Abstract
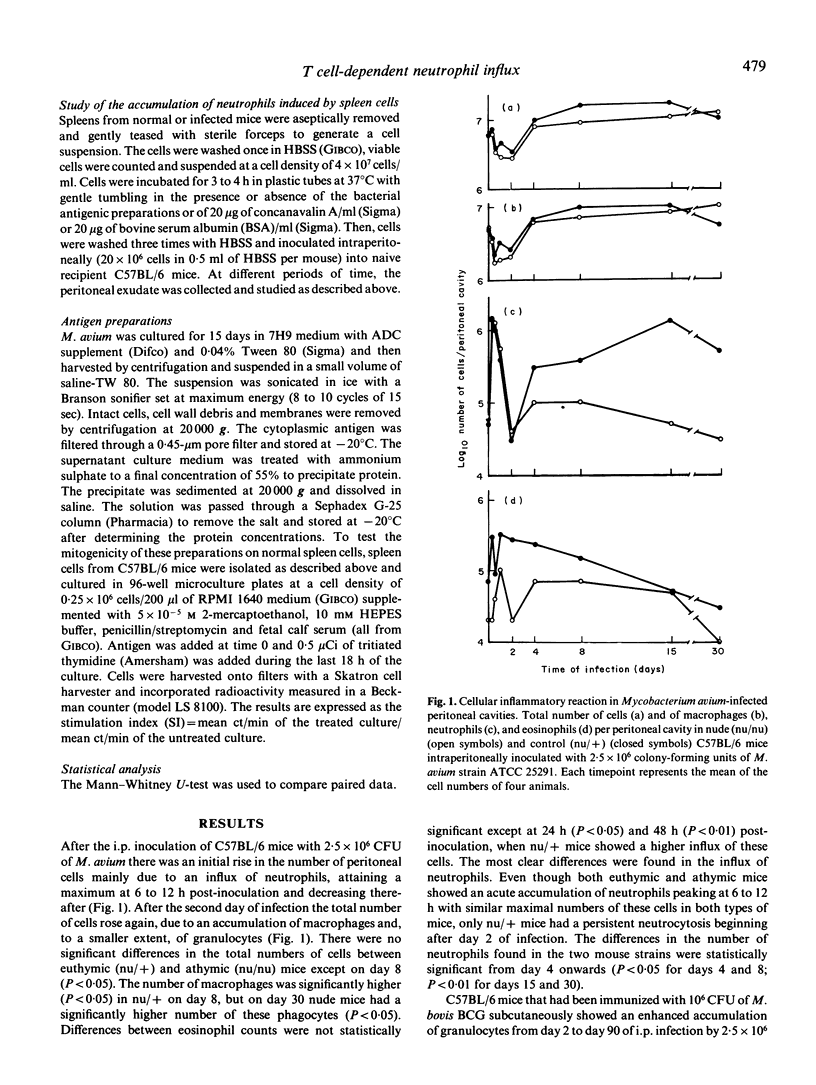
Euthymic (nu/+) C57BL/6 mice intraperitoneally inoculated with 2.5 x 10(6) colony-forming units (CFU) of Mycobacterium avium developed a chronic peritoneal neutrophilic granulocytosis during the 30 days of infection studied; in contrast, congenitally athymic nude (nu/nu) mice of C57BL/6 background did not show such persistent neutrophil influx. The acute phase of peritoneal infection, characterized by an extensive accumulation of neutrophils peaking at 6 to 12 h post-inoculation, was similar in euthymic and athymic mice. Subcutaneous vaccination of C57BL/6 mice with BCG enhanced the peritoneal influx of granulocytes after the i.p. inoculation of 2.5 x 10(60 CFU of M. avium. Finally, spleen cells from M. avium-infected mice pulsed in vitro with mycobacterial antigen induced a higher neutrophil accumulation after inoculation into the peritoneal cavity of naive recipient mice than unpulsed spleen cells or spleen cells from noninfected mice. These data indicate that the immune system is involved in the regulation of the chronic neutrophil influx during mycobacterial infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelberg R., Soares R., Ferreira P., Silva M. T. Induction of non-specific immunosuppression in mice by mycobacterial infections and its relationship to macrophage activation. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Aug;30(2):165–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson Y. H., Lopez A. F., Marasco W. A., Lucas C. M., Wong G. G., Burns G. F., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rH GM-CSF) regulates f Met-Leu-Phe receptors on human neutrophils. Immunology. 1988 Jul;64(3):519–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson Y. H., Marasco W. A., Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulation of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine receptor affinity and function on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):759–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI113381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Wang D., Larrick J. W., Dodson R. W., Howard T. H. Enhancement of neutrophil superoxide production by preincubation with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3783–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Cappelli R., Della Bianca V., Grzeskowiak M., Dusi S., Berton G. Interferon-gamma activates human neutrophil oxygen metabolism and exocytosis. Immunology. 1988 Mar;63(3):499–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Lowell G. H. Stimulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte bactericidal activity by supernatants of activated human mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):502–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.502-507.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Enhanced accumulation of inflammatory neutrophils and macrophages mediated by transfer of T cells from mice immunized with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3449–3454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davatelis G., Tekamp-Olson P., Wolpe S. D., Hermsen K., Luedke C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Merryweather J., Cerami A. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA for murine macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP), a novel monokine with inflammatory and chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1939–1944. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D., Kirkpatrick C. H. The immunology of mycobacterial diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;134(5):1062–1071. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Mocatta T. J. Human neutrophils require activation by mononuclear leucocyte conditioned medium to kill the pathogenic free-living amoeba, Naegleria fowleri. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Nandoskar M., Bates E. J., Goh D. H., Beard L. J. Tumour necrosis factor beta (lymphotoxin) inhibits locomotion and stimulates the respiratory burst and degranulation of neutrophils. Immunology. 1988 Mar;63(3):507–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figari I. S., Mori N. A., Palladino M. A., Jr Regulation of neutrophil migration and superoxide production by recombinant tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta: comparison to recombinant interferon-gamma and interleukin-1 alpha. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):979–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Weisbart R. H., Kaufman S. E., Clark S. C., Hewick R. M., Wong G. G., Golde D. W. Purified human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: direct action on neutrophils. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1339–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.6390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Fales H. M., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor for neutrophils. Stimuli and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI109878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierowski J. A., Gallin J. I., Reynolds H. Y. Mechanism for the inflammatory response in primate lungs. Demonstration and partial characterization of an alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor with preferential activity for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):273–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI108638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowanko I. C., Ferrante A. Interleukin 2 inhibits migration and stimulates respiratory burst and degranulation of human neutrophils in vitro. Immunol Lett. 1987 Aug;15(4):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowanko I. C., Ferrante A. Stimulation of neutrophil respiratory burst and lysosomal enzyme release by human interferon-gamma. Immunology. 1987 Sep;62(1):149–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownatzki E., Kapp A., Uhrich S. Modulation of human neutrophilic granulocyte functions by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor and recombinant human lymphotoxin. Promotion of adherence, inhibition of chemotactic migration and superoxide anion release from adherent cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Oct;74(1):143–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownatzki E., Kapp A., Uhrich S. Novel neutrophil chemotactic factor derived from human peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):214–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Graham D., Toy K., Lin L. S., Senyk G., Fendly B. M. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor causes activation of human granulocytes. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomnitzer R., Glover A., Rabson A. R. The effect of PHA-activated MN-cell supernatants on polymorphonuclear leucocyte function. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):501–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestrelli P., O'Hehir R. E., Lamb J. R., Tsai J. J., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Antigen-induced neutrophil chemotactic factor from cloned human T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1988 Dec;65(4):605–609. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestrelli P., Tsai J. J., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. The identification and partial characterization of a human mononuclear cell-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor apparently distinct from IL-1, IL-2, GM-CSF, TNF and IFN-gamma. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):219–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor: kinetics of in vitro production and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):268–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI109668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. J., Brummer E., Isenberg R. A., Stevens D. A. Activation of murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils for fungicidal activity by recombinant gamma interferon. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 May;41(5):434–440. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.5.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Neutrophil activation on biological surfaces. Massive secretion of hydrogen peroxide in response to products of macrophages and lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1550–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI113241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Rossing T. H., Boerth L. W., Lee T. H. Isolation and partial characterization of a human alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1230–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI111820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Purification and partial biologic characterization of a human lymphocyte-derived peptide with potent neutrophil-stimulating activity. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3534–3540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Morita E., Christophers E. Purification and partial biochemical characterization of a human monocyte-derived, neutrophil-activating peptide that lacks interleukin 1 activity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3474–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Silva M. N., Appelberg R. Neutrophil-macrophage cooperation in the host defence against mycobacterial infections. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbeck M. J., Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Activation of bovine neutrophils by recombinant interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1986 Mar;98(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Griffin J. D., Simons E. R., Schafer A. I., Meshulam T., Fredette J. P., Maas A. K., Gadenne A. S., Leavitt J. L., Melnick D. A. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors on signal transduction pathways in human granulocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3422–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. J., Maestrelli P., Cromwell O., Moqbel R., Fitzharris P., Kay A. B. A T-lymphocyte-derived factor that enhances IgG-dependent release of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) from human neutrophils. Immunology. 1988 Nov;65(3):449–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yokota S., Vilcek J., Weissmann G. Tumor necrosis factor provokes superoxide anion generation from neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1094–1100. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Van Beeumen J., Opdenakker G., Billiau A. A novel, NH2-terminal sequence-characterized human monokine possessing neutrophil chemotactic, skin-reactive, and granulocytosis-promoting activity. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1364–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. M., Colella S., Allavena P., Mantovani A. Chemotactic activity of human recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):439–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Remold H. G., David J. R. The production by antigen-stimulated lymphocytes of a leukotactic factor distinct from migration inhibitory factor. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):162–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Tanaka S., Robinson E. A., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Purification of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor that has peptide sequence similarity to other host defense cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9233–9237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



