Abstract
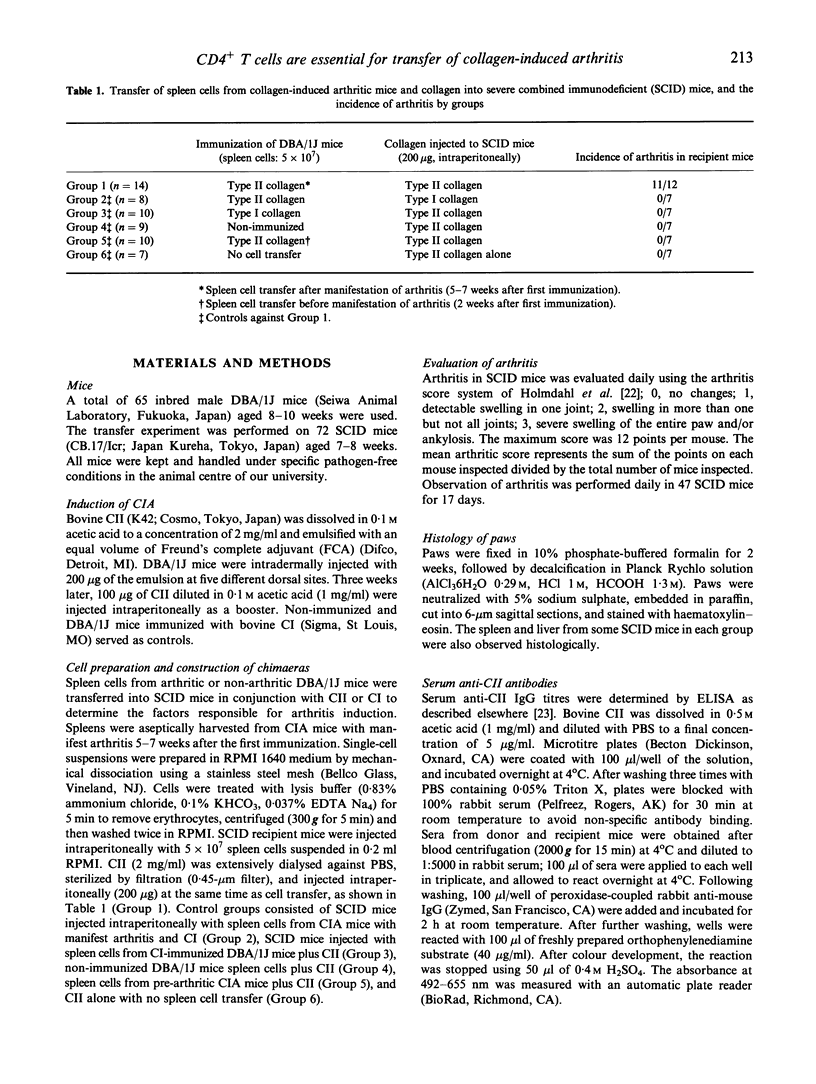
The role of T lymphocytes in the adoptive transfer of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DBA/1J mice to severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice was investigated. Spleen cells from non-immunized, type I collagen (CI) or type II collagen (CII)-immunized DBA/1J mice were injected into SCID mice which lack functional T and B cells. Specific antigenic stimulation of arthritogenic cells was required since only lymphocytes from arthritic CIA mice plus simultaneous administration of CII transferred arthritis to 11 of 12 SCID mice with a marked increase in CII antibody titre. However, CI-immunized or non-immunized DBA/1J mice cells did not induce arthritis in SCID mice. SCID recipients of pre-arthritic CIA lymphocytes presented increase in CII antibody, but showed no clinical signs of arthritis, suggesting that antibodies to CII alone can not induce CIA. Depletion of CD4+ T cells inhibited the transfer of arthritis to SCID mice, with a decrease in CII antibody titre in chimaeras. In contrast, depletion of CD8+ T cells enhanced the onset of arthritis in SCID mice. The results imply that CD4+ T cells are required for the induction of CIA. In addition, CD8+ T cells might have a suppressive role in the etiology of this disease. It is probable that memory CD4+ T cells stimulate production of antibodies to CII and subsequent arthritis. This study clarifies the role of T lymphocytes in the transfer of CIA to SCID mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahn E., Trentham D. E. Experimental synovitis induced by collagen-specific T cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1989 Feb;118(2):491–503. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
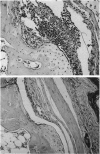
- Caulfield J. P., Hein A., Dynesius-Trentham R., Trentham D. E. Morphologic demonstration of two stages in the development of type II collagen-induced arthritis. Lab Invest. 1982 Mar;46(3):321–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtenay J. S., Dallman M. J., Dayan A. D., Martin A., Mosedale B. Immunisation against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):666–668. doi: 10.1038/283666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchosal M. A., McConahey P. J., Robinson C. A., Dixon F. J. Transfer of human systemic lupus erythematosus in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):985–988. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durie F. H., Fava R. A., Foy T. M., Aruffo A., Ledbetter J. A., Noelle R. J. Prevention of collagen-induced arthritis with an antibody to gp39, the ligand for CD40. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.7689748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Ashany D. The SCID mouse as a vehicle to study autoimmunity. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Jan;32(1):4–12. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Hakim F. T., Hieny S., Shearer G. M., Sher A. Synergistic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in IFN-gamma production and protective immunity induced by an attenuated Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt T. J., Holmdahl R. Anti-T cell receptor antibody treatment of rats with established autologous collagen-induced arthritis: suppression of arthritis without reduction of anti-type II collagen autoantibody levels. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
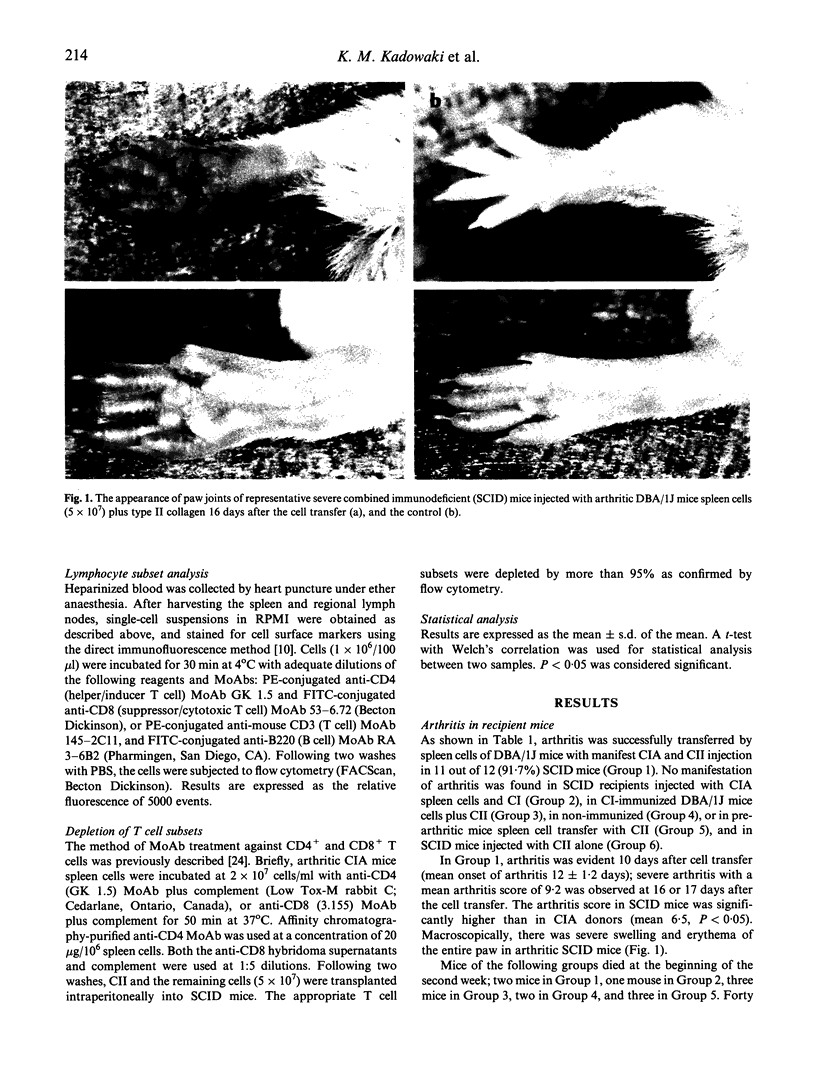
- Holmdahl R., Jonsson R., Larsson P., Klareskog L. Early appearance of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes and class II antigen-expressing cells in joints of DBA/1 mice immunized with type II collagen. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Klareskog L., Rubin K., Larsson E., Wigzell H. T lymphocytes in collagen II-induced arthritis in mice. Characterization of arthritogenic collagen II-specific T-cell lines and clones. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Sep;22(3):295–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., Bourdette D. N., Whitham R. H., Offner H., Vandenbark A. A. Induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in severe combined immunodeficient mice reconstituted with allogeneic or xenogeneic hematopoietic cells. J Immunol. 1993 May 15;150(10):4620–4629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Holmdahl R., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Role of T lymphocytes in collagen II induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jan;51(1):117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macht L. M., Corrall R. J., Banga J. P., Elson C. J. Control of human thyroid autoantibody production in SCID mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Mar;91(3):390–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malynn B. A., Blackwell T. K., Fulop G. M., Rathbun G. A., Furley A. J., Ferrier P., Heinke L. B., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The scid defect affects the final step of the immunoglobulin VDJ recombinase mechanism. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno H., Kadowaki K. M., Suzuki H., Ochiai H., Tsuji H. T-cell receptor V beta 8 has no significant suppressive effect on collagen-induced arthritis. Int J Tissue React. 1993;15(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
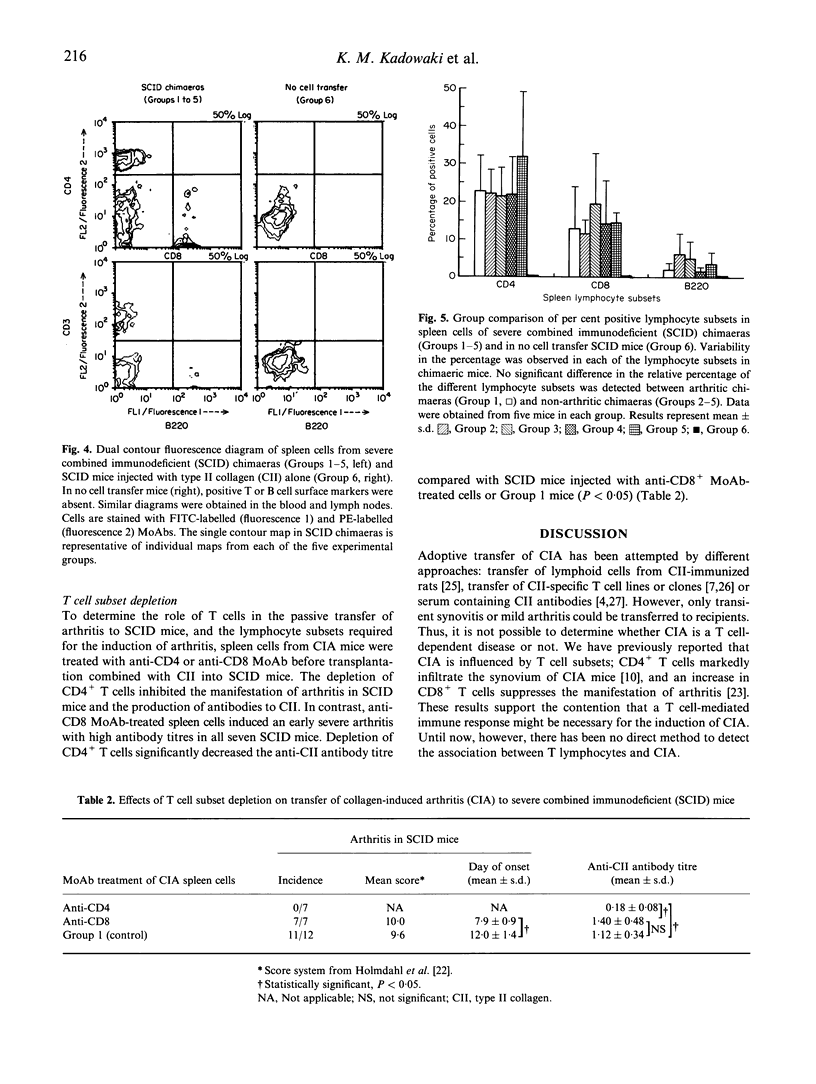
- Matsuno H., Matsushita I., Okada C., Suzuki M., Tsuji H., Ochiai H., Tsui H. Role of lymphocytes in collagen induced arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1991 Sep;18(9):1344–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Namikawa R., Kaneshima H., Shultz L. D., Lieberman M., Weissman I. L. The SCID-hu mouse: murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1632–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pals S. T., Radaszkiewicz T., Roozendaal L., Gleichmann E. Chronic progressive polyarthritis and other symptoms of collagen vascular disease induced by graft-vs-host reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1475–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Lanchbury J. S., Kingsley G. H. The importance of the T cell in initiating and maintaining the chronic synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Sriram S., Cooper S. M. Prevention of type II collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo treatment with anti-L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter C., Kakavand B., Rieber E. P., Schattenkirchner M., Riethmüller G., Krüger K. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with monoclonal CD4 antibody M-T151. Clinical results and immunopharmacologic effects in an open study, including repeated administration. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):525–536. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki Y., Mima T., Sakoda S., Fujimura H., Arita N., Nomura T., Kishimoto T. Transfer of multiple sclerosis into severe combined immunodeficiency mice by mononuclear cells from cerebrospinal fluid of the patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6157–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler W., Weiler I. J., Schuler A., Phillips R. A., Rosenberg N., Mak T. W., Kearney J. F., Perry R. P., Bosma M. J. Rearrangement of antigen receptor genes is defective in mice with severe combined immune deficiency. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90695-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal R., Globerson A., Zinger H., Mozes E. Induction of experimental systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):239–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. C., Allen P. M. Myosin-induced acute myocarditis is a T cell-mediated disease. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2141–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Dixon F. J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):378–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tary-Lehmann M., Saxon A. Human mature T cells that are anergic in vivo prevail in SCID mice reconstituted with human peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):503–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tighe H., Silverman G. J., Kozin F., Tucker R., Gulizia R., Peebles C., Lotz M., Rhodes G., Machold K., Mosier D. E. Autoantibody production by severe combined immunodeficient mice reconstituted with synovial cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1843–1848. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., David J. R. Passive transfer by cells of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):359–366. doi: 10.1172/JCI109136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunru I. S., Suzuki H., Yano S. Effect of macrophages on interleukin-2 (IL-2)- and IL-4-induced murine lymphokine-activated killer activity. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jun 19;48(4):568–573. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson W. C., Townes A. S. Genetic susceptibility to murine collagen II autoimmune arthritis. Proposed relationship to the IgG2 autoantibody subclass response, complement C5, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and non-MHC loci. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1878–1891. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Plater-Zyberk C., Williams D. G., Maini R. N. Successful transfer of collagen-induced arthritis to severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Williams D. G., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Increased limb involvement in murine collagen-induced arthritis following treatment with anti-interferon-gamma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 May;92(2):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Krco C. J., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. II. Passive transfer and suppression by intravenous injection of anti-type II collagen antibody or free native type II collagen. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Sep;27(9):1010–1017. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):688–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]