Abstract
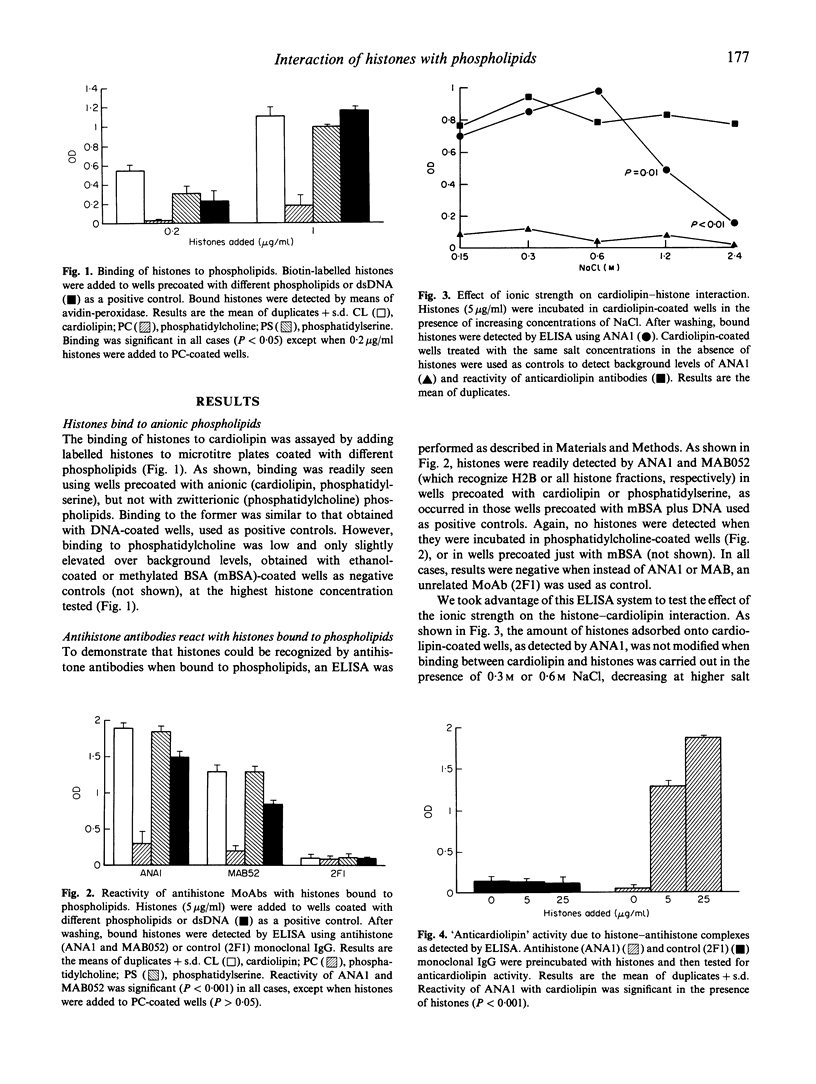
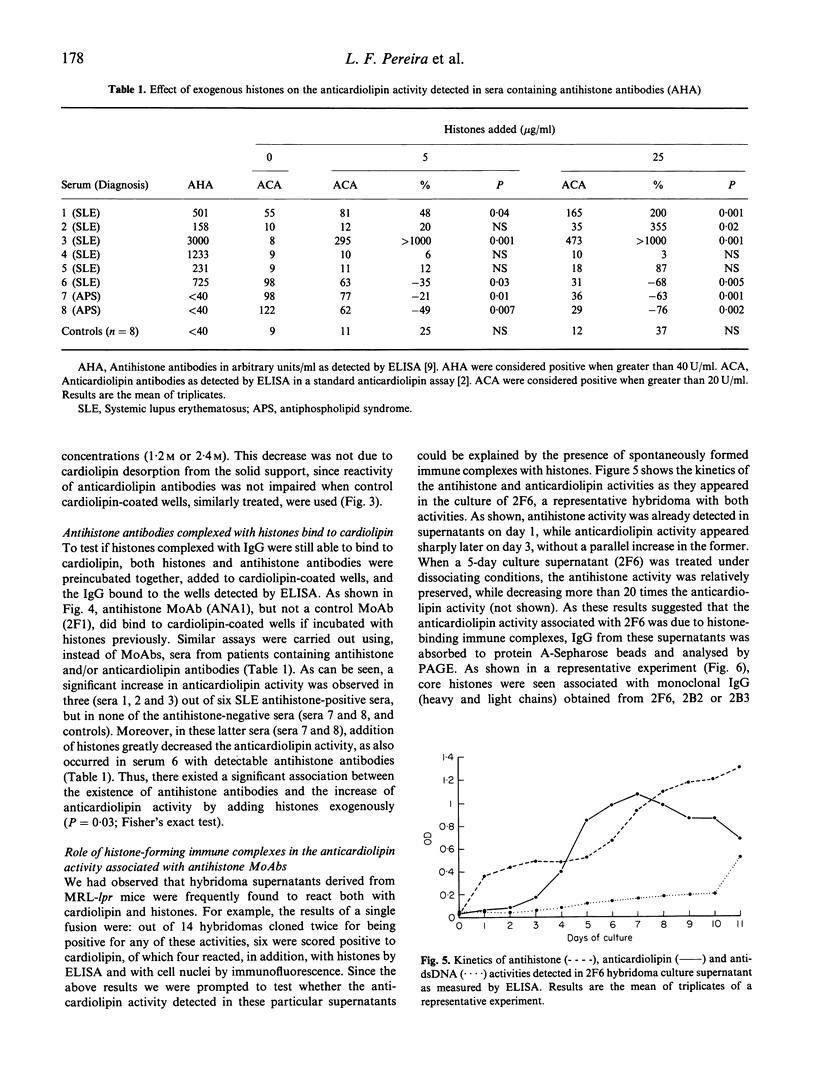
Antibodies recognizing anionic phospholipids have been described in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and other autoimmune diseases. Recent studies have shown that some of these antibodies may recognize a cardiolipin-binding protein (apolipoprotein H) rather than phospholipids. A similar possibility is conceivable for other cardiolipin-binding proteins that are targets of autoantibodies. In this study we have addressed whether this might be the case for histones, a set of highly cationic and widely distributed proteins that react in a well known autoantibody system. Our results indicate that: (i) histones bind to anionic phospholipids (cardiolipin and phosphatidylserine) with high avidity, but not to zwitterionic phospholipids (phosphatidylcholine); (ii) monoclonal and polyclonal antihistone antibodies recognize histones bound to cardiolipin; (iii) the addition of histones to serum samples containing antihistone antibodies often enhances their anticardiolipin reactivity. In addition, we have found that antihistone-producing hybridomas derived from MRL-lpr mice may show anticardiolipin activity due to the presence of histones in the cell culture supernatants with the resultant formation of immune complexes. Taken together, the results suggest a potential role for histones in the anti-cardiolipin activity detected in sera containing antihistone antibodies. These histone-phospholipid interactions should be taken into account when evaluating the pathogenic effects of antihistone antibodies or other autoantibodies reacting with nuclear components (e.g. nucleosomes) containing histones.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvieux J., Roussel B., Ponard D., Colomb M. G. Reactivity patterns of anti-phospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus sera in relation to erythrocyte binding and complement activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):466–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahar A. M., Kwak J. Y., Beer A. E., Kim J. H., Nelson L. A., Beaman K. D., Gilman-Sachs A. Antibodies to phospholipids and nuclear antigens in non-pregnant women with unexplained spontaneous recurrent abortions. J Reprod Immunol. 1993 Aug;24(3):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(93)90076-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. A., Morrison B., VandenBygaart P. Immunogenic DNA-related factors. Nucleosomes spontaneously released from normal murine lymphoid cells stimulate proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis of normal mouse lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1487–1496. doi: 10.1172/JCI114595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caturla A., Colome J. A., Bustos A., Chamorro M. J., Figueredo M. A., Subiza J. L., de la Concha E. G. Occurrence of antibodies to protease-treated histones in a patient with vasculitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jul;60(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90112-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa O., Marion C., Monier J. C., Roux B. Non-specific binding of heat-aggregated IgG to histone detected by ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Holers V. M., Arend W. P., Kotzin B. Regulation of nuclear antigen expression on the cell surface of human monocytes. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3042–3048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogler W. E., Swartz G. M., Jr, Alving C. R. Antibodies to phospholipids and liposomes: binding of antibodies to cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 2;903(2):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Maassen C., Hemker H. C., de Baets M. H., van Breda-Vriesman P. J., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA) directed not to cardiolipin but to a plasma protein cofactor. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1544–1547. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91374-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Sammaritano L. R., Wen J., Elkon K. B. Induction of antiphospholipid autoantibodies by immunization with beta 2 glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1105–1109. doi: 10.1172/JCI115927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N. E., Pierangeli S. What is the "true" antigen for antiphospholipid antibodies? Lancet. 1990 Dec 15;336(8729):1505–1505. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselaar P., Triplett D. A., LaRue A., Derksen R. H., Blokzijl L., de Groot P. G., Wagenknecht D. R., McIntyre J. A. Heat treatment of serum and plasma induces false positive results in the antiphospholipid antibody ELISA. J Rheumatol. 1990 Feb;17(2):186–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeling D. M., Wilson A. J., Mackie I. J., Isenberg D. A., Machin S. J. Lupus anticoagulant activity of some antiphospholipid antibodies against phospholipid bound beta 2 glycoprotein I. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Jul;46(7):665–667. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.7.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita Y., Sumida T., Ichikawa K., Maeda T., Yonaha F., Iwamoto I., Yoshida S., Koike T. V gene analysis of anticardiolipin antibodies from MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda S., Kanayama Y., Okamura M., Amatsu K., Negoro N., Takeda T., Inoue T. Clinical significance of antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jan;16(1):24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. L., Wang C. T. Activation of human platelets by the rabbit anticardiolipin antibodies. Blood. 1992 Dec 15;80(12):3135–3143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Fujimoto M., Ichikawa K., Koike T. Anticardiolipin cofactor(s) and differential diagnosis of autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91697-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Immunology and clinical importance of antiphospholipid antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:193–280. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minota S., Jarjour W. N., Roubey R. A., Mimura T., Winfield J. B. Reactivity of autoantibodies and DNA/anti-DNA complexes with a novel 110-kilodalton phosphoprotein in systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1263–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Cheronis J. C., Blodgett J. K., Kotzin B. L. Histone autoantigens in murine lupus. Definition of a major epitope within an accessible region of chromatin. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4633–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Theofilopoulos A. N. Monoclonal autoantibodies reacting with multiple structurally related and unrelated macromolecules. Int Rev Immunol. 1988 Mar;3(1-2):71–95. doi: 10.3109/08830188809051183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T. M., Stöckl F. W., Weber R., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Histones have high affinity for the glomerular basement membrane. Relevance for immune complex formation in lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1879–1894. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T., Stoeckl F., Muller S., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S., Woitas R., Vogt A. Glomerular immune deposits in murine lupus models may contain histones. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. beta 2-Glycoprotein I: a plasma inhibitor of the contact activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1086–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R. J., Brinkman K., van den Brink H. G., Westgeest A. A. Reaction patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3786–3792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subiza J. L., Caturla A., Pascual-Salcedo D., Chamorro M. J., Gazapo E., Figueredo M. A., de la Concha E. G. DNA-anti-DNA complexes account for part of the antihistone activity found in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Apr;32(4):406–412. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subiza J. L., Caturla A., Pereira L. F., Camargo M. C., Bustos A., Boimorto R., de la Concha E. G. Evidence that a putative anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody may actually be recognizing circulating immune complexes. J Autoimmun. 1992 Jun;5(3):363–377. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90149-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Assmann K. J., Dijkman H. B., van Gompel F., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-DNA antibodies can bind to the glomerulus via two distinct mechanisms. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1363–1371. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., van Gompel F., van den Heuvel L. P., Veerkamp J. H., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate is mediated via bound DNA/histone complexes. J Autoimmun. 1990 Oct;3(5):531–545. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaarala O. Binding profiles of anticardiolipin antibodies in sera from patients with SLE and infectious diseases. J Autoimmun. 1991 Oct;4(5):819–830. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90176-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Tan E. M., Rubin R. L. Identification and isolation of soluble histones from bovine milk and serum. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):675–682. doi: 10.1042/bj2440675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. Blood cell membranes and haemostasis. Haemostasis. 1982;11(1):12–39. doi: 10.1159/000214638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]