Abstract
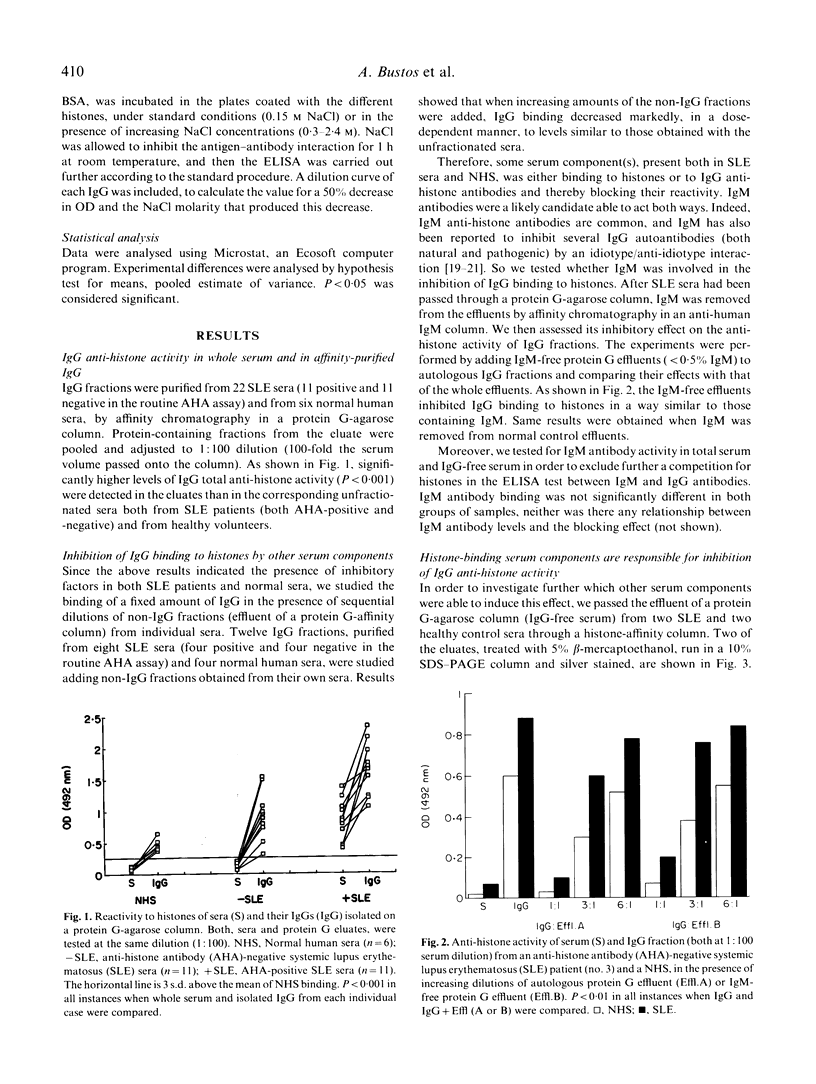
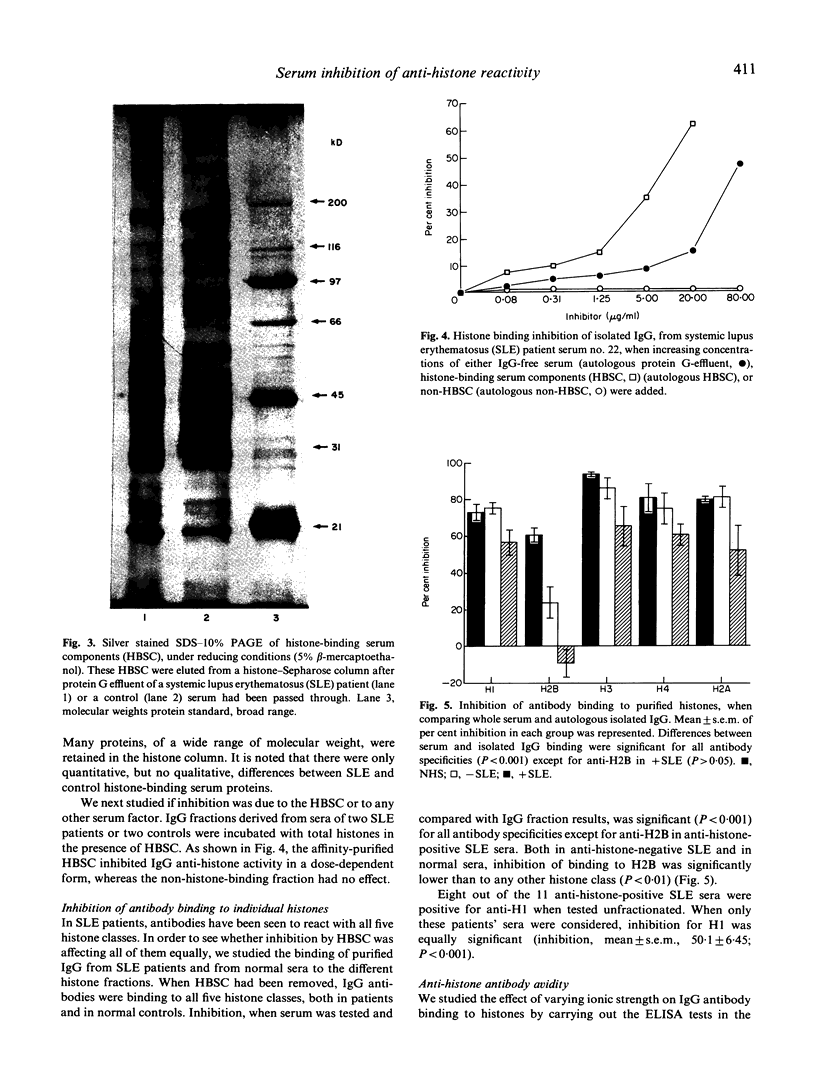
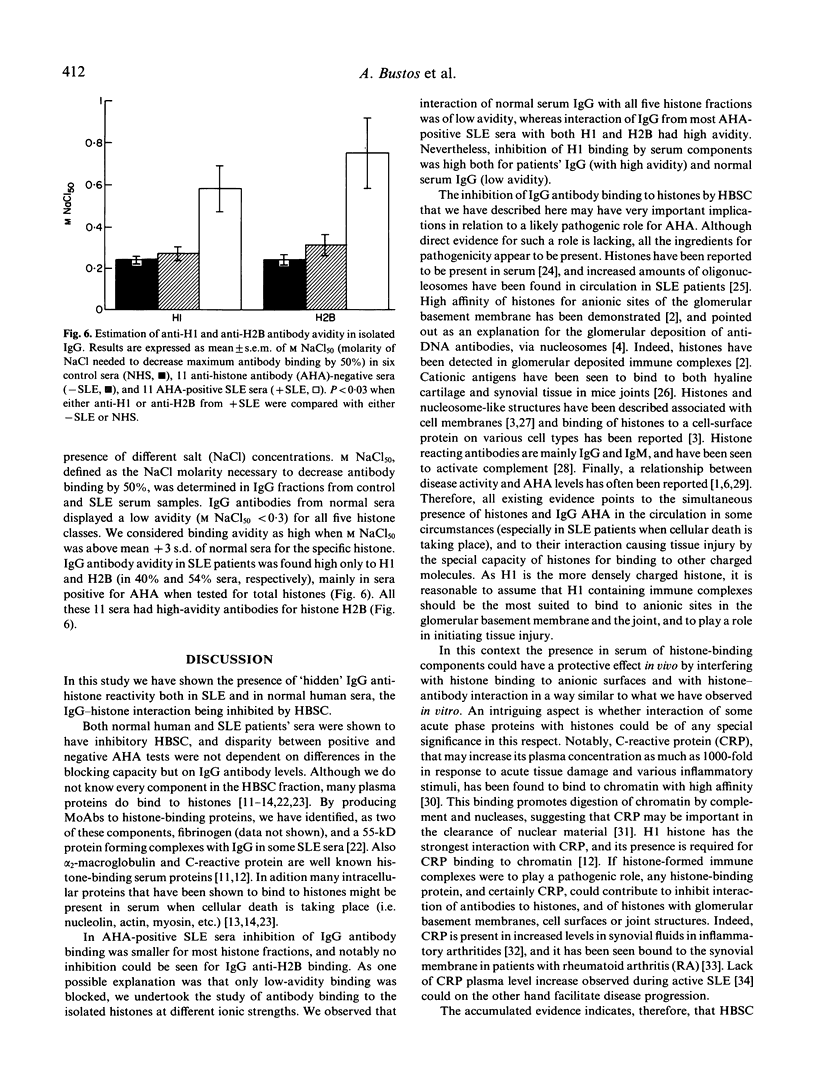
IgG fractions were purified on a protein G-agarose column from sera of both systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and healthy donors. All IgG fractions, after elution with 0.5 M acetic acid, reacted with histones in an anti-histone ELISA assay, and IgG anti-histone activity was in all instances higher in the IgG fraction than in the corresponding whole serum. This was shown to be due to the presence in serum of histone-binding components that inhibited IgG binding to histones. Both normal human and SLE patients' sera had these histone-binding components, and disparity between serum-positive and -negative anti-histone antibody (AHA) tests was not dependent on differences in the blocking capacity but on IgG antibody levels and avidity. Interaction of normal serum IgG fraction with all five histones was of low avidity, whereas interaction of IgG from AHA-positive SLE sera with both H1 and H2B had high avidity. Low-affinity antibodies to every histone fraction, but also high-affinity anti-H1 antibodies, were preferentially inhibited. Our data indicate that several serum protein components are inhibiting histone/anti-histone interaction and may play a protective role against both high-affinity anti-H1 antibodies present in SLE patients, and natural, low-affinity, anti-histone antibodies. As some acute phase proteins, notably C-reactive protein, bind to histones, it is conceivable that they play such a role. High-affinity anti-H2B antibodies, present in some SLE patients, and not inhibited by these serum components, may, on the other hand, participate in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adib M., Ragimbeau J., Avrameas S., Ternynck T. IgG autoantibody activity in normal mouse serum is controlled by IgM. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3807–3813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batsford S. R. Cationic antigens as mediators of inflammation. APMIS. 1991 Jan;99(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Hobbs R. N., Lea D. J., Ward D. J., Hughes G. R. Patterns of antihistone antibody specificity in systemic rheumatic disease. I Systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease, primary sicca syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Mar;28(3):285–293. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman K., Termaat R., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Anti-DNA antibodies and lupus nephritis: the complexity of crossreactivity. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):232–234. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90095-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Lehn D. A., Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90092-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caturla A., Colome J. A., Bustos A., Chamorro M. J., Figueredo M. A., Subiza J. L., de la Concha E. G. Occurrence of antibodies to protease-treated histones in a patient with vasculitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jul;60(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90112-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Zlock L. T., Marnell L. Definition of a C-reactive protein binding determinant on histones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2167–2171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard M. S., Belenguer P., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Pantaloni A., Amalric F. A major nucleolar protein, nucleolin, induces chromatin decondensation by binding to histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Antibodies to histones in drug-induced and idiopathic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):560–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI109161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioud M., Kaci M. A., Monier J. C. Histone antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. A possible diagnostic tool. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):407–413. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin J. D., Gitlin J. I., Gitlin D. Localizing of C-reactive protein in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1491–1499. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröschel-Stewart U., Heurich P., Stewart D. I., Golosinska K., Smillie L. B. Non-specific interactions of histones with serum components and contractile proteins. Biochem Int. 1986 Dec;13(6):927–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holers V. M., Kotzin B. L. Human peripheral blood monocytes display surface antigens recognized by monoclonal antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):991–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI112100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Viard J. P., Allenet B., Anin M. F., Slama F. B., Vandekerckhove J., Primo J., Markovits J., Jacob F., Bach J. F. A monoclonal anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody binds to a 94-kDa cell-surface protein on various cell types via nucleosomes or a DNA-histone complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda S., Kanayama Y., Okamura M., Amatsu K., Negoro N., Takeda T., Inoue T. Clinical significance of antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jan;16(1):24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinov K., Russanova V., Russeva V. Antibodies to histones and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparative study with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblotting. Arch Dermatol Res. 1986;278(5):410–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00418172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Barakat S., Watts R., Joubaud P., Isenberg D. Longitudinal analysis of antibodies to histones, Sm-D peptides and ubiquitin in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and tuberculosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Sep-Oct;8(5):445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Lanham J. G., De Beer F. C. C-reactive protein in SLE. Clin Rheum Dis. 1982 Apr;8(1):91–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Arndt R. E., Tan E. M., Kotzin B. L. Anti-histone antibodies in idiopathic and drug-induced lupus recognize distinct intrahistone regions. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Jones K. D., Steinberg A. D. C-reactive protein mediates the solubilization of nuclear DNA by complement in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1344–1356. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Jayne D. R., Lockwood C. M., Kazatchkine M. D. Anti-idiotypes against anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antigen autoantibodies in normal human polyspecific IgG for therapeutic use and in the remission sera of patients with systemic vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):298–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Joslin F. G., Tan E. M. Specificity of anti-histone antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):779–782. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumore P. M., Steinman C. R. Endogenous circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence as multimeric complexes bound to histone. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):69–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI114716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T. M., Stöckl F. W., Weber R., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Histones have high affinity for the glomerular basement membrane. Relevance for immune complex formation in lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1879–1894. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. R., Arnold P. I. Properties of four acute phase proteins: C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A protein, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, and fibrinogen. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;20(3):129–147. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(90)90055-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R. J., Brinkman K., van den Brink H. G., Westgeest A. A. Reaction patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3786–3792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Rezuke W. Separation of anti-histone antibodies from nonimmune histone-precipitating serum proteins, predominantly alpha2-macroglobulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subiza J. L., Caturla A., Pascual-Salcedo D., Chamorro M. J., Gazapo E., Figueredo M. A., de la Concha E. G. DNA-anti-DNA complexes account for part of the antihistone activity found in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Apr;32(4):406–412. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subiza J. L., Caturla A., Pereira L. F., Camargo M. C., Bustos A., Boimorto R., de la Concha E. G. Evidence that a putative anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody may actually be recognizing circulating immune complexes. J Autoimmun. 1992 Jun;5(3):363–377. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90149-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukenik S., Henkin J., Zimlichman S., Skibin A., Neuman L., Pras M., Horowitz J., Shainkin-Kestenbaum R. Serum and synovial fluid levels of serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein in inflammatory and noninflammatory arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jun;15(6):942–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Bleux C., Gregoire J., Avrameas S., Kanellopoulos-Langevin C. Comparison between autoantibodies arising during Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice and natural autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1504–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triolo G., Giardina E., Scarantino G., Seddio G., Cardella F., Meli F., Bompiani G. Cross-reactivity of anti-ssDNA antibodies with heparan sulfate in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):718–722. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Tan E. M., Rubin R. L. Identification and isolation of soluble histones from bovine milk and serum. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):675–682. doi: 10.1042/bj2440675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., Joosten L. A. Electrical charge of the antigen determines intraarticular antigen handling and chronicity of arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1850–1859. doi: 10.1172/JCI111604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]