Abstract
The NOD mouse is a model of human juvenile type I diabetes mellitus. As in humans and in the BB rat model, the development of diabetes in NOD mice is accompanied by evident manifestations of cell-mediated and humoral autoimmunity. Beside autoantibodies directed at putative islet cell antigens, NOD sera contain antibodies with specificity for lymphocyte cell-surface determinants. Here we demonstrate that these anti-lymphocyte antibodies have the same characteristics of target cell specificity, of isotype, and of temperature reactivity, as do natural thymocytotoxic autoantibodies (NTA) from lupic NZB mice, or from mice undergoing polyclonal B cell activation. We also demonstrate that the thymocytotoxic activity of NOD sera is not due to cross-reactive anti-insulin antibodies. Biochemical characterization of the determinants recognized by these anti-lymphocyte antibodies reveals two membrane-associated proteins of 28 and 33 kD, partially similar to the two peptides recognized by NTA from NZB mice (30 and 33 kD). Altogether, these results suggest that NOD mice develop manifestations of polyclonal B cell activation similar to those observed in lupus-prone mice. The relationship of these anomalies with the organ-specific pancreatic disease remains to be properly evaluated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado M. T., Balderas R. S., Rubin R. L., Duchosal M. A., Kofler R., Birshtein B. K., Secher D. S., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Specificity and molecular characteristics of monoclonal IgM rheumatoid factors from arthritic and non-arthritic mice. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1080–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A., Carnaud C., Boitard C., Bach J. F. Syngeneic transfer of autoimmune diabetes from diabetic NOD mice to healthy neonates. Requirement for both L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):823–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boitard C., Bach J. F. Cell-mediated versus humoral immunity in autoimmune diseases and their pharmacologic control with particular reference to type I diabetes mellitus. Concepts Immunopathol. 1986;3:193–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Peake P., Campbell L. V., Rumma J., Pussell B. A., Howard N., Elder G. J. Detection of lymphocytotoxic antibodies in relatives of patients with type I diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Feb 1;292(6516):292–294. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6516.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Holmberg D., Lundquist I., Coutinho A., Avrameas S. High frequency of natural autoantibodies in normal newborn mice. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrberg T., Poussier P., Nakhooda F., Marliss E. B., Lernmark A. Islet cell surface and lymphocyte antibodies often precede the spontaneous diabetes in the BB rat. Diabetologia. 1984 Feb;26(2):159–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00281126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M., Feng H. M., Engers H., Hochman A., Louis J., Lambert P. H. Autoimmunity and immune complex disease after neonatal induction of transplantation tolerance in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa Y., Komeda K., Sato S., Mori S., Akanuma K., Takaku F. Non-obese-diabetic mice: immune mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell destruction. Diabetologia. 1984 Jul;27 (Suppl):113–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00275663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
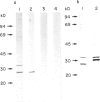
- Lehuen A., Carnaud C. Characterization of two molecules at 30,33 kDa as major target antigens of natural thymocytotoxic autoantibodies. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., McHugh L. L., Rothstein T. L. Mouse lymphocytes with and without surface immunoglobulin: preparative scale separation in polystyrene tissue culture dishes coated with specifically purified anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Kunimoto K., Muraoka Y., Mizushima Y., Katagiri K., Tochino Y. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Jikken Dobutsu. 1980 Jan;29(1):1–13. doi: 10.1538/expanim1978.29.1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. S., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Murine leukaemogenesis: monoclonal antibodies to T-cell determinants arrest T-lymphoma cell proliferation. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):259–261. doi: 10.1038/285259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel C., Boitard C., Bach J. F. Insulin autoantibodies in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Mar;75(3):457–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. J., Appel M. C., O'Neil J. J., Wicker L. S. Both the Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ T cell subsets are required for the transfer of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Distaso J. A., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus T cell subsets, anti-T cell antibodies, and T cell functions. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):689–700. doi: 10.1172/JCI111261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontesilli O., Carotenuto P., Gazda L. S., Pratt P. F., Prowse S. J. Circulating lymphocyte populations and autoantibodies in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice: a longitudinal study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):84–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Saegusa J., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Lymphocytes capable of making monoclonal autoantibodies that react with multiple organs are a common feature of the normal B cell repertoire. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2815–2817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S., Theophilus J., Zimmet P., Court J., Crossley J. R., Elliott R. B. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies and histocompatibility antigens in juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):26–29. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural cytotoxic autoantibody against thymocytes in NZB mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):133–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Zamir R., Joshua H., Lavie G., Pinkhas J. Human monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies react as lymphocytotoxic antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Oct;15(10):1024–1028. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin T., Nicholson S., Casey C. A micro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for insulin antibodies in serum. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokono K., Shii K., Hari J., Yaso S., Imamura Y., Ejiri K., Ishihara K., Fujii S., Kazumi T., Taniguchi H. Production of monoclonal antibodies to islet cell surface antigens using hybridization of spleen lymphocytes from non-obese diabetic mice. Diabetologia. 1984 May;26(5):379–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00266041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen J. P., Rolink A. G., Gleichmann E. Diseases caused by reactions of T lymphocytes to incompatible structures of the major histocompatibility complex. III. Autoantibodies to thymocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1281–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]