Abstract
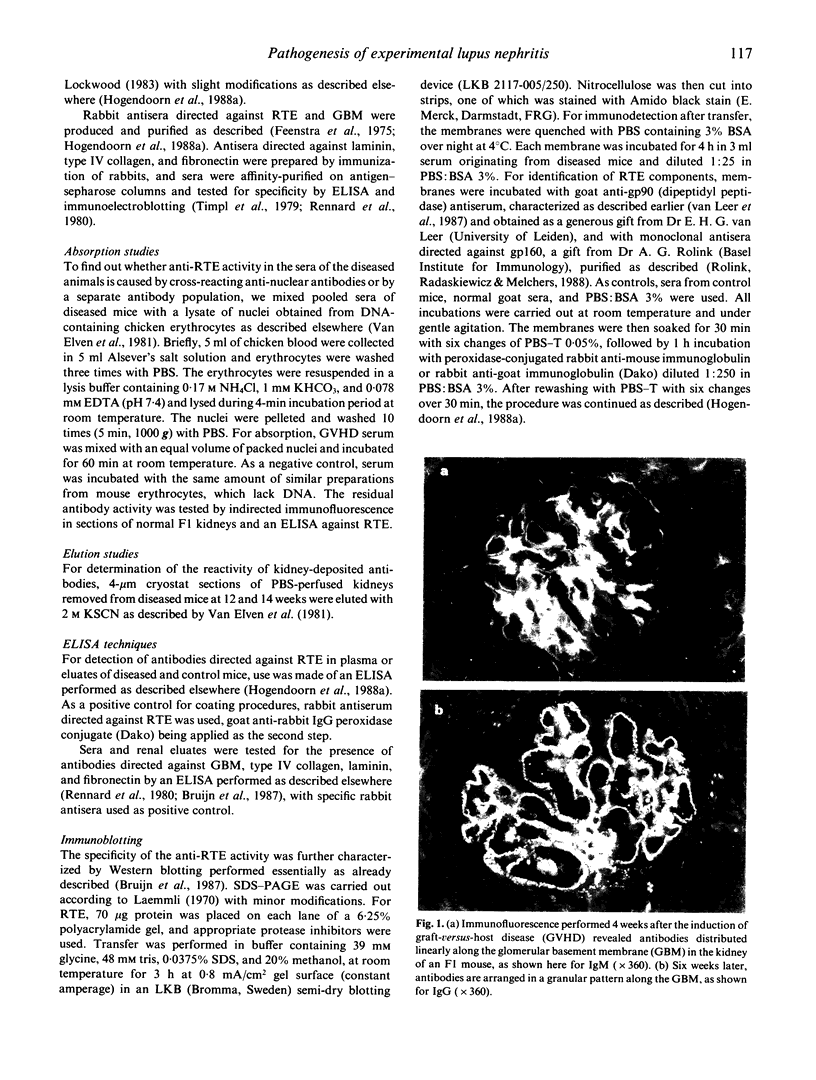
The pathogenesis of renal involvement was studied in murine chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), which is a model for human systemic lupus erythematosus. GVHD was induced by four i.v. injections of lymphocytes from DBA/2 donor mice into (C57BL/10 x DBA/2)F1 hybrids at 3-4-day intervals. Two weeks after the first injection, antibodies were found to have been deposited in the mesangium and along the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in a linear arrangement, which changed to a granular pattern after 6-8 weeks. In this stage, large electron-dense complexes were present both subepithelially and subendothelially along the GBM. Proteinuria increased up to 11,300 +/- 2140 micrograms/18 h. Indirect immunofluorescence studies and ELISA showed that sera and kidney eluates contained autoantibodies directed against nuclear antigens and GBM component laminin as well as against renal tubular epithelial antigens (RTE). The specificity of the anti-RTE antibodies was further characterized by the use of absorption techniques as well as immunoblotting. The early linear immunofluorescence pattern seems to be associated with glomerular binding of anti-GBM antibodies, while electron-dense complex formation in later stages may be induced by the superimposed deposition of anti-RTE antibodies. Similar phenomena were recently described in Heymann's nephritis in the rat, a model for human membranous nephropathy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J., Hang L., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Lack of relationship between serum gp70 levels and the severity of systemic lupus erythematosus in MRL/l mice. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):458–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann K. J., Ronco P., Tangelder M. M., Lange W. P., Verroust P., Koene R. A. Comparison of antigenic targets involved in antibody-mediated membranous glomerulonephritis in the mouse and rat. Am J Pathol. 1985 Oct;121(1):112–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabas A. Z., Cornish J., Lannigan R. Passive Heymann nephritis in the rat produced by a heterologous antibody to a heterologous kidney fraction 3 antigen. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Dec;63(6):667–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C., Peters D. K., Lockwood C. M. Anti-glomerular basement membrane autoantibodies in the Brown Norway rat: detection by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijn J. A., Hoedemaeker P. J., Fleuren G. J. Pathogenesis of anti-basement membrane glomerulopathy and immune-complex glomerulonephritis: dichotomy dissolved. Lab Invest. 1989 Nov;61(5):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijn J. A., Hogendoorn P. C., Hoedemaeker P. J., Fleuren G. J. The extracellular matrix in pathology. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Feb;111(2):140–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijn J. A., Oemar B. S., Ehrich J. H., Foidart J. M., Fleuren G. J. Anti-basement membrane glomerulopathy in experimental trypanosomiasis. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2482–2488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijn J. A., Van Elven E. H., Corver W. E., Oudshoorn-Snoek M., Fleuren G. J. Genetics of experimental lupus nephritis: non-H-2 factors determine susceptibility for renal involvement in murine chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):284–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijn J. A., van Elven E. H., Hogendoorn P. C., Corver W. E., Hoedemaeker P. J., Fleuren G. J. Murine chronic graft-versus-host disease as a model for lupus nephritis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):639–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Manny N., Andrzejewski C., André-Schwartz J., Schwartz R. S. Genetic studies of autoimmunity and retrovirus expression in crosses of New Zealand black mice I. Xenotropic virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):854–871. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., McConahey P. J., Manny N., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J., Schwartz R. S. Genetic studies of autoimmunity and retrovirus expression in crosses of New Zealand black mice. II. The viral envelope glycoprotein gp70. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):872–881. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Capel P. J., Rijke G. P., Vierwinden G., van de Putte L. B., Koene R. A. Cross-reactivity of anti-DNA antibodies with proteoglycans. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):502–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra K., van den Lee R., Greben H. A., Arends A., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. I. The natural history: a histologic and immunohistologic study at the light microscopic and the ultrastructural level. Lab Invest. 1975 Feb;32(2):235–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleuren G. J., Grond J., Hoedemaeker P. J. The pathogenetic role of free-circulating antibody in autologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):205–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukatsu A., Brentjens J. R., Killen P. D., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Andres G. A. Studies on the formation of glomerular immune deposits in brown Norway rats injected with mercuric chloride. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Oct;45(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzler E. M., Diamond H. S., Weiner M., Schlesinger M., Fries J. F., Wasner C., Medsger T. A., Jr, Ziegler G., Klippel J. H., Hadler N. M. A multicenter study of outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Entry variables as predictors of prognosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jun;25(6):601–611. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleichmann H., Gleichmann E., André-Schwartz J., Schwartz R. S. Chronic allogeneic disease. 3. Genetic requirements for the induction of glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):516–532. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleichmann H., Gleichmann E., Peters K. Induction of immune complex glomerulonephritis in F1 hybrid mice: superiority of cortisone-resistant parental thymocytes over spleen cells. Cell Immunol. 1974 Oct;14(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granholm N. A., Graves K., Izui S., Cavallo T. Pathogenic role of anti-DNA antibodies in murine lupus nephritis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1985 Nov;18(3):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogendoorn P. C., Bruijn J. A., vd Broek L. J., De Heer E., Foidart J. M., Hoedemaeker P. J., Fleuren G. J. Antibodies to purified renal tubular epithelial antigens contain activity against laminin, fibronectin, and type IV collagen. Lab Invest. 1988 Mar;58(3):278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogendoorn P. C., de Heer E., Weening J. J., Daha M. R., Hoedemaeker P. J., Fleuren G. J. Glomerular capillary wall charge and antibody binding in passive Heymann nephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Feb;111(2):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai H., Yano S., Naruse T. Isolation and characterization of rat nephritogenic and non nephritogenic brush border antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):414–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
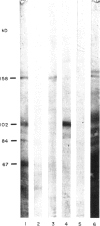
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Carlson J., Cataldo J., Ucci A., Migliorini P., Pankewycz O. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2883–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Stow J. L., Mentone S., Farquhar M. G. Antibodies to basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans bind to the laminae rarae of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and induce subepithelial GBM thickening. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1064–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Oberley T. D. Immune-mediated injury to basement membranes in mice immunized with murine laminin. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Apr;31(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Gehron P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Valentine T., Swarm R. A murine tumor producing a matrix of basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Berg R., Martin G. R., Foidart J. M., Robey P. G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for connective tissue components. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Gleichmann H., Gleichmann E. Diseases caused by reactions of T lymphocytes to incompatible structures of the major histocompatibility complex. VII. Immune-complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):209–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
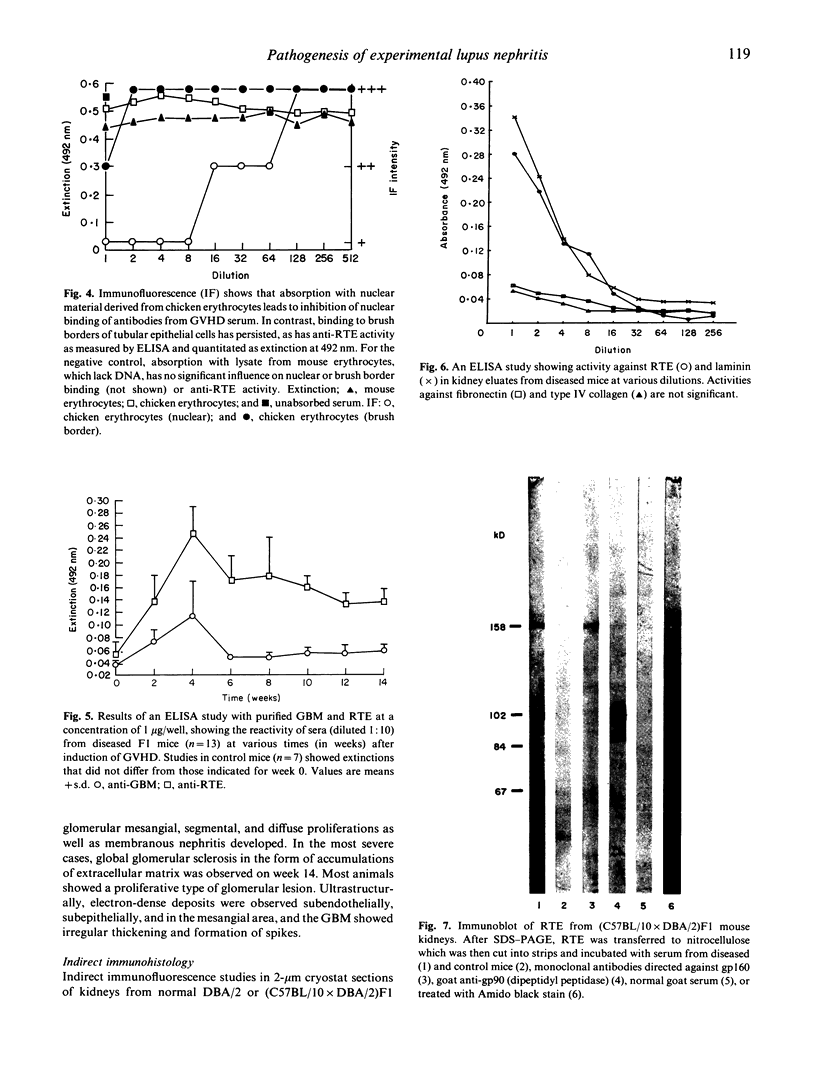
- Rolink A. G., Radaszkiewicz T., Melchers F. Monoclonal autoantibodies specific for kidney proximal tubular brush border from mice with experimentally induced chronic graft-versus-host disease. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Jul;28(1):29–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Radaszkiewicz T., Melchers F. The autoantigen-binding B cell repertoires of normal and of chronically graft-versus-host-diseased mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1675–1687. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Allegri L., Melcion C., Pirotsky E., Appay M. D., Bariety J., Pontillon F., Verroust P. A monoclonal antibody to brush border and passive Heymann nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):319–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Wieslander J., Avila J. L., Rojas M., Szarfman A., Esser K., Nowack H., Timpl R. Circulating antibodies to mouse laminin in Chagas disease, American cutaneous leishmaniasis, and normal individuals recognize terminal galactosyl(alpha 1-3)-galactose epitopes. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):419–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leer E. H., Moullier P., Ronco P., Verroust P. Lymphocyte expression of a 90 kD brush border antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Mar;67(3):572–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elven E. H., Agterberg J., Sadal S., Gleichmann E. Diseases caused by reactions of T lymphocytes to incompatible structures of the major histocompatibility complex. II. Autoantibodies deposited along the basement membrane of skin and their relationship to immune-complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1684–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]