoimmune disease. Possible mechanisms for the action of DFMO include its inhibitory action on cell proliferation as well as its ability to prevent DNA from assuming an immunogenic left-handed Z-DNA conformation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholeyns J., Mamont P., Casara P. Antitumor properties of (2R,5R)-6-heptyne-2,5-diamine, a new potent enzyme-activated irreversible inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase, in rodents. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):4972–4977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie N., Pasquali J. L., Mamont P. S., Danzin C., Weil-Bousson M., Siat M. Immunosuppressive effects of (2R,5R)-6-heptyne-2,5-diamine, an inhibitor of polyamine synthesis: II. Beneficial effects on the development of a lupus-like disease in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 May;72(2):293–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandecha B. M., Brown J. R., Crampton M. R. Dissociation kinetics of DNA-anthracycline and DNA-anthraquinone complexes determined by stopped-flow spectrophotometry. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 15;34(6):733–736. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. A., Sjoerdsma A., Santi D. V. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia treated with alpha-difluoromethylornithine. A prospective study among patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. West J Med. 1984 Nov;141(5):613–623. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabra P. M., Lee H. K., Lubich W. P., Marton L. J. Solid-phase extraction and determination of dansyl derivatives of unconjugated and acetylated polyamines by reversed-phase liquid chromatography: improved separation systems for polyamines in cerebrospinal fluid, urine and tissue. J Chromatogr. 1986 Jul 11;380(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83621-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Möller A., Nordheim A., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Antibodies specific for left-handed Z-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Valle R. P., Möller A., Nordheim A., Schur P. H., Rich A., Stollar B. D. Z-DNA-specific antibodies in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):314–321. doi: 10.1172/JCI110771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima G., Shiu R. P. Role of polyamines in estradiol-induced growth of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2466–2470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountz J. D., Smith H. R., Wilder R. L., Reeves J. P., Steinberg A. D. CS-A therapy in MRL-lpr/lpr mice: amelioration of immunopathology despite autoantibody production. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer C. F., Strandberg J. D., Reinisch C. L. Systemic mononuclear-cell vasculitis in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. A histologic and immunocytochemical analysis. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):229–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquali J. L., Mamont P. S., Weryha A., Knapp A. M., Blervaque A., Siat M. Immunosuppressive effects of (2R,5R)-6-heptyne-2,5-diamine an inhibitor of polyamine synthesis: I. Effects on mitogen-induced immunoglobulin production in human cultured lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Apr;72(1):141–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. Recent advances in the biochemistry of polyamines in eukaryotes. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):249–262. doi: 10.1042/bj2340249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash N. J., Schechter P. J., Grove J., Koch-Weser J. Effect of alpha-difluoromethylornithine, an enzyme-activated irreversible inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase, on L1210 leukemia in mice. Cancer Res. 1978 Sep;38(9):3059–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley J. T., Lee J. S., Decoteau W. E. Left-handed "Z" DNA antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjoerdsma A., Schechter P. J. Chemotherapeutic implications of polyamine biosynthesis inhibition. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Mar;35(3):287–300. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Baarsch M. J., Messner R. P. Immunological detection of B-DNA to Z-DNA transition of polynucleotides by immobilization of the DNA conformation on a solid support. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):358–366. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Meryhew N. L., Messner R. P. DNA sequence and conformation specificity of lupus autoantibodies. Preferential binding to the left-handed Z-DNA form of synthetic polynucleotides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):367–377. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Messner R. P. A left-handed (Z) conformation of poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT) induced by polyamines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6721–6733. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Messner R. P. Structural specificity of polyamines in left-handed Z-DNA formation. Immunological and spectroscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden P. D. Potential Z-DNA-forming elements in serum DNA from human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Ledbetter J. A., Hendler P. L., Seaman W. E. Treatment of murine lupus with monoclonal anti-T cell antibody. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):852–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


