Abstract
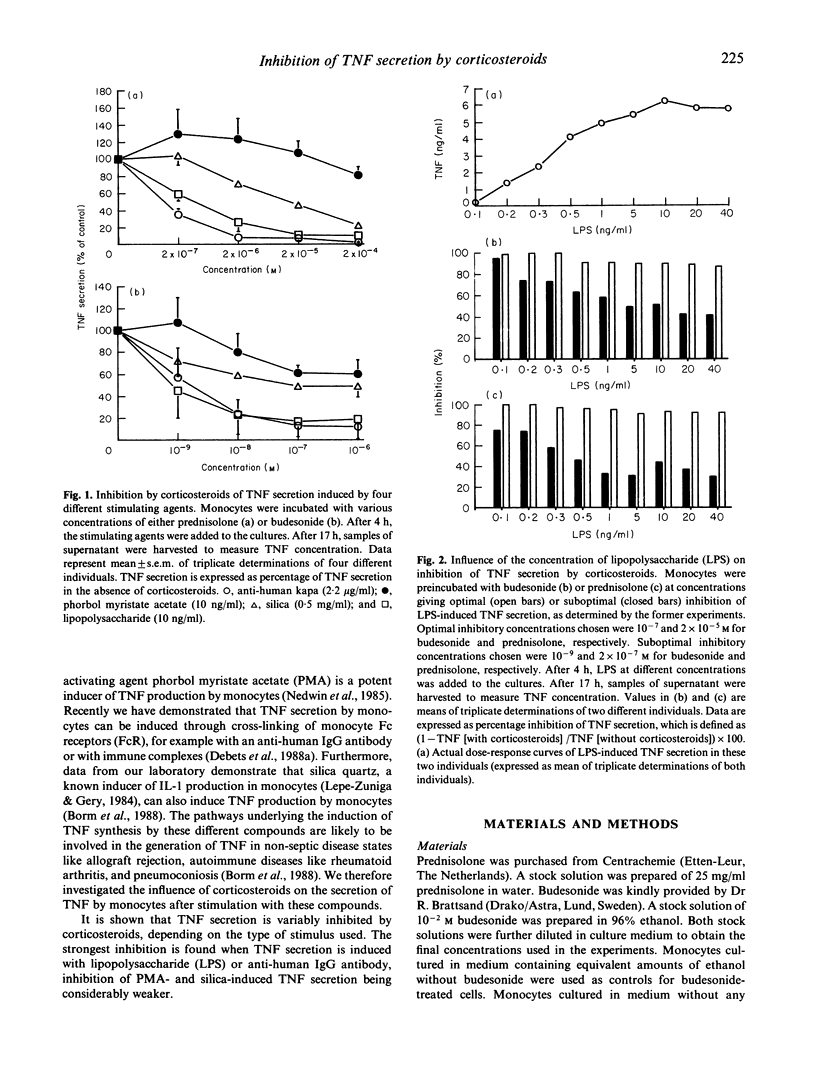
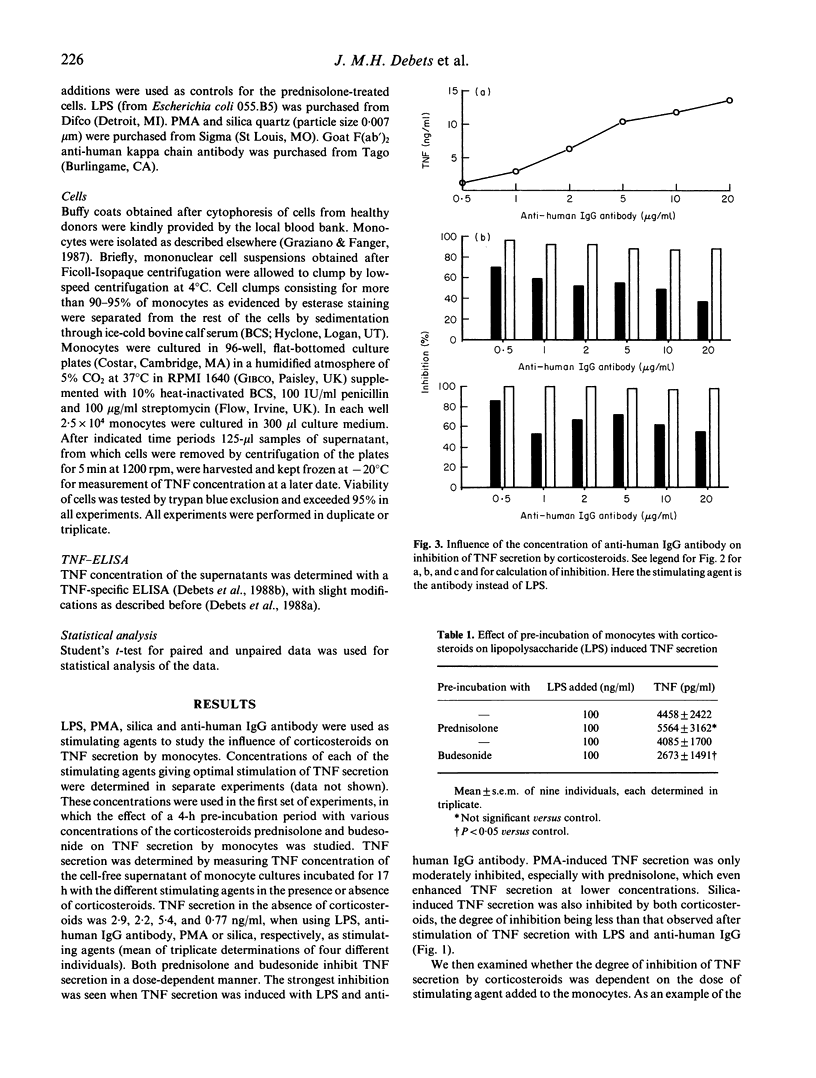
The cytokine tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is believed to be involved in the pathophysiology of several human disease states, both septic and non-septic. Different pathways of induction are involved in the generation ofTNF in these disease states. We therefore used four different stimulatory agents, lipopolysaccharide, phorbol myristate acetate, silica quartz, and anti-human IgG antibody to study the influence of the corticosteroids prednisolone and budesonide on the secretion of TNF by human monocytes. Both prednisolone and budesonide inhibited TNF secretion induced by these four stimulating agents in a different degree. Inhibition was strong when TNF secretion was induced by lipopolysaccharide or anti-human IgG antibody. A weaker inhibitory effect was observed when TNF secretion was induced by silica quartz. Only minimal inhibition of phorbol myristate acetate induced TNF secretion was observed. Furthermore, it is shown that inhibition is dependent on the dose of corticosteroid, but not or only minimally on the dose of stimulating agent, indicating that inhibition cannot be overcome by increasing the cell-activating stimulus. Finally, optimal inhibition of TNF secretion by corticosteroids is shown to be dependent on the presence of corticosteroids during the phase of cell stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of human T cell growth factor and gamma-interferon messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini D. R., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Smith D. D., Mundy G. R. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):516–518. doi: 10.1038/319516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):653–658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borm P. J., Palmen N., Engelen J. J., Buurman W. A. Spontaneous and stimulated release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) from blood monocytes of miners with coal workers' pneumoconiosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Dec;138(6):1589–1594. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.6.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Ikeda Y., Le Trang N., Hotez P. J., Beutler B. Weight loss associated with an endotoxin-induced mediator from peritoneal macrophages: the role of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor). Immunol Lett. 1985;11(3-4):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmas S. E., Meager A., Moore M. Production of interferon and tumour necrosis factor by cloned human natural cytotoxic lymphocytes and T cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Aug;69(2):441–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Cowden W. B., Butcher G. A., Hunt N. H. Possible roles of tumor necrosis factor in the pathology of malaria. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):192–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupps T. R., Fauci A. S. Corticosteroid-mediated immunoregulation in man. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:133–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuturi M. C., Murphy M., Costa-Giomi M. P., Weinmann R., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Independent regulation of tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin production by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1581–1594. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., Kampmeijer R., van der Linden M. P., Buurman W. A., van der Linden C. J. Plasma tumor necrosis factor and mortality in critically ill septic patients. Crit Care Med. 1989 Jun;17(6):489–494. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198906000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., Van der Linden C. J., Dieteren I. E., Leeuwenberg J. F., Buurman W. A. Fc-receptor cross-linking induces rapid secretion of tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1197–1201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., van der Linden C. J., Spronken I. E., Buurman W. A. T cell-mediated production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha by monocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano R. F., Fanger M. W. Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII on monocytes and granulocytes are cytotoxic trigger molecules for tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3536–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., McDevitt H. O. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha in murine autoimmune 'lupus' nephritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):356–358. doi: 10.1038/331356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern J. A., Lamb R. J., Reed J. C., Daniele R. P., Nowell P. C. Dexamethasone inhibition of interleukin 1 beta production by human monocytes. Posttranscriptional mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):237–244. doi: 10.1172/JCI113301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen P. J., Dinarello C. A., Strom T. B. Glucocorticoids inhibit transcriptional and post-transcriptional expression of interleukin 1 in U937 cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4129–4134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth R. S., Edgington T. S. Tumor necrosis factor production by human monocytes is a regulated event: induction of TNF-alpha-mediated cellular cytotoxicity by endotoxin. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2585–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepe-Zuniga J. L., Gery I. Production of intra- and extracellular interleukin-1 (IL-1) by human monocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;31(2):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Teppo A. M. Raised serum levels of cachectin/tumor necrosis factor alpha in renal allograft rejection. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1132–1137. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Defeo-Jones D., Boyer M., Martinez D., Kiefer D., Vuocolo G., Wolfe A., Socher S. H. Tumors secreting human TNF/cachectin induce cachexia in mice. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Allet B., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is an effector of skin and gut lesions of the acute phase of graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruers T. J., Buurman W. A., van Boxtel C. J., van der Linden C. J., Kootstra G. Immunohistological observations in rat kidney allografts after local steroid administration. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1205–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruers T. J., Daemen M. J., Thijssen H. H., van der Linden C. J., Buurman W. A. Sensitivity of graft rejection in rats to local immunosuppressive therapy. Transplantation. 1988 Dec;46(6):820–825. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198812000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):547–549. doi: 10.1038/322547a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Heinegård D., Talal N., Wollheim F. A. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprung C. L., Caralis P. V., Marcial E. H., Pierce M., Gelbard M. A., Long W. M., Duncan R. C., Tendler M. D., Karpf M. The effects of high-dose corticosteroids in patients with septic shock. A prospective, controlled study. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 1;311(18):1137–1143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411013111801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stashenko P., Dewhirst F. E., Peros W. J., Kent R. L., Ago J. M. Synergistic interactions between interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and lymphotoxin in bone resorption. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1464–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson B. M., Mundy G. R., Chambers T. J. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta induce osteoblastic cells to stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veterans Administration Systemic Sepsis Cooperative Study Group Effect of high-dose glucocorticoid therapy on mortality in patients with clinical signs of systemic sepsis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):659–665. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Bakke O. Glucocorticoids suppress the production of tumour necrosis factor by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):299–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A. Production and clearance of tumor necrosis factor in rats exposed to endotoxin and dexamethasone. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;45(3):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



