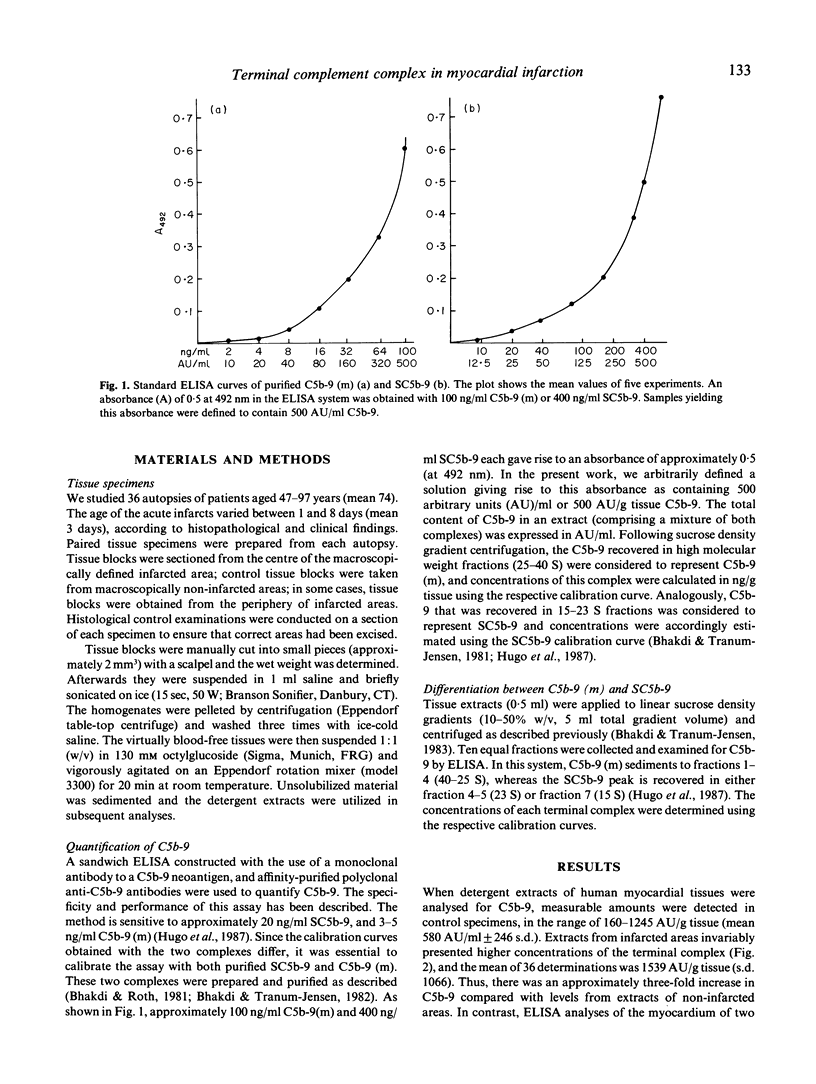
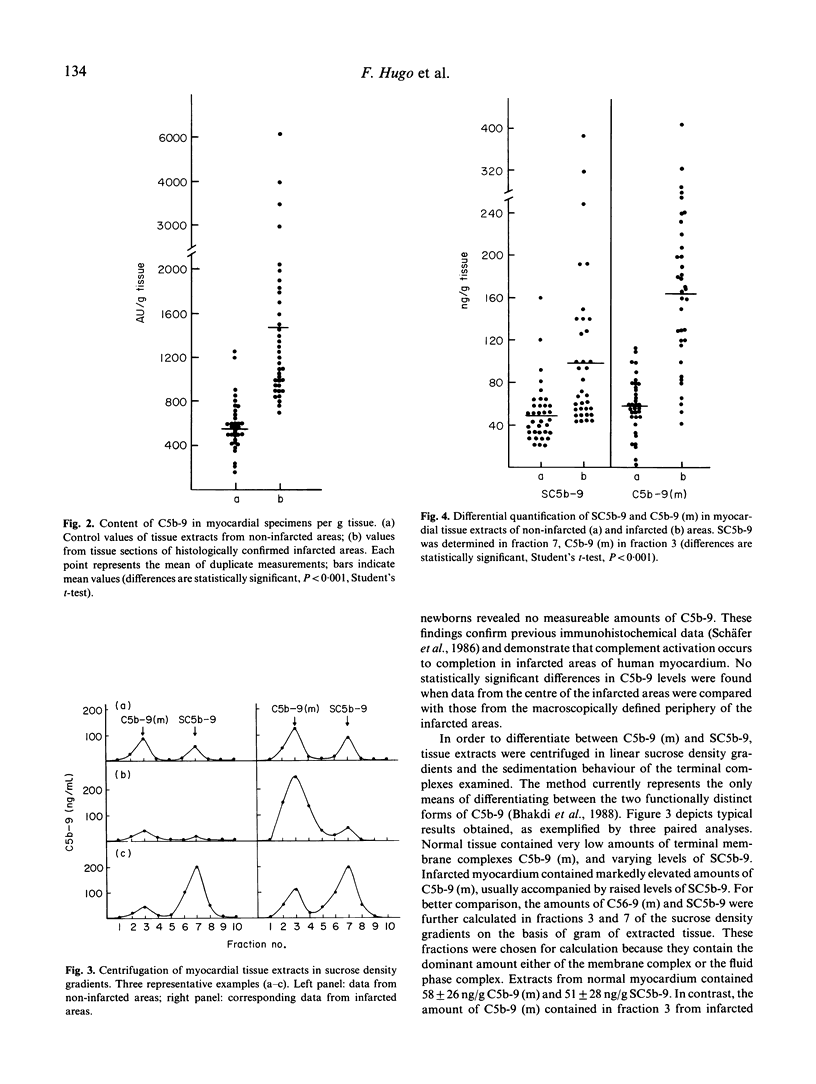
Abstract
Previous immunohistochemical work has indicated that terminal C5b-9 complement complexes are selectively deposited in infarcted areas of human myocardium. In the present study, we sought to quantify C5b-9 levels in myocardial tissue, and to differentiate between the membrane-bound C5b-9 (m) and the cytolytically inactive SC5b-9 complex. Paired tissue specimens from infarcted and non-infarcted myocardium were obtained from 36 autopsies. The homogenized and washed tissues were extracted with n-octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (octylglucoside) detergent, and the concentrations of C5b-9 in the extracts were determined by ELISA. Membrane-derived C5b-9 (m) and SC5b-9 were differentiated from each other on the basis of their characteristic sedimentation behaviour in sucrose density gradients. It was found that infarcted myocardial tissue contained on average an approximately three-fold higher concentration of C5b-9, compared with non-infarcted tissue. This increase was due in part to an increase in levels of C5b-9 (m). The results corroborate previous immunohistochemical data and show that complement activation occurs to completion with the generation of potentially cytotoxic C5b-9 complexes in infarcted myocardial tissues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Bjerrum O. J., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Tranum-Jensen J. Complement lysis: evidence for an amphiphilic nature of the terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2526–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Käflein R., Halstensen T. S., Hugo F., Preissner K. T., Mollnes T. E. Complement S-protein (vitronectin) is associated with cytolytic membrane-bound C5b-9 complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Dec;74(3):459–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M. A simple immunoradiometric assay for the terminal SC5b-9 complex of human complement. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Roth M. Fluid-phase SC5b-8 complex of human complement: generation and isolation from serum. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by complement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):343–372. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular weight of the membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: characterization of the terminal complex as a C5b-9 monomer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1818–1822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: transition from an amphiphilic to a hydrophilic state through binding of the S protein from serum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):755–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. K., Daw R. A., Hallett M. B., Luzio J. P. Direct measurement of the increase in intracellular free calcium ion concentration in response to the action of complement. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):551–560. doi: 10.1042/bj1940551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. K., Daw R. A., Luzio J. P. Rapid increase in intracellular free Ca2+ induced by antibody plus complement. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Human C5a and C5a analogs as probes of the neutrophil C5a receptor. Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Jenne D., Bhakdi S. Monoclonal antibodies against neoantigens of the terminal C5b-9 complex of human complement. Biosci Rep. 1985 Aug;5(8):649–658. doi: 10.1007/BF01116996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Krämer S., Bhakdi S. Sensitive ELISA for quantitating the terminal membrane C5b-9 and fluid-phase SC5b-9 complex of human complement. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 20;99(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Neoantigens of the membrane attack complex of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1687–1689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroko P. R., Carpenter C. B., Chiariello M., Fishbein M. C., Radvany P., Knostman J. D., Hale S. L. Reduction by cobra venom factor of myocardial necrosis after coronary artery occlusion. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):661–670. doi: 10.1172/JCI108978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):159–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Lea T., Harboe M., Tschopp J. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing a neoantigen of poly(C9) detect the human terminal complement complex in tissue and plasma. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):183–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Olson M. S., Giclas P. C., Terry R., Boyer J. T., O'Rourke R. A. Consumption of classical complement components by heart subcellular membranes in vitro and in patients after acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):740–750. doi: 10.1172/JCI108145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Olson M. S., Kelley R. E., DeHeer D. H., Palmer J. D., O'Rourke R. A., Goldfein S. Antibody-independent activation of human C1 after interaction with heart subcellular membranes. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1376–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer H., Mathey D., Hugo F., Bhakdi S. Deposition of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex in infarcted areas of human myocardium. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1945–1949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Suttorp N., Hellwig A., Bhakdi S. Noncytolytic terminal complement complexes may serve as calcium gates to elicit leukotriene B4 generation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs S. B., Kolb W. P., Pinckard R. N., Olson M. S. Characterization of the binding of purified human C1q to heart mitochondrial membranes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10924–10929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


