Abstract
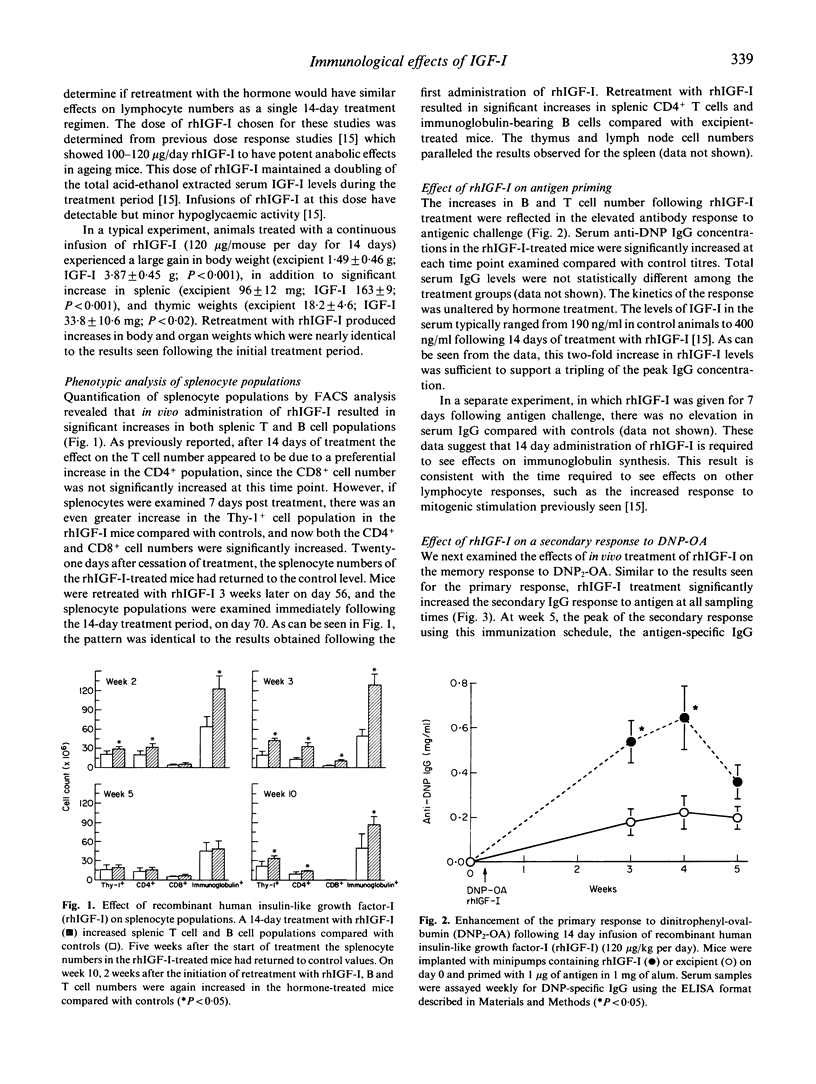
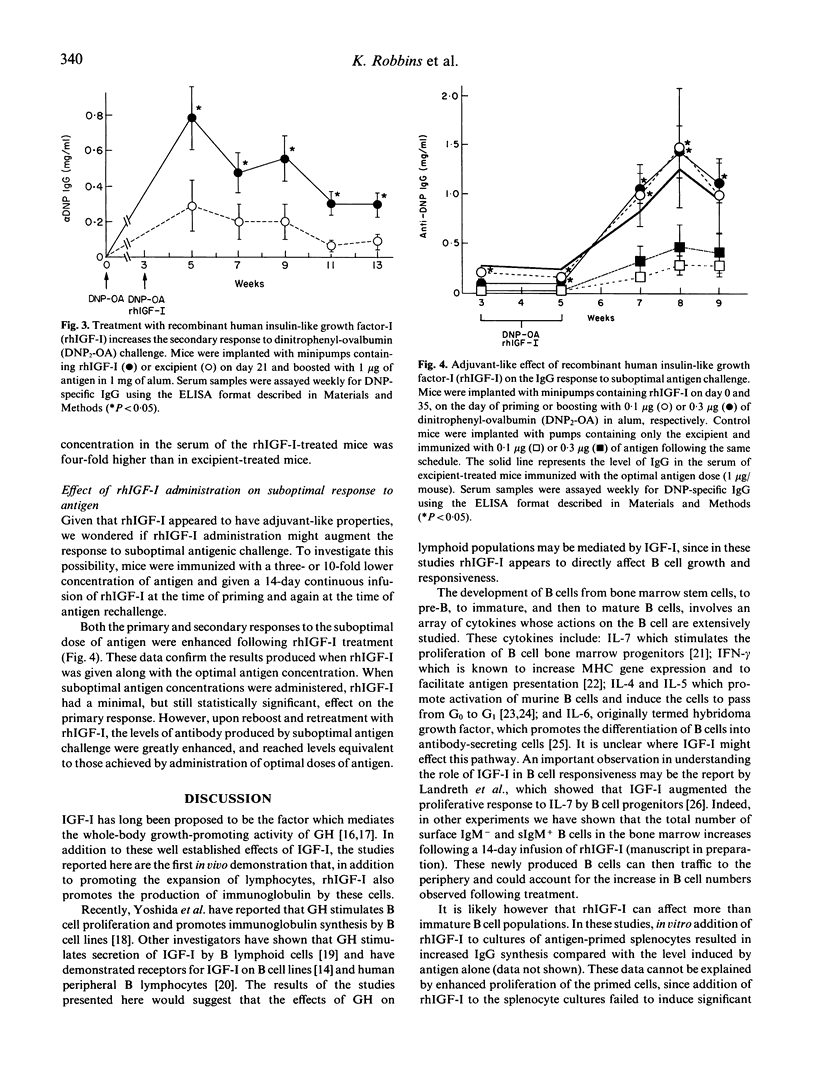
In addition to its activity as a metabolic hormone and a regulator of somatic growth, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) has cytokine-like activities on lymphoid cells. A 14-day infusion of recombinant human (rh)IGF-I increased lymphocyte numbers in all the peripheral lymphoid organs examined. This increase was apparent for up to 3 weeks following cessation of hormone treatment. A second administration of rhIGF-I, given when the lymphocyte numbers in the rhIGF-I-treated mice had returned to control values, resulted in similar increases in the peripheral T and B cell populations. This increase in lymphocyte numbers had functional significance, since rhIGF-I-treated mice produced elevated antibody titres following primary or secondary antigen challenge compared with controls. In addition, when rhIGF-I-treated mice were immunized with a suboptimal dose of antigen they produced antibody titres which were equivalent to those generated by immunization with optimal doses of antigen. When examined in vitro, addition of rhIGF-I alone to cultures of splenocytes from antigen-primed mice stimulated immunoglobulin synthesis. These studies suggest that IGF-I produced locally by thymic and bone marrow stromal cells may be a natural component of B and T cell lymphopoiesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz K., Joller P., Froesch P., Binz H., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Repopulation of the atrophied thymus in diabetic rats by insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3690–3694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butch A. W., Nahm M. H. Functional properties of human germinal center B cells. Cell Immunol. 1992 Apr;140(2):331–344. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Strasser J., McCabe S., Robbins K., Jardieu P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulation of lymphopoiesis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):540–548. doi: 10.1172/JCI116621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Van Wyk J. J. Factors controlling blood concentration of somatomedin C. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):113–143. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Hall K., Raben M. S., Salmon W. D., Jr, van den Brande J. L., van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin: proposed designation for sulphation factor. Nature. 1972 Jan 14;235(5333):107–107. doi: 10.1038/235107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Hall K., Salmon W. D., Jr, Van den Brande J. L., Van Wyk J. J. On the nomenclature of the somatomedins and insulin-like growth factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Nov;65(5):1075–1076. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-5-1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffner M. E., Bersch N., Lippe B. M., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L., Golde D. W. Growth hormone mediates the growth of T-lymphoblast cell lines via locally generated insulin-like growth factor-I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Aug;71(2):464–469. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-2-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Lupton S., Schmierer A., Hjerrild K. J., Jerzy R., Clevenger W., Gillis S., Cosman D., Namen A. E. Human interleukin 7: molecular cloning and growth factor activity on human and murine B-lineage cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Scheiwiller E., Froesch E. R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth and has distinct effects on organ size in hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P., Eardley D. D. Suppressive effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) on immune responses. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):3994–3999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. W., Jones L. A., Kozak R. W. Expression and function of insulin-like growth factor receptors on anti-CD3-activated human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Cox A. J. Insulin-like growth factor binding to the atypical insulin receptors of a human lymphoid-derived cell line (IM-9). Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):737–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2660737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth K. S., Narayanan R., Dorshkind K. Insulin-like growth factor-I regulates pro-B cell differentiation. Blood. 1992 Sep 1;80(5):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Grant M. B., Broder C. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Insulin-like growth factor secretion by human B-lymphocytes: a comparison of cells from normal and pygmy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Nov;69(5):978–984. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-5-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H., Suzuki M., Mizutani H., Fujiwara K., Shibata S., Arishima K., Hoshino M., Ushijima H., Honma H., Kitamura T. Sensitive detection of viral antigens with a new method, "laser magnet immunoassay". Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(9):717–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murasko D. M., Nelson B. J., Silver R., Matour D., Kaye D. Immunologic response in an elderly population with a mean age of 85. Am J Med. 1986 Oct;81(4):612–618. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Durum S. K., Longo D. L. Human growth hormone promotes engraftment of murine or human T cells in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Durum S. K., Longo D. L. Role of neuroendocrine hormones in murine T cell development. Growth hormone exerts thymopoietic effects in vivo. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):3851–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierpaoli W., Sorkin E. Hormones and immunologic capacity. I. Effect of heterologous anti-growth hormone (ASTH) antiserum on thymus and peripheral lymphatic tissue in mice. Induction of a wasting syndrome. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):1036–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieckmann P., D'Alessandro F., Nordan R. P., Fauci A. S., Kehrl J. H. IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Autocrine and paracrine cytokines involved in B cell function. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3462–3468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff R. M., Repellin A. M., Salvatoni A., Thieriot-Prevost G., Chatelain P. Effect of purified somatomedins on thymidine incorporation into lectin-activated human lymphocytes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Jan;102(1):21–26. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skottner A., Clark R. G., Fryklund L., Robinson I. C. Growth responses in a mutant dwarf rat to human growth hormone and recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2519–2526. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A., Meehan R. T., Neale L. S., Cintron N. M., Furlanetto R. W. Insulin-like growth factor-I binds selectively to human peripheral blood monocytes and B-lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 May;72(5):1117–1122. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-5-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapson V. F., Boni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F., Center D. M., Berman J. S. Structural and functional characterization of the human T lymphocyte receptor for insulin-like growth factor I in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):950–957. doi: 10.1172/JCI113703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timsit J., Savino W., Safieh B., Chanson P., Gagnerault M. C., Bach J. F., Dardenne M. Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I stimulate hormonal function and proliferation of thymic epithelial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):183–188. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonkonogy S. L., McKenzie D. T., Swain S. L. Regulation of isotype production by IL-4 and IL-5. Effects of lymphokines on Ig production depend on the state of activation of the responding B cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4351–4360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Ishioka C., Kimata H., Mikawa H. Recombinant human growth hormone stimulates B cell immunoglobulin synthesis and proliferation in serum-free medium. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1992 Jun;126(6):524–529. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1260524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buul-Offers S., Van den Brande J. L. The growth of different organs of normal and dwarfed Snell mice, before and during growth hormone therapy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Jan;96(1):46–58. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0960046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


