Abstract
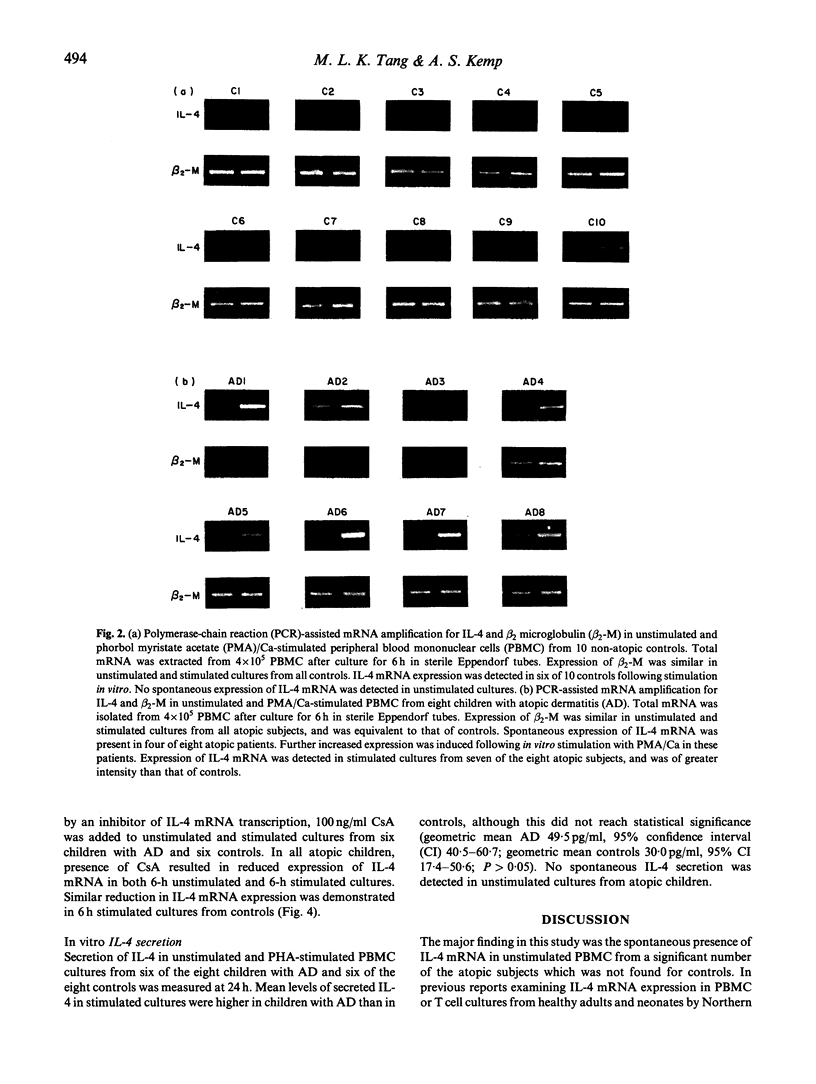
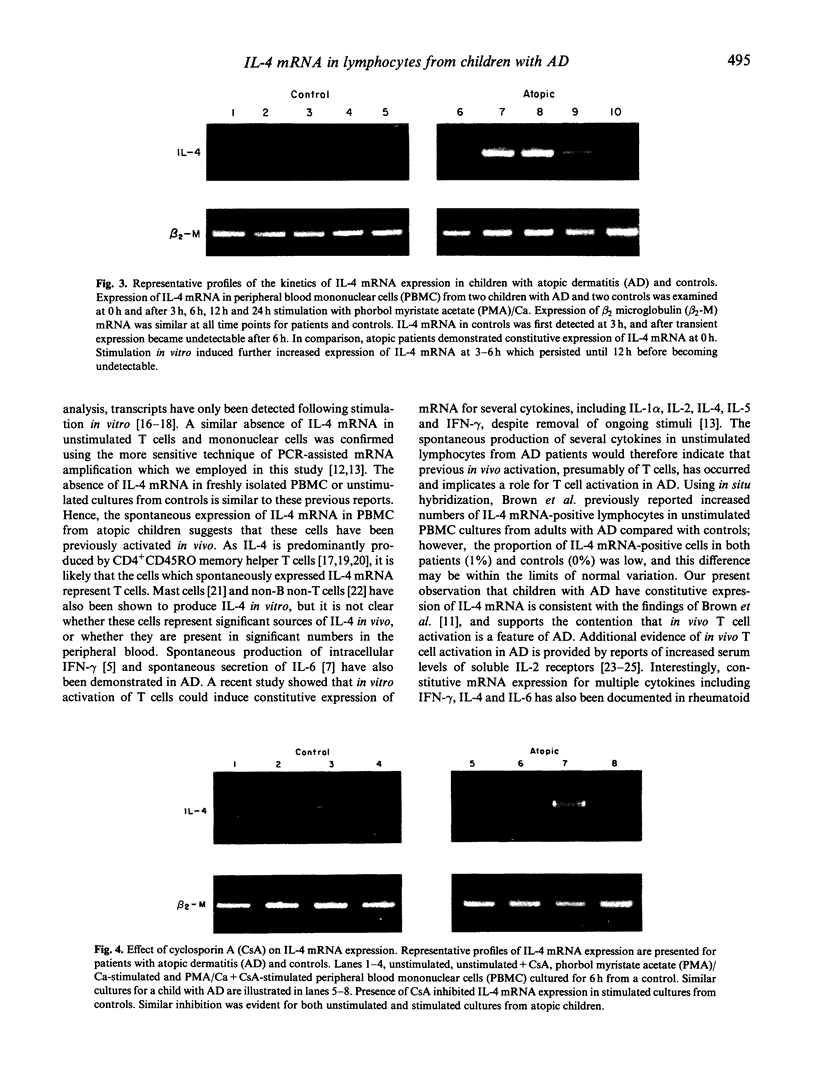
Normal lymphocytes do not generally produce or secrete lymphokines in the resting or unstimulated state and only express or release cytokines following activation. Recently, the spontaneous production of intracellular interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and spontaneous secretion of IL-6 has been documented in patients with atopic dermatitis. These findings indicated that lymphocytes had been previously activated in vivo. Such in vivo activation may also be associated with spontaneous production of IL-4. As measurement of IL-4 secretion by immunoassay is complicated by poor sensitivity, and only provides information on the net amount of cytokine present after secretion, adsorption, consumption and degradation have occurred, IL-4 mRNA expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes from children with atopic dermatitis and controls was examined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-assisted mRNA amplification. Spontaneous expression of IL-4 mRNA was detected in four of eight patients with severe atopic dermatitis. Following stimulation in vitro, seven of eight atopic patients demonstrated detectable IL-4 mRNA. In comparison, no spontaneous expression of IL-4 mRNA was found in controls, and only six of 10 controls expressed IL-4 mRNA in stimulated cultures. The spontaneous expression of IL-4 mRNA in unstimulated cultures from children with atopic dermatitis supports the possibility that previous in vivo activation has occurred, and suggests that IL-4 production is increased in vivo in atopic dermatitis. This in vivo activation together with the constitutive expression of IL-4 mRNA are likely to contribute to the spontaneous in vitro production of IgE in atopic patients.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abehsira-Amar O., Gibert M., Joliy M., Thèze J., Jankovic D. L. IL-4 plays a dominant role in the differential development of Tho into Th1 and Th2 cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3820–3829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradding P., Feather I. H., Howarth P. H., Mueller R., Roberts J. A., Britten K., Bews J. P., Hunt T. C., Okayama Y., Heusser C. H. Interleukin 4 is localized to and released by human mast cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1381–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan G., Barrett K., Fujita T., Taniguchi T., Maini R., Feldmann M. Detection of activated T cell products in the rheumatoid joint using cDNA probes to Interleukin-2 (IL-2) IL-2 receptor and IFN-gamma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colver G. B., Symons J. A., Duff G. W. Soluble interleukin 2 receptor in atopic eczema. BMJ. 1989 May 27;298(6685):1426–1428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6685.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokter W. H., Esselink M. T., Sierdsema S. J., Halie M. R., Vellenga E. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of the interleukin-4 and interleukin-3 genes in human T cells. Blood. 1993 Jan 1;81(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Smith K. A. Differentiation of T cell lymphokine gene expression: the in vitro acquisition of T cell memory. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Klee C. B., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. Calcineurin phosphatase activity in T lymphocytes is inhibited by FK 506 and cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Joyce J., Fitch F. W. Antiproliferative effect of IFN-gamma in immune regulation. III. Differential selection of TH1 and TH2 murine helper T lymphocyte clones using recombinant IL-2 and recombinant IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauchat J. F., Gauchat D., De Weck A. L., Stadler B. M. Cytokine mRNA levels in antigen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jun;19(6):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. Regulation of IgE synthesis in humans. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Aug;90(2):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewe M., Gyufko K., Schöpf E., Krutmann J. Lesional expression of interferon-gamma in atopic eczema. Lancet. 1994 Jan 1;343(8888):25–26. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90879-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jujo K., Renz H., Abe J., Gelfand E. W., Leung D. Y. Decreased interferon gamma and increased interleukin-4 production in atopic dermatitis promotes IgE synthesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Sep;90(3 Pt 1):323–331. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(05)80010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Borrebaeck C. A., Carlsson R. Human CD4+ T cells expressing CD45RA acquire the lymphokine gene expression of CD45RO+ T-helper cells after activation in vitro. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):103–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Bhan A. K., Schneeberger E. E., Geha R. S. Characterization of the mononuclear cell infiltrate in atopic dermatitis using monoclonal antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Jan;71(1 Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90546-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Yu C. C., Meyer J., English B. K., Kahn S. J., Wilson C. B. Cellular and molecular mechanisms for reduced interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma production by neonatal T cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):194–202. doi: 10.1172/JCI114970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi E., Parronchi P., Manetti R., Simonelli C., Piccinni M. P., Rugiu F. S., De Carli M., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Reciprocal regulatory effects of IFN-gamma and IL-4 on the in vitro development of human Th1 and Th2 clones. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2142–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Bal V., Quint D., Moqbel R., Kay A. B., Zanders E. D., Lamb J. R. An in vitro model of allergen-dependent IgE synthesis by human B lymphocytes: comparison of the response of an atopic and a non-atopic individual to Dermatophagoides spp. (house dust mite). Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):499–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parronchi P., Macchia D., Piccinni M. P., Biswas P., Simonelli C., Maggi E., Ricci M., Ansari A. A., Romagnani S. Allergen- and bacterial antigen-specific T-cell clones established from atopic donors show a different profile of cytokine production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccinni M. P., Macchia D., Parronchi P., Giudizi M. G., Bani D., Alterini R., Grossi A., Ricci M., Maggi E., Romagnani S. Human bone marrow non-B, non-T cells produce interleukin 4 in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon and Fc gamma receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8656–8660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa E. K., Pisa P., Hansson M., Wigzell H. OKT3-induced cytokine mRNA expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells measured by polymerase chain reaction. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Nov;36(5):745–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo W. J., Conrad L., Janeway C. A., Jr Receptor-directed focusing of lymphokine release by helper T cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):378–380. doi: 10.1038/332378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold U., Pawelec G., Wehrmann W., Kukel S., Oehr P., Kreysel H. W. Cytokine release from cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with severe atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1989;69(6):497–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold U., Wehrmann W., Kukel S., Kreysel H. W. Evidence that defective interferon-gamma production in atopic dermatitis patients is due to intrinsic abnormalities. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):374–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Del Prete G. F., Maggi E., Troncone R., Giudizi G. M., Almerigogna F., Ricci M. In vitro production of IgE by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. II. Cells involved in the spontaneous IgE production in atopic patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):579–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Robert J., Andary M., Bonnin J. P., Souillet G., Chrétien I., Brière F., Pène J., de Vries J. E. Shifts in interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma production by T cells of patients with elevated serum IgE levels and the modulatory effects of these lymphokines on spontaneous IgE synthesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Jan;87(1 Pt 1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager N., Feldmann A., Schilling G., Kreitsch P., Neumann C. House dust mite-specific T cells in the skin of subjects with atopic dermatitis: frequency and lymphokine profile in the allergen patch test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Apr;89(4):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon M., Kitas G. D., Bacon P. A. Production of lymphokine mRNA by CD45R+ and CD45R- helper T cells from human peripheral blood and by human CD4+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):907–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Matthes T., Carballido-Perrig N., Zubler R. H., Kindler V. Differential induction of T cell cytokine mRNA in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cell clones: constitutive and inducible expression of interleukin-4 mRNA. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):899–903. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M. L., Varigos G., Kemp A. S. Reduced interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) secretion with increased IFN-gamma mRNA expression in atopic dermatitis: evidence for a post-transcriptional defect. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Sep;97(3):483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M., Kemp A. Production and secretion of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in children with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Jan;95(1):66–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M., Kemp A., Varigos G. IL-4 and interferon-gamma production in children with atopic disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Apr;92(1):120–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thestrup-Pedersen K., Larsen C. S., Kristensen M., Zachariae C. Interleukin-1 release from peripheral blood monocytes and soluble interleukin-2 and CD8 receptors in serum from patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70(5):395–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshitani A., Ansel J. C., Chan S. C., Li S. H., Hanifin J. M. Increased interleukin 6 production by T cells derived from patients with atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Mar;100(3):299–304. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider S., Saurat J. H., Röcken M., Hauser C. Evidence suggesting involvement of interleukin-4 (IL-4) production in spontaneous in vitro IgE synthesis in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Jun;87(6):1088–1095. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)92154-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalen K., Sioud M., Natvig J. B., Førre O. Spontaneous in vivo gene transcription of interleukin-2, interleukin-3, interleukin-4, interleukin-6, interferon-gamma, interleukin-2 receptor (CD25) and proto-oncogene c-myc by rheumatoid synovial T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Dec;36(6):865–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Bode E., Boer L., Hansel T. T., Blaser K., Virchow J. C., Jr Allergic and nonallergic asthmatics have distinct patterns of T-cell activation and cytokine production in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):109–115. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., Jansen H. M., Bos J. D., van Lier R. A., Kapsenberg M. L. Human atopen-specific types 1 and 2 T helper cell clones. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2942–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., de Groot C., Chrétien I., Bos J. D., Jansen H. M., Kapsenberg M. L. Evidence for compartmentalization of functional subsets of CD2+ T lymphocytes in atopic patients. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4651–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich B., Joller-Jemelka H., Helfenstein U., Grob P. J. Levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors correlate with the severity of atopic dermatitis. Dermatologica. 1990;181(2):92–97. doi: 10.1159/000247893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Reijsen F. C., Bruijnzeel-Koomen C. A., Kalthoff F. S., Maggi E., Romagnani S., Westland J. K., Mudde G. C. Skin-derived aeroallergen-specific T-cell clones of Th2 phenotype in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Aug;90(2):184–193. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90070-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]