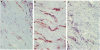
Abstract
Immunoperoxidase staining of skin sections obtained from 11 hypertrophic scars, six normotrophic scars and three samples of normal skin were performed using anti-HLA monoclonal antibodies (HLA-DR, -DQ, class I), anti-interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) and anti-CD1. Sections from all hypertrophic scars showed an anomalous expression of HLA-DR molecules on keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Moreover hypertrophic scars were characterized by dense infiltrates of IL-2R-positive cells and by the presence of abundant Langerhans (CD1+) cells in the epidermis and dermis. These results support the hypothesis that immunologic mechanisms play an important role in hypertrophic scarring and point to an involvement of cell-mediated immune phenomena.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloch E. F., Hall M. G., Jr, Denson M. J., Slay-Solomon V. General immune reactivity in keloid patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984 Mar;73(3):448–451. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198403000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepaldi T., Fasano M. E., Frattasio C., Centis D., Curtoni E. S., Richiardi P. Identification of anti-DQ alloantisera correlated with DR5. J Immunogenet. 1985 Dec;12(6):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernielewski J. M., Bagot M. Class II MHC antigen expression by human keratinocytes results from lympho-epidermal interactions and gamma-interferon production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernielewski J. M. Mixed skin cell-lymphocyte culture reaction (MSLR) as a model for the study of lympho-epidermal interactions. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Jul;113 (Suppl 28):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb15622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen de Limpens A. M., Cormane R. H. Studies on the immunologic aspects of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Arch Dermatol Res. 1982;274(3-4):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00403728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchum L. D., Cohen I. K., Masters F. W. Hypertrophic scars and keloids. A collective review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1974 Feb;53(2):140–154. doi: 10.1097/00006534-197402000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischer C. W., Shetlar M. R., Shetlar C. L., Chvapil M. Immunoglobulins in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983 Jun;71(6):821–825. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198306000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A. Expression of HLA-DR (Ia like) antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in human dermatoses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):93–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecchi M., Lovisone E., Genetta C., Peruccio D., Resegotti L., Richiardi P. Gamma-IFN induces a differential expression of HLA-DR, DQ and DP antigens on peripheral blood myeloid leukemic blasts at various stages of differentiation. Leuk Res. 1989;13(3):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(89)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei M., Lamb J. R., Bottazzo G. F., Feldmann M. Epithelial cells expressing aberrant MHC class II determinants can present antigen to cloned human T cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):639–641. doi: 10.1038/312639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavasi F., Milanese C., Fabbi M., Richiardi P., Caligaris-Cappio F., Ferrero E., Roggero S., Dellabona P., Ceppellini R. Generation and characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies against HLA Class II molecules. Diagn Immunol. 1984;2(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. S., Deitch E. A. Hypertrophic skin grafts in burned patients: a prospective analysis of variables. J Trauma. 1987 Feb;27(2):147–150. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198702000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., Segatto O., Ferrone S., Tosi R., Corte G. Differential tissue distribution and ontogeny of DC-1 and HLA-DR antigens. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(2):109–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00387853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P., Bigotti A., Cavalieri R., Nicotra M. R., Tecce R., Manfredi D., Chen Y. X., Nadler L. M., Ferrone S. Gene products of the HLA-D region in normal and malignant tissues of nonlymphoid origin. Hum Immunol. 1986 Feb;15(2):220–233. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quismorio F. P., Bland S. L., Friou G. J. Autoimmunity in thermal injury: occurrence of rheumatoid factors, antinuclear antibodies and antiepithelial antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):701–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radka S. F., Charron D. J., Brodsky F. M. Class II molecules of the major histocompatibility complex considered as differentiation markers. Hum Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(4):390–400. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakespeare P. G., van Renterghem L. Some observations on the surface structure of collagen in hypertrophic scars. Burns Incl Therm Inj. 1985 Feb;11(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0305-4179(85)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volc-Platzer B., Majdic O., Knapp W., Wolff K., Hinterberger W., Lechner K., Stingl G. Evidence of HLA-DR antigen biosynthesis by human keratinocytes in disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1784–1789. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Hála K., Wolf H., Ziemiecki A., Sundick R. S., Stöffler-Meilicke M., DeBaets M. The role of genetically-determined primary alterations of the target organ in the development of spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis in obese strain (OS) chickens. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:113–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]