Abstract
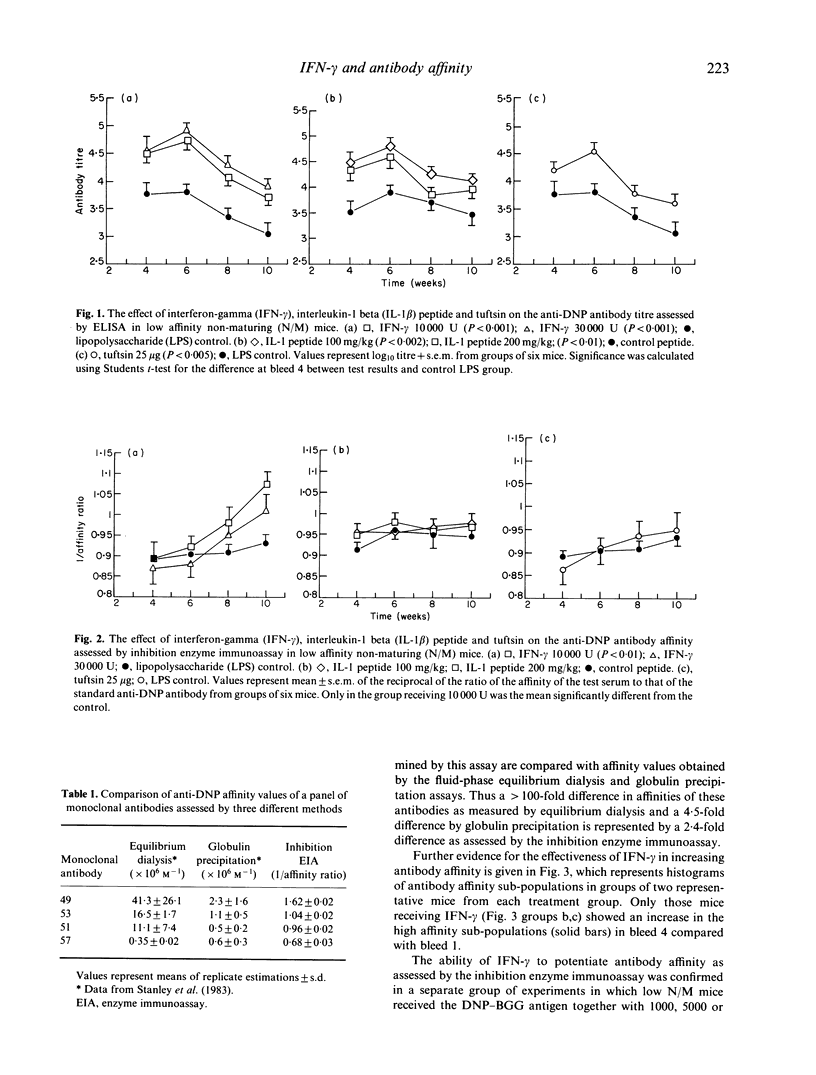
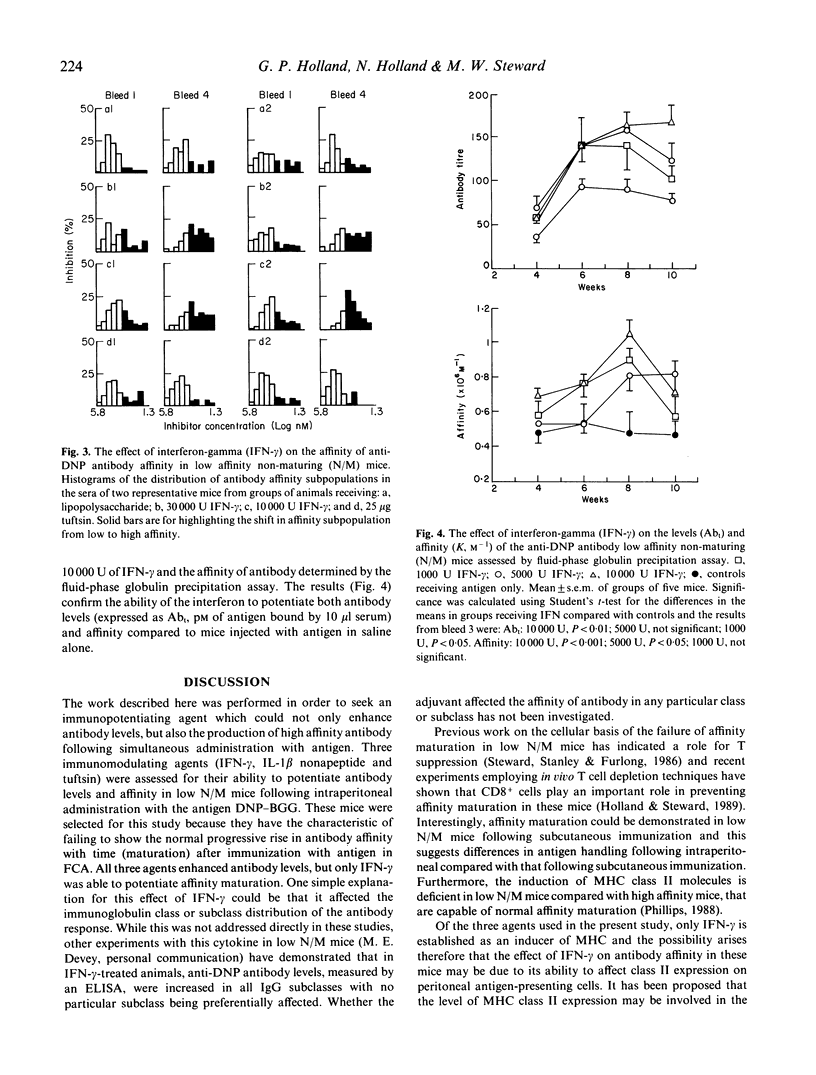
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), the tetrapeptide tuftsin and the synthetic nonapeptide from interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) (amino acids 163-171) have previously been shown to act on macrophages and/or T cells and to enhance antibody titres to T cell-dependent antigens. The ability of these immunomodulatory agents to potentiate antibody affinity in addition to antibody titre has been studied in a line of mice that fail to demonstrate normal maturation of antibody affinity (low N/M mice). The results presented here confirm that each of the agents potentiate antibody levels following simultaneous injection with a T cell-dependent antigen but demonstrate that only IFN-gamma is able to enhance antibody affinity in these mice. The observation that IFN-gamma can enhance both antibody affinity and antibody levels suggests that it could be an important adjuvant for vaccine use.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoni G., Presentini R., Perin F., Tagliabue A., Ghiara P., Censini S., Volpini G., Villa L., Boraschi D. A short synthetic peptide fragment of human interleukin 1 with immunostimulatory but not inflammatory activity. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3201–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Volpini G., Villa L., Nencioni L., Scapigliati G., Nucci D., Antoni G., Matteucci G., Cioli F., Tagliabue A. A monoclonal antibody to the IL-1 beta peptide 163-171 blocks adjuvanticity but not pyrogenicity of IL-1 beta in vivo. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):131–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braley-Mullen H. Regulatory role of T cells in IgG antibody formation and immune memory to type III Pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1909–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale K., Stanley C., Steward M. W. Failure of affinity maturation leads to increased susceptibility to immune complex glomerulonephritis. Immunology. 1984 Jun;52(2):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasca D., Boraschi D., Baschieri S., Bossu P., Tagliabue A., Adorini L., Doria G. In vivo restoration of T cell functions by human IL-1 beta or its 163-171 nonapeptide in immunodepressed mice. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2651–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland G. P., Steward M. W. Antibody affinity maturation: the role of CD8+ cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):488–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. E., Steward M. W. The genetic control of antibody affinity in mice. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):543–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M. The effect of epitope density and antibody affinity on the ELISA as analysed by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J. M., King D. P., Jones P. P. Biosynthesis and expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on a macrophage cell line are stimulated by products of activated spleen cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):449–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Ben-Zvi A. Studies on the role of lymphocyte-activating factor (Interleukin 1) in antigen-induced lymph node lymphocyte proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Manser T., Pearson G. D., Daley M. J., Gefter M. L. Effect of IFN-gamma on the immune response in vivo and on gene expression in vitro. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):381–382. doi: 10.1038/307381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Villa L., Tagliabue A., Antoni G., Presentini R., Perin F., Silvestri S., Boraschi D. In vivo immunostimulating activity of the 163-171 peptide of human IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):800–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. The heterogeneity of antibody affinity in inbred mice and its possible immunopathologic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W. The effect of immunological adjuvants on the relative affinity of anti-protein antibodies. Immunology. 1977 Jan;32(1):49–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Germain R. N. Antigen-specific T cell-mediated suppression. IV. Role of macrophages in generation of L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 (GAT)-specific suppressor T cells in responder mouse strains. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1306–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath S., Stanley C. M., Steward M. W. An inhibition enzyme immunoassay for estimating relative antibody affinity and affinity heterogeneity. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh-Nasseri S., Dessi V., Sercarz E. E. Selective reversal of H-2-linked genetic unresponsiveness to lysozymes. II. Alteration in the T helper/T suppressor balance, owing to gene(s) linked to Ir-2, leads to responsiveness in BALB.B. Eur J Immunol. 1986 May;16(5):486–492. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri N., Kawahara D. J., Miller A., Sercarz E. E. Antigen-specific T helper clones in a nonresponder strain require augmentation for expression of helper activity. Evidence for a possible antigen presentation defect in B cells. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1215–1221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Shultz L. D., Gray P. W., Johnson H. M. Gamma-interferon is one of several direct B cell-maturing lymphokines. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):801–804. doi: 10.1038/309801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C., Lew A. M., Steward M. W. The measurement of antibody affinity: a comparison of five techniques utilizing a panel of monoclonal anti-DNP antibodies and the effect of high affinity antibody on the measurement of low affinity antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90390-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W. Immunopathological mechanisms in the induction of parasitic diseases with particular reference to type III hypersensitivity reactions. Parasitology. 1987;94 (Suppl):S139–S158. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000085863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Stanley C., Furlong M. D. Antibody affinity maturation in selectively bred high and low-affinity mice. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):59–63. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


