Abstract
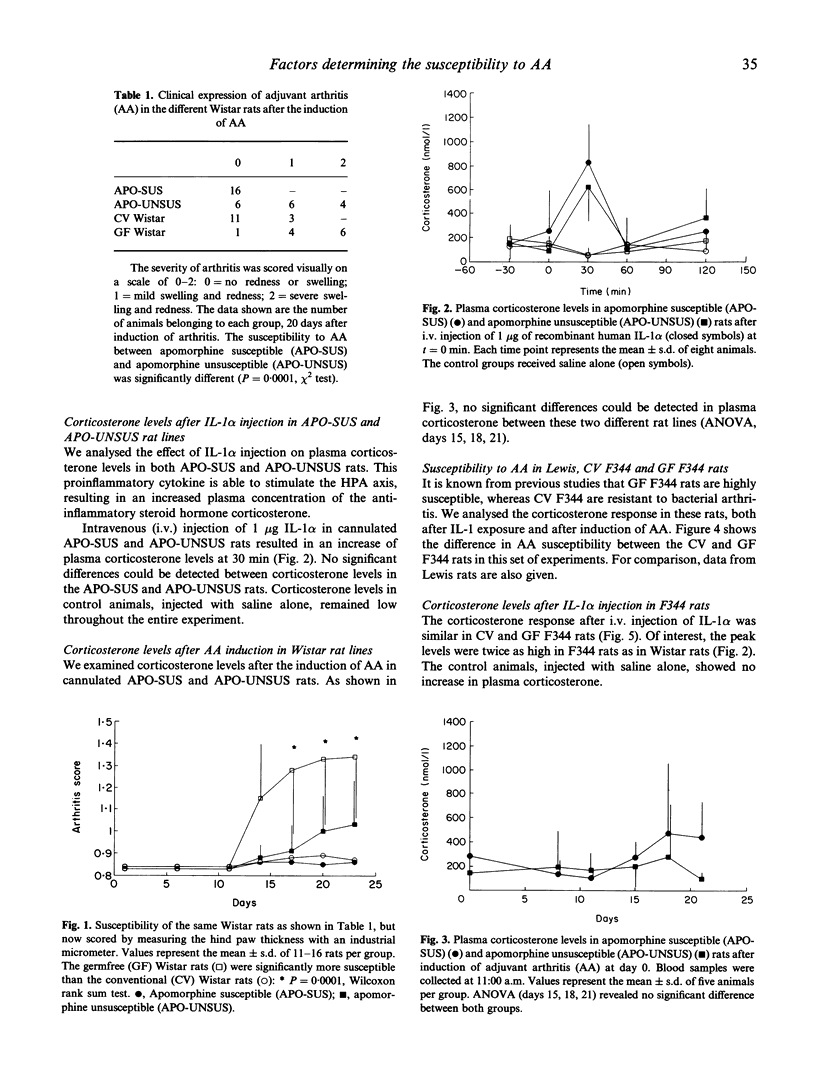
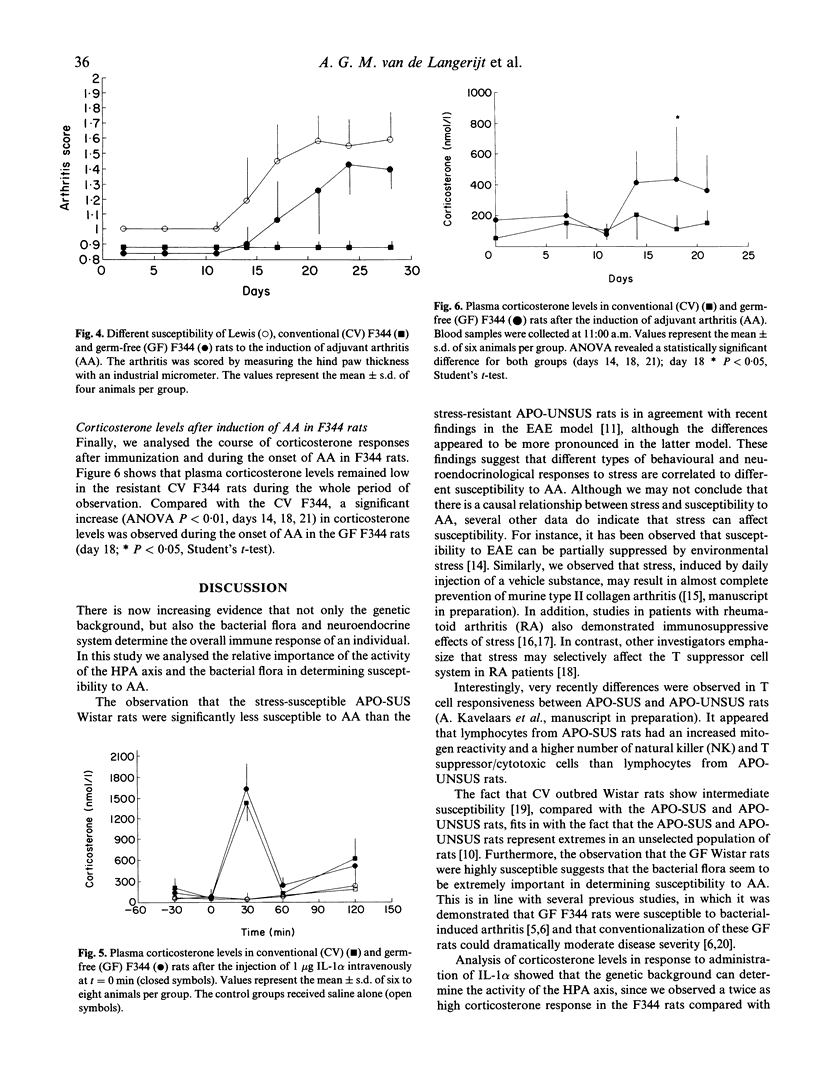
Previous studies on the regulation of bacterial-induced arthritis in rats have focused on endocrine aspects as well as differences in T cell immunity against bacterial epitopes. We analysed the role of both adrenal activity and bacterial flora in determining susceptibility to bacterial-induced arthritis. Outbred Wistar rats show a low incidence of adjuvant arthritis. Moderate sensitivity to adjuvant arthritis was found in a selected, stress-resistant line of the Wistar rat, whereas no arthritis was found in a stress-susceptible Wistar line. Plasma corticosterone responses after IL-1 alpha exposure were, however, identical in these two lines, excluding a direct correlation between susceptibility and corticosterone levels. In line with previous findings in germ-free (GF) F344 rats, GF Wistars also appeared highly susceptible to arthritis. We further analysed the corticosterone responses in GF and conventional (CV) rats. Administration of IL-1 alpha induced identical corticosterone responses in both CV and GF F344 rats. In addition, plasma corticosterone levels were measured around the time of onset of arthritis. Whereas no rise was seen in the arthritis-resistant CV rats, a significant increase was observed from day 14 in GF rats, at the moment of onset of arthritis. Although this corticosterone response was insufficient to prevent arthritis, it may have ameliorated disease expression in the GF F344 rats. Our data indicate that the bacterial flora, and therefore T cell tolerance, is of prime importance in determining susceptibility, whereas the activity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis may modulate disease severity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battisto J. R., Smith R. N., Beckman K., Sternlicht M., Welles W. L. Susceptibility to adjuvant arthritis in DA and F344 rats. A dominant trait controlled by an autosomal gene locus linked to the major histocompatibility complex. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Oct;25(10):1194–1200. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikanza I. C., Petrou P., Kingsley G., Chrousos G., Panayi G. S. Defective hypothalamic response to immune and inflammatory stimuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1281–1288. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., Brachten R., Heeren D., Willemen A., Ellenbroek B. Search after neurobiological profile of individual-specific features of Wistar rats. Brain Res Bull. 1990 Jan;24(1):49–69. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(90)90288-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., Rots N. Y., Ellenbroek B., de Kloet E. R. Bimodal shape of individual variation in behavior of Wistar rats: the overall outcome of a fundamentally different make-up and reactivity of the brain, the endocrinological and the immunological system. Neuropsychobiology. 1993;28(1-2):100–105. doi: 10.1159/000119009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromartie W. J., Craddock J. G., Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Yang C. H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1585–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington L., Affleck G., Urrows S., Tennen H., Higgins P., Zautra A., Hoffman S. Temporal covariation of soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels, daily stress, and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Feb;36(2):199–203. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Kohashi Y., Takahashi T., Ozawa A., Shigematsu N. Suppressive effect of Escherichia coli on adjuvant-induced arthritis in germ-free rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):547–553. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Kuwata J., Umehara K., Uemura F., Takahashi T., Ozawa A. Susceptibility to adjuvant-induced arthritis among germfree, specific-pathogen-free, and conventional rats. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):791–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.791-794.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., STREBEL R., WENK E. J., HARMAN P. J. Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by stress. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Feb;109:294–298. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R., Steinetz B. Effects of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis on thymus and adrenal: relation to remission and relapse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Nov;165(2):218–224. doi: 10.3181/00379727-165-40961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee I. A., Antoni F. A., Mason D. W. Spontaneous recovery of rats from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is dependent on regulation of the immune system by endogenous adrenal corticosteroids. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):431–445. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D., MacPhee I., Antoni F. The role of the neuroendocrine system in determining genetic susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat. Immunology. 1990 May;70(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. C., Brooks P. M. Psychoimmunology and rheumatoid arthritis: concepts and methodologies. Int J Psychiatry Med. 1990;20(3):307–322. doi: 10.2190/51T9-RPXK-GP2L-67P5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary A. Stress, emotion, and human immune function. Psychol Bull. 1990 Nov;108(3):363–382. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.108.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Development of arthritis, periarthritis and periostitis in rats given adjuvants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):95–101. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarlis N. J., Chowdrey H. S., Stephanou A., Lightman S. L. Chronic activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and loss of circadian rhythm during adjuvant-induced arthritis in the rat. Endocrinology. 1992 Apr;130(4):1775–1779. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.4.1312424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Hill J. M., Chrousos G. P., Kamilaris T., Listwak S. J., Gold P. W., Wilder R. L. Inflammatory mediator-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation is defective in streptococcal cell wall arthritis-susceptible Lewis rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Young W. S., 3rd, Bernardini R., Calogero A. E., Chrousos G. P., Gold P. W., Wilder R. L. A central nervous system defect in biosynthesis of corticotropin-releasing hormone is associated with susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis in Lewis rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4771–4775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweep C. G., van der Meer M. J., Hermus A. R., Smals A. G., van der Meer J. W., Pesman G. J., Willemsen S. J., Benraad T. J., Kloppenborg P. W. Chronic stimulation of the pituitary-adrenal axis in rats by interleukin-1 beta infusion: in vivo and in vitro studies. Endocrinology. 1992 Mar;130(3):1153–1164. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.3.1311230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Langerijt A. G., van Lent P. L., Hermus A. R., van de Putte L. B., van den Berg W. B. Regulation of resistance against adjuvant arthritis in the Fisher rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Oct;94(1):150–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05993.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., van Bruggen M. C., Koopman J. P., Hazenberg M. P., van den Berg W. B. Gut flora induces and maintains resistance against streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis in F344 rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 May;88(2):313–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., van Bruggen M. C., van de Putte L. B., van den Berg W. B. T cell responses to streptococcal antigens in rats: relation to susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Cell Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;116(1):216–229. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


