Abstract
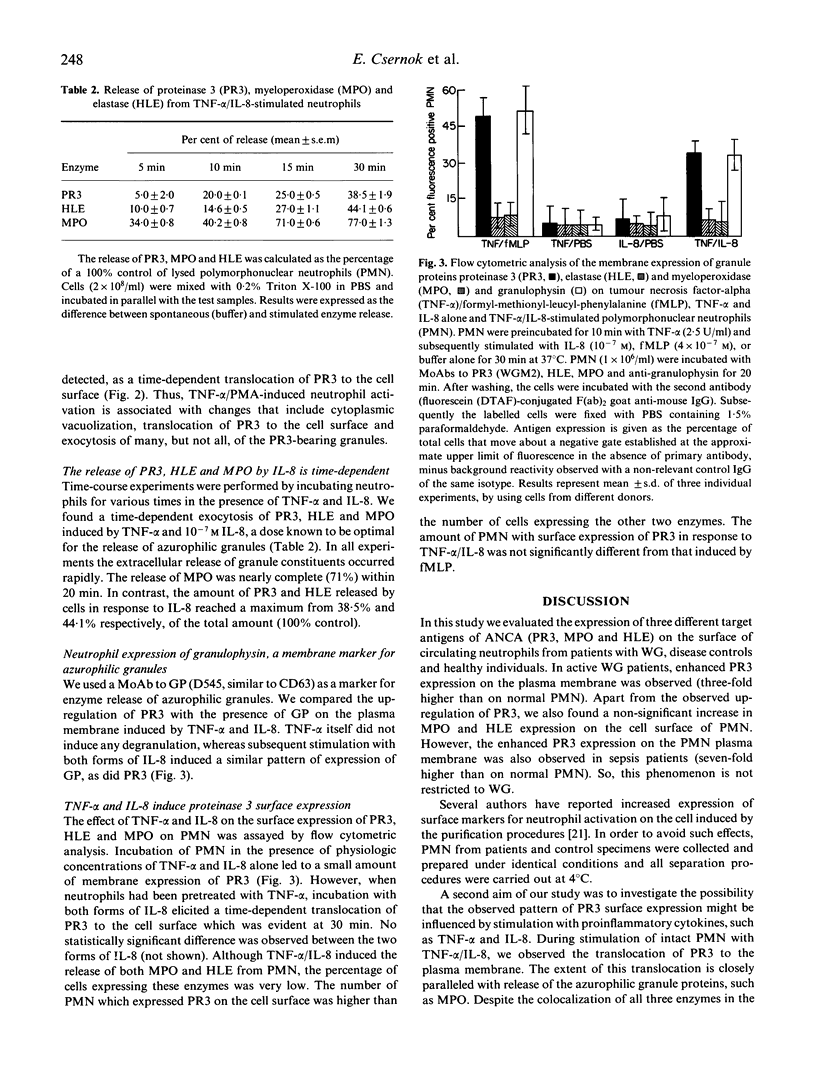
Apart from the diagnostic value of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), their detailed characterization and that of their corresponding antigens have opened new ways for the exploration of the pathogenesis of primary systemic vasculitis. ANCA are now thought to play an important functional role via activation of phagocytic cells (e.g. polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN)). In this study we examined the mechanisms by which ANCA could gain access to proteinase 3 (PR3) in intact PMN, at two levels: ex vivo by analysing the presence of PR3 on the plasma membrane of PMN from patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, and in vitro by stimulation of PMN using different cytokines, including recombinant tumour necrosis factor-alpha (rhTNF-alpha) and two forms of IL-8 (produced by monocytic and endothelial cells). Using immunocytochemical staining techniques (FACS and immunoelectronmicroscopy) PR3 has been detected on the plasma membrane of PMN from patients with active ANCA-associated vasculitis. However, this phenomenon is also seen in patients with sepsis who do not have ANCA. In addition, TNF-alpha and both forms of IL-8 act synergistically and induce a translocation of PR3 from the intragranular loci to the cell surface of PMN. These results provide strong evidence for the hypothesis that ANCA are directly pathogenic by binding to PR3 which is expressed on the cell surface of primed/activated PMN.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson Y. H., Marasco W. A., Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulation of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine receptor affinity and function on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):759–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI113381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Miller L. J., Kishimoto T. K., Springer T. A. Leukocyte adhesion receptors are stored in peroxidase-negative granules of human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1641–1653. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltaro R. J., Hoffman G. S., Sechler J. M., Suffredini A. F., Shelhamer J. H., Fauci A. S., Fleisher T. A. Immunoglobulin G antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies are produced in the respiratory tract of patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Feb;143(2):275–278. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles L. A., Caldas M. L., Falk R. J., Terrell R. S., Jennette J. C. Antibodies against granule proteins activate neutrophils in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Dec;50(6):539–546. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csernok E., Lüdemann J., Gross W. L., Bainton D. F. Ultrastructural localization of proteinase 3, the target antigen of anti-cytoplasmic antibodies circulating in Wegener's granulomatosis. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1113–1120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst M., Kern P., Flad H. D., Ulmer A. J. Effects of systemic in vivo interleukin-2 (IL-2) reconstitution in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex (ARC) on phenotypes and functions of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). J Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;6(2):170–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00918750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert B. H., Jennette J. C., Falk R. J. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies stimulate neutrophils to damage human endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Feb;41(2):375–383. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Jennette J. C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1651–1657. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Terrell R. S., Charles L. A., Jennette J. C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies induce neutrophils to degranulate and produce oxygen radicals in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4115–4119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Balow J. E., Brown R., Chazan J., Steinman T., Sahyoun A. I., Monoaco A. P., Wolff S. M. Successful renal transplantation in Wegener's granulomatosis. Am J Med. 1976 Mar;60(3):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross W. L., Csernok E., Schmitt W. H. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies: immunobiological aspects. Klin Wochenschr. 1991 Sep 3;69(13):558–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01649318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross W. L., Lüdemann G., Kiefer G., Lehmann H. Anticytoplasmic antibodies in Wegener's granulomatosis. Lancet. 1986 Apr 5;1(8484):806–806. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91820-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross W. L., Schmitt W. H., Csernok E. ANCA and associated diseases: immunodiagnostic and pathogenetic aspects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03345.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenberg C. G., Mulder A. H., Tervaert J. W. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies: a still-growing class of autoantibodies in inflammatory disorders. Am J Med. 1992 Dec;93(6):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90202-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogan M. T., Esnault V. L., Green A. J., Lockwood C. M., Brown D. L. Activation of normal neutrophils by anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(2):228–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb07934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers T. W., Tool A. T., van der Schoot C. E., Ginsel L. A., Onderwater J. J., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. Membrane surface antigen expression on neutrophils: a reappraisal of the use of surface markers for neutrophil activation. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):1105–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. O., Pottinger B. E., Gaskin G., Lockwood C. M., Pusey C. D., Pearson J. D. Vascular damage in Wegener's granulomatosis and microscopic polyarteritis: presence of anti-endothelial cell antibodies and their relation to anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):14–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Woude F. J., Daha M. R., van Es L. A. The current status of neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Nov;78(2):143–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Woude F. J., Rasmussen N., Lobatto S., Wiik A., Permin H., van Es L. A., van der Giessen M., van der Hem G. K., The T. H. Autoantibodies against neutrophils and monocytes: tool for diagnosis and marker of disease activity in Wegener's granulomatosis. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):425–429. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




