Abstract
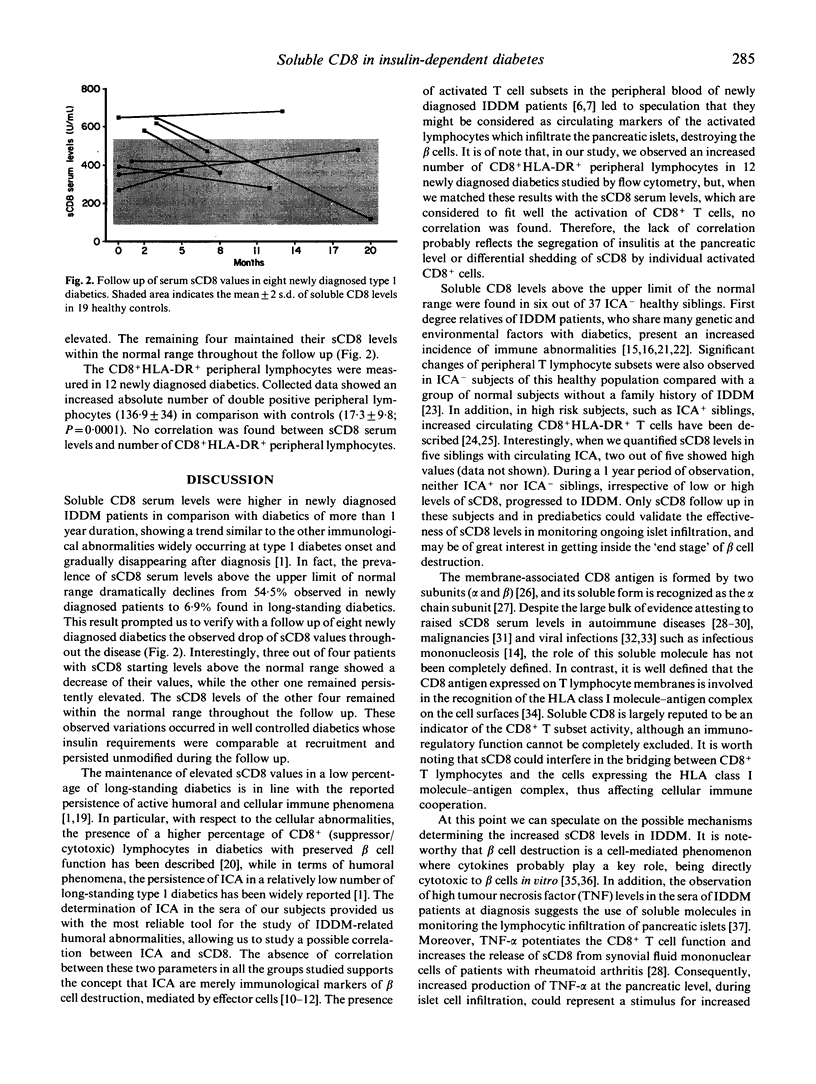
In type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus (IDDM) CD8+ T cells represent the majority of lymphocytes which infiltrate the pancreatic islets during beta cell destruction. Soluble CD8 antigen (sCD8) has been shown to correlate with CD8 cell subset activation. In this study we measured by ELISA sCD8 levels in sera from: 33 newly diagnosed IDDM patients; 29 type 1 diabetics with duration of disease more than 1 year; 37 healthy siblings of IDDM patients; 19 healthy controls. Sera from both groups of IDDM patients and from healthy siblings exhibited soluble CD8 mean levels significantly higher than controls (P = 0.0001, P < 0.003, P < 0.03 respectively). Soluble CD8 levels above the normal range (mean +/- 2 s.d. of controls) were found in a percentage of newly diagnosed subjects (54.5%) significantly higher than in subjects with a long-standing duration of disease (6.9%, P < 0.0005) and healthy siblings (16.2%, P < 0.002). Our results suggest that the raised levels of soluble CD8 near to diabetes onset may indicate the activation of CD8+ T cells probably responsible for the autoimmune beta cell destruction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostini C., Semenzato G., Vinante F., Sinicco A., Trentin L., Zambello R., Zuppini B., Zanotti R., Siviero F., Veneri D. Increased levels of soluble CD8 molecule in the serum of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related disorders. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Jan;50(1 Pt 1):146–153. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sakkaf L., Pozzilli P., Tarn A. C., Schwarz G., Gale E. A., Bottazzo G. F. Persistent reduction of CD4/CD8 lymphocyte ratio and cell activation before the onset of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1989 May;32(5):322–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00265550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra A., Corica F., Di Cesare E., Giacobbe M. S., Buda G., Ceruso D. The influence of hypercholesterolemia on some aspects of immune pattern in the elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 1992 Jul-Aug;15(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0167-4943(92)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Landin M., Kristensen J. K., Srikanta S., Bruining G. J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., de Beaufort C., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G., Lindgren F. Antibodies to a 64,000 Mr human islet cell antigen precede the clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):926–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI112903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Lernmark A., Dawkins R. L. Serum exchange and use of dilutions have improved precision of measurement of islet cell antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jan 21;106(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Dejgaard A., Madsbad S., Röpke C. Different percentages of CD8+ lymphocytes in long-term type 1 diabetics with and without residual beta cell function. Diabetes Res. 1989 Nov;12(3):105–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo M. G., Pozzilli P., Bird C., Wadhwa M., Meager A., Visalli N., Gearing A. J., Andreani D., Thorpe R. Cytokines in sera from insulin-dependent diabetic patients at diagnosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Nov;86(2):256–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean B. M., Becker F., McNally J. M., Tarn A. C., Schwartz G., Gale E. A., Bottazzo G. F. Insulin autoantibodies in the pre-diabetic period: correlation with islet cell antibodies and development of diabetes. Diabetologia. 1986 May;29(5):339–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00452073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drell D. W., Notkins A. L. Multiple immunological abnormalities in patients with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1987 Mar;30(3):132–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00274217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A., Hardman R. Aberrant expression of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules by B cells and hyperexpression of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules by insulin containing islets in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1987 May;30(5):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00299027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Levy S., Levy R. Spontaneous release of the Leu-2 (T8) molecule from human T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):752–766. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Stewart S. J., Levy R. Immunochemical analysis of the released Leu-2 (T8) molecule. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):116–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Ward B. J., Jauregui E., Johnson R. T., Vaisberg A. Immune activation in measles. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 22;320(25):1667–1672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906223202506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock C. L., Riley W. J., Alamo A., Pyka R., Maclaren N. K. Lymphocyte subsets and activation in prediabetes. Diabetes. 1986 Dec;35(12):1416–1422. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.12.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. W., Haedt L. H., Rich S., Barbosa J. Prevalence of antibodies to nucleic acids in insulin-dependent diabetics and their relatives. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):873–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay T. W., Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C. Characterization of pancreatic T lymphocytes associated with beta cell destruction in the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse. J Autoimmun. 1991 Apr;4(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Helqvist S., Wogensen L. D., Mølvig J., Pociot F., Johannesen J., Nerup J. Cytokine and free radicals as effector molecules in the destruction of pancreatic beta cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;164:169–193. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75741-9_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaoka K., Sakurami T., Nabeya N., Imura H., Kuno S. Thyroglobulin and microsomal antibodies in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and their relatives. Endocrinol Jpn. 1979 Apr;26(2):213–217. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.26.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri Aria K. T., Lombard M., Williams R. High serum levels of CD8 antigen in primary biliary cirrhosis: a possible cause of suppressor cell dysfunction? Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Oct;86(1):140–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly L. A., Hutchings P. R., Crocker P. R., Simpson E., Lund T., Kioussis D., Takei F., Baird J., Cooke A. Characterization of pancreatic islet cell infiltrates in NOD mice: effect of cell transfer and transgene expression. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1171–1180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Asplin C. M., Clemons P., Lyen K., Tatpati O., Raghu P. K., Paquette T. L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6362005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzilli P., Zuccarini O., Iavicoli M., Andreani D., Sensi M., Spencer K. M., Bottazzo G. F., Beverley P. C., Kyner J. L., Cudworth A. G. Monoclonal antibodies defined abnormalities of T-lymphocytes in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):91–94. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H., Ip S. H., Dodge R. K., Carrabis S., Brown M., Crist W. M., Berard C. W., Kung P., Dahl G. V., Murphy S. B. Serum levels of CD8 antigen in childhood lymphoid malignancies: a possible indicator of increased suppressor cell activity in poor-risk patients. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1015–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria P., Nakhleh R. E., Sutherland D. E., Barbosa J. J. Characterization of T lymphocytes infiltrating human pancreas allograft affected by isletitis and recurrent diabetes. Diabetes. 1992 Jan;41(1):53–61. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiue L., Gorman S. D., Parnes J. R. A second chain of human CD8 is expressed on peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):1993–2005. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley R. K., Sutherland D. E., Goetz F., Michael A. F. Recurrent diabetes mellitus in the pancreas iso- and allograft. A light and electron microscopic and immunohistochemical analysis of four cases. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):132–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikanta S., Ganda O. P., Rabizadeh A., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. First-degree relatives of patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Islet-cell antibodies and abnormal insulin secretion. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 22;313(8):461–464. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508223130801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. T cell subsets and the recognition of MHC class. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:129–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons J. A., Wood N. C., di Giovine F. S., Duff G. W. Soluble CD8 in patients with rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):354–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarn A. C., Thomas J. M., Dean B. M., Ingram D., Schwarz G., Bottazzo G. F., Gale E. A. Predicting insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1988 Apr 16;1(8590):845–850. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91601-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B. E., Brown M. C., Ip S. H., Carrabis S., Sullivan J. L. Soluble CD8 during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2230–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski C. C., Pesau B., Müller C. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor and soluble CD8 antigen in active rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Oct;57(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90023-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Kassab A. S., Raziuddin S. Immune activation and T cell subset abnormalities in circulation of patients with recently diagnosed type I diabetes mellitus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):267–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


