Abstract
Interleukin-5 (IL-5) has previously been demonstrated to enhance immunoglobulin synthesis, especially IgA. Thus, it could be hypothesized that a defect production of IL-5 may cause immunoglobulin deficiency. We have analysed the frequency of IL-5 mRNA-producing cells in healthy adults and in patients with common variable immunodeficiency or selective IgA deficiency. Unstimulated lymphocytes were rarely found to synthesize IL-5 as measured by in situ hybridization. However, pokeweed mitogen and several other activating ligands induced the synthesis of IL-5 mRNA in peripheral blood and spleen lymphocyte cultures. After pokeweed mitogen activation, the number of IL-5 mRNA-producing cells most often peaked on day 3 with a maximal frequency of around 1-2% of mononuclear cells. In a kinetic study we were unable to detect any peak frequency differences between healthy controls (mean 0.44%) and 20 patients (mean 0.58%). Thus, although IL-5 has been reported to be an important regulator of IgA synthesis, a defect production does not seem to be the underlying mechanism in human immunoglobulin deficiency.
Full text
PDF
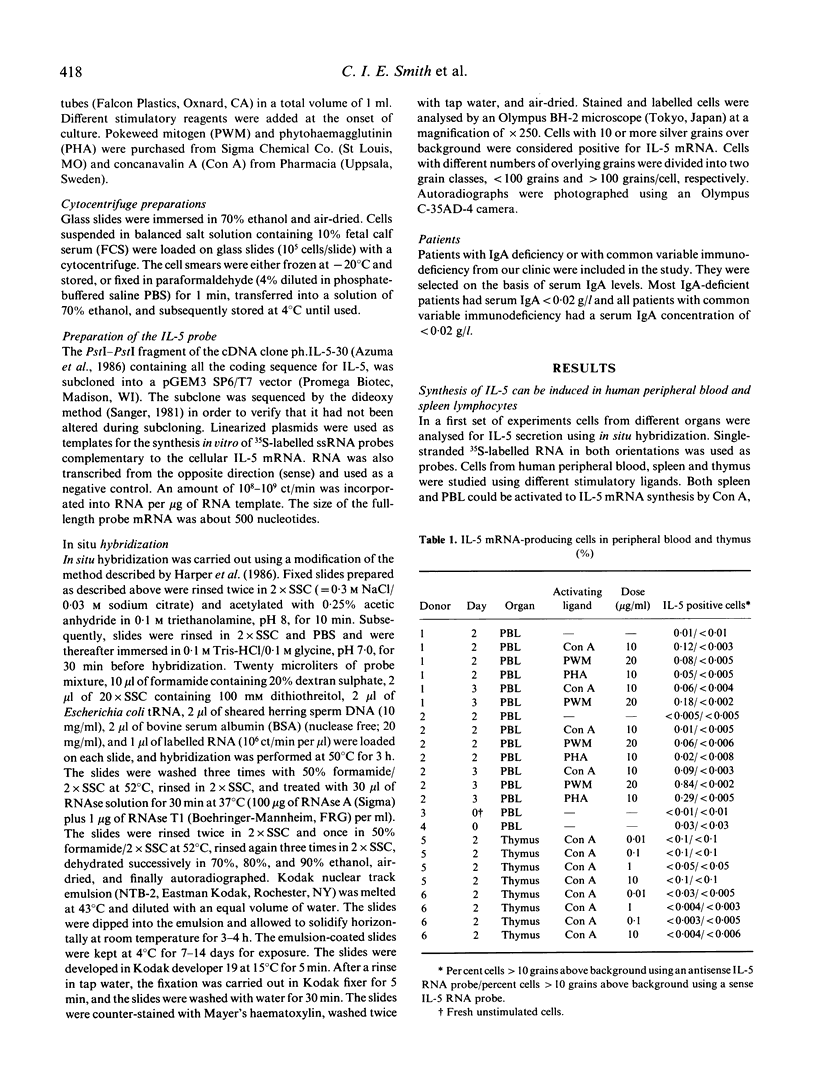
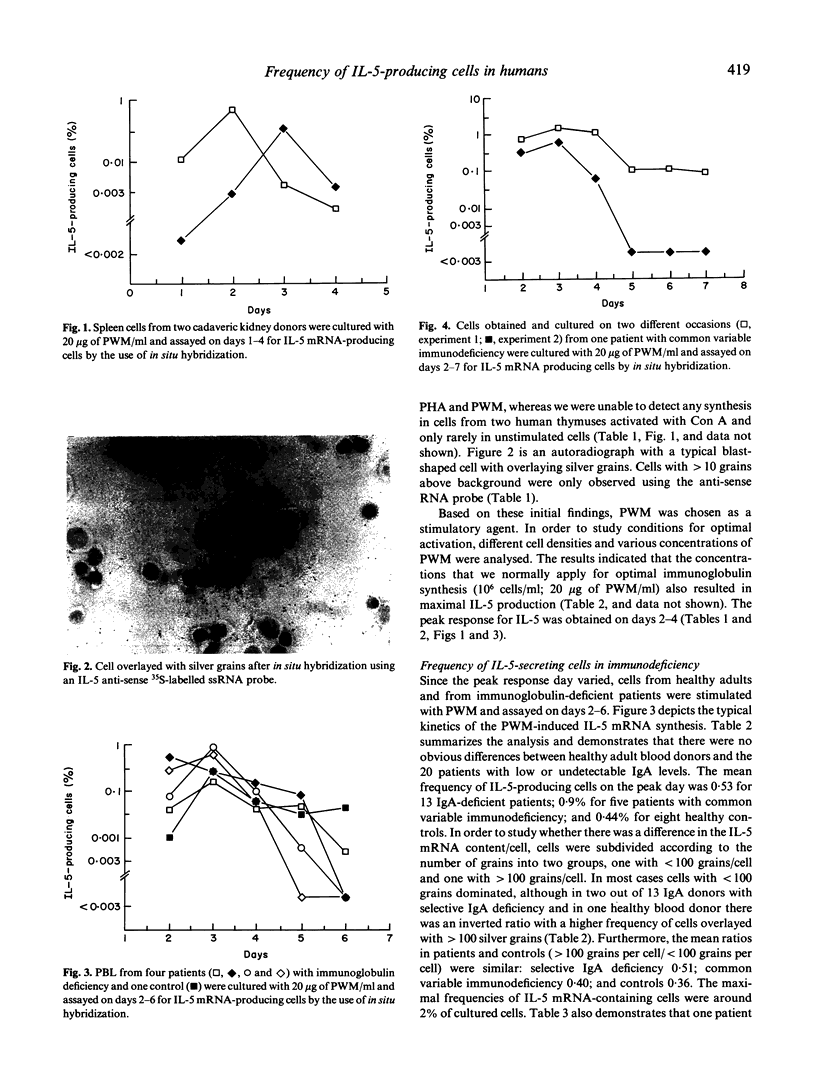
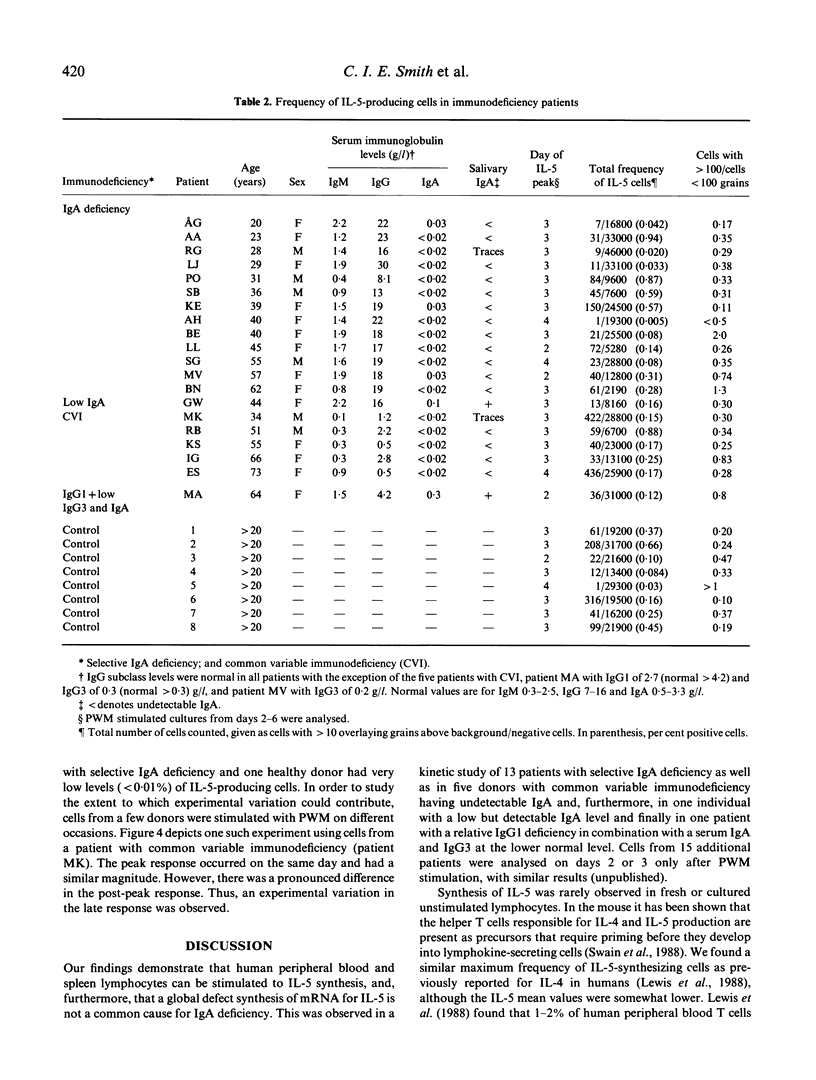


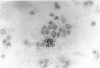
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma C., Tanabe T., Konishi M., Kinashi T., Noma T., Matsuda F., Yaoita Y., Takatsu K., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. Cloning of cDNA for human T-cell replacing factor (interleukin-5) and comparison with the murine homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9149–9158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Kiyono H., Everson M. P., Koopman W. J., Honjo T., McGhee J. R. Recombinant murine IL-5 induces high rate IgA synthesis in cycling IgA-positive Peyer's patch B cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Lee F., Kiyono H., Everson M. P., Koopman W. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., McGhee J. R. Interleukins and IgA synthesis. Human and murine interleukin 6 induce high rate IgA secretion in IgA-committed B cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2133–2148. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrant J., Bryant A., Almandoz F., Spickett G., Evans S. W., Webster A. D. B cell function in acquired "common-variable" hypogammaglobulinemia: proliferative responses to lymphokines. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 May;51(2):196–204. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G., Doenhoff M. Selective triggering of human T and B lymphocytes in vitro by polyclonal mitogens. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., de Lange G. G., Smith C. I. IgA2 allotypes determined by restriction fragment length polymorphism in IgA deficiency. Re-expression of the silent A2m(2) allotype in the children of IgA-deficient patients. J Immunogenet. 1987 Aug-Oct;14(4-5):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1987.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Detection of lymphocytes expressing human T-lymphotropic virus type III in lymph nodes and peripheral blood from infected individuals by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harriman G. R., Kunimoto D. Y., Elliott J. F., Paetkau V., Strober W. The role of IL-5 in IgA B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3033–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi T., Harada N., Severinson E., Tanabe T., Sideras P., Konishi M., Azuma C., Tominaga A., Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., Takahashi M. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding T-cell replacing factor and identity with B-cell growth factor II. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):70–73. doi: 10.1038/324070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Lefranc G., Rabbitts T. H. Inherited deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes in normal human individuals. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):760–762. doi: 10.1038/300760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Sanderson C. J., Gamble J. R., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is a selective activator of human eosinophil function. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):219–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Harada N., Naomi S., Hitoshi Y., Sakamoto K., Akagi M., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Receptors for T cell-replacing factor/interleukin 5. Specificity, quantitation, and its implication. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):863–878. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Wideman J., Bonnefoy J. Y., De Vries J. E. Interleukin 5 enhances interleukin 4-induced IgE production by normal human B cells. The role of soluble CD23 antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):929–935. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular and cellular biology of eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin-5) and its effects on human and mouse B cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.7302589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Funa K., Zalcberg-Quintana I., Xanthopoulos K. G., Kisielow P., Palacios R. Analysis by in situ hybridization of cells expressing mRNA for interleukin 4 in the developing thymus and in peripheral lymphocytes from mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):218–221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. I., Hammarström L. Cellular basis of immunodeficiency. Ann Clin Res. 1987;19(4):220–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. I., Hammarström L., Henter J. I., de Lange G. G. Molecular and serologic analysis of IgG1 deficiency caused by new forms of the constant region of the Ig H chain gene deletions. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4514–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Radcliffe G., Lin Y. C., Nietupski J., Berggren L., Sitia R., Severinson E. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain switching may be directed by prior induction of transcripts from constant-region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7704–7708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E., Callen D. F., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Sanderson C. J., Garson O. M., Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A. Interleukin-5 is at 5q31 and is deleted in the 5q- syndrome. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1150–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., McKenzie D. T., Weinberg A. D., Hancock W. Characterization of T helper 1 and 2 cell subsets in normal mice. Helper T cells responsible for IL-4 and IL-5 production are present as precursors that require priming before they develop into lymphokine-secreting cells. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3445–3455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Kikuchi Y., Takahashi T., Honjo T., Matsumoto M., Harada N., Yamaguchi N., Tominaga A. Interleukin 5, a T-cell-derived B-cell differentiation factor also induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4234–4238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Tominaga A., Harada N., Mita S., Matsumoto M., Takahashi T., Kikuchi Y., Yamaguchi N. T cell-replacing factor (TRF)/interleukin 5 (IL-5): molecular and functional properties. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:107–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu D. T., Jabara H. H., DeKruyff R. H., Abbas A. K., Abrams J. S., Geha R. S. Functional heterogeneity among human inducer T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4211–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Coffman R. L., Hagiwara H., Rennick D. M., Takebe Y., Yokota K., Gemmell L., Shrader B., Yang G., Meyerson P. Isolation and characterization of lymphokine cDNA clones encoding mouse and human IgA-enhancing factor and eosinophil colony-stimulating factor activities: relationship to interleukin 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7388–7392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]