Abstract
The Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) cell adhesion motif has been demonstrated in various studies to play a pivotal role in leucocyte and platelet interactions with plasma and extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoproteins. The recognition of the RGD sequence is mediated by heterodimeric receptors designated integrins of the beta 1 subfamily, expressed on distinct cell types, including T lymphocytes. We have recently shown that flexible non-peptidic mimetics of RGD, in which the two ionic side groups were separated by a linear spacer of 11 atoms, bound specifically to the platelet integrin alpha 11b beta 3, and inhibited T cell-mediated immune responses. The present study was designed to (i) further characterize the structural requirements for RGD interactions with CD4+ T cells, and (ii) examine the mechanisms by which the RGD mimetics interfere with immune cell reactivity in vivo. We now report that freezing the conformational degrees of freedom in the spacer chain, which fixes the relative orientation of the guanidinium and carboxylate side groups in a favourable manner, results in a higher level of inhibition of T cell binding to immobilized fibronectin, an RGD-containing ECM glycoprotein. In vivo, treatment of mice with relatively low doses of the RGD mimetics, but not the RGD peptide, inhibited the elicitation of an adoptively transferred DTH reaction. This inhibition was achieved by direct impairment of the ability of antigen-primed lymph node cells to migrate and accumulate in inflammatory sites. Hence, we suggest that the design and production of non-peptidic mimetics of RGD offers a novel approach to study defined parameters related to the structure-function requirements of small adhesion epitopes. Furthermore, this approach could be used therapeutically to inhibit pathological processes which depend on RGD recognition.
Full text
PDF
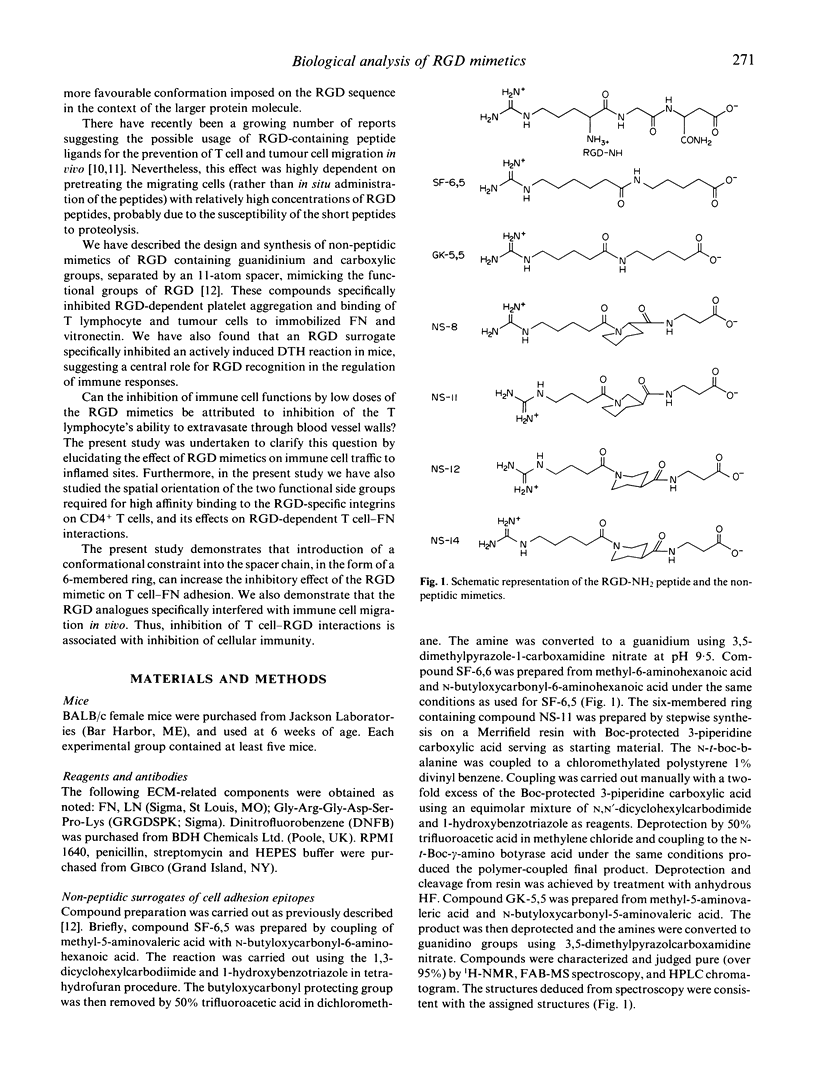

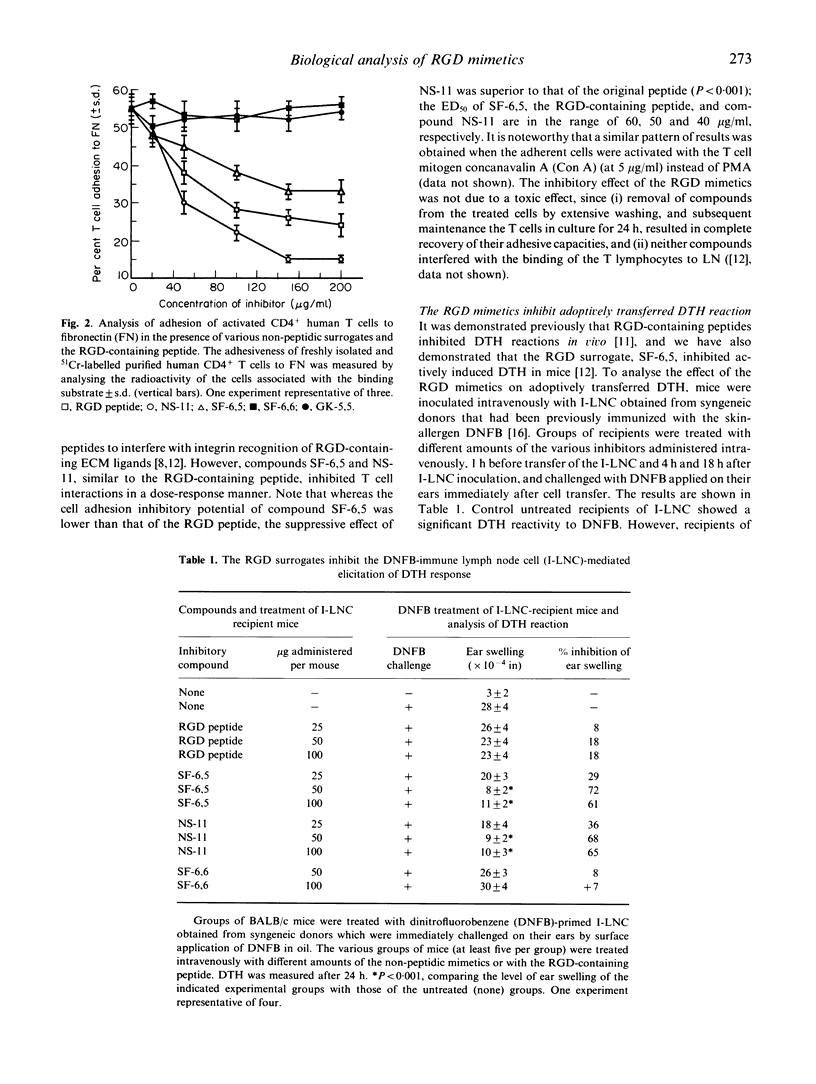
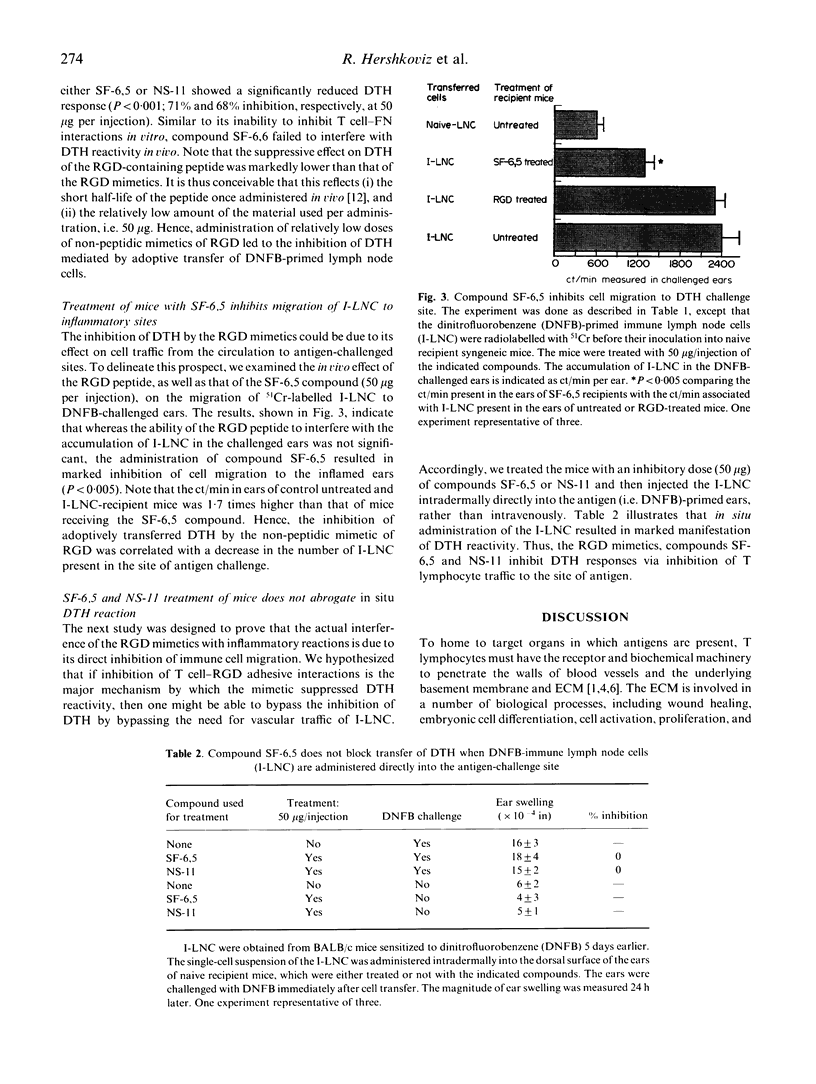


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alon R., Hershkoviz R., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M., Lider O. Streptavidin blocks immune reactions mediated by fibronectin-VLA-5 recognition through an Arg-Gly-Asp mimicking site. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):893–898. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid (RGD): a cell adhesion motif. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jul;16(7):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90096-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson T. A., Mizutani H., Kupper T. S. Two integrin-binding peptides abrogate T cell-mediated immune responses in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8072–8076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspoon N., Hershkoviz R., Alon R., Varon D., Shenkman B., Marx G., Federman S., Kapustina G., Lider O. Structural analysis of integrin recognition and the inhibition of integrin-mediated cell functions by novel nonpeptidic surrogates of the Arg-Gly-Asp sequence. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1001–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershkoviz R., Alon R., Gilat D., Lider O. Activated T lymphocytes and macrophages secrete fibronectin which strongly supports cell adhesion. Cell Immunol. 1992 May;141(2):352–361. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90154-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Olden K., Yamada K. M. A synthetic peptide from fibronectin inhibits experimental metastasis of murine melanoma cells. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3726541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lider O., Mekori Y. A., Miller T., Bar-Tana R., Vlodavsky I., Baharav E., Cohen I. R., Naparstek Y. Inhibition of T lymphocyte heparanase by heparin prevents T cell migration and T cell-mediated immunity. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):493–499. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miron S., Hershkoviz R., Tirosh I., Schechter Y., Yayun A., Lider O. Involvement of a protein kinase C and protein phosphatases in adhesion of CD4+ T cells to and detachment from extracellular matrix proteins. Cell Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;144(1):182–189. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90235-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Yamakawa N., Aota S., Yamada S. S., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Monoclonal antibody characterization of two distant sites required for function of the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin in cell adhesion, cell migration, and matrix assembly. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1295–1305. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki I., Murata J., Iida J., Nishi N., Sugimura K., Azuma I. The inhibition of murine lung metastasis by synthetic polypeptides [poly(arg-gly-asp) and poly(tyr-ile-gly-ser-arg)] with a core sequence of cell adhesion molecules. Br J Cancer. 1989 Feb;59(2):194–197. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seftor R. E., Seftor E. A., Gehlsen K. R., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Ruoslahti E., Hendrix M. J. Role of the alpha v beta 3 integrin in human melanoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1557–1561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Shaw S. Lymphocyte interactions with extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2292–2299. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1860621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Regulated expression and binding of three VLA (beta 1) integrin receptors on T cells. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):250–253. doi: 10.1038/345250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenco P. D., Schittny J. C. Molecular architecture of basement membranes. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1577–1590. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2180767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


