Abstract
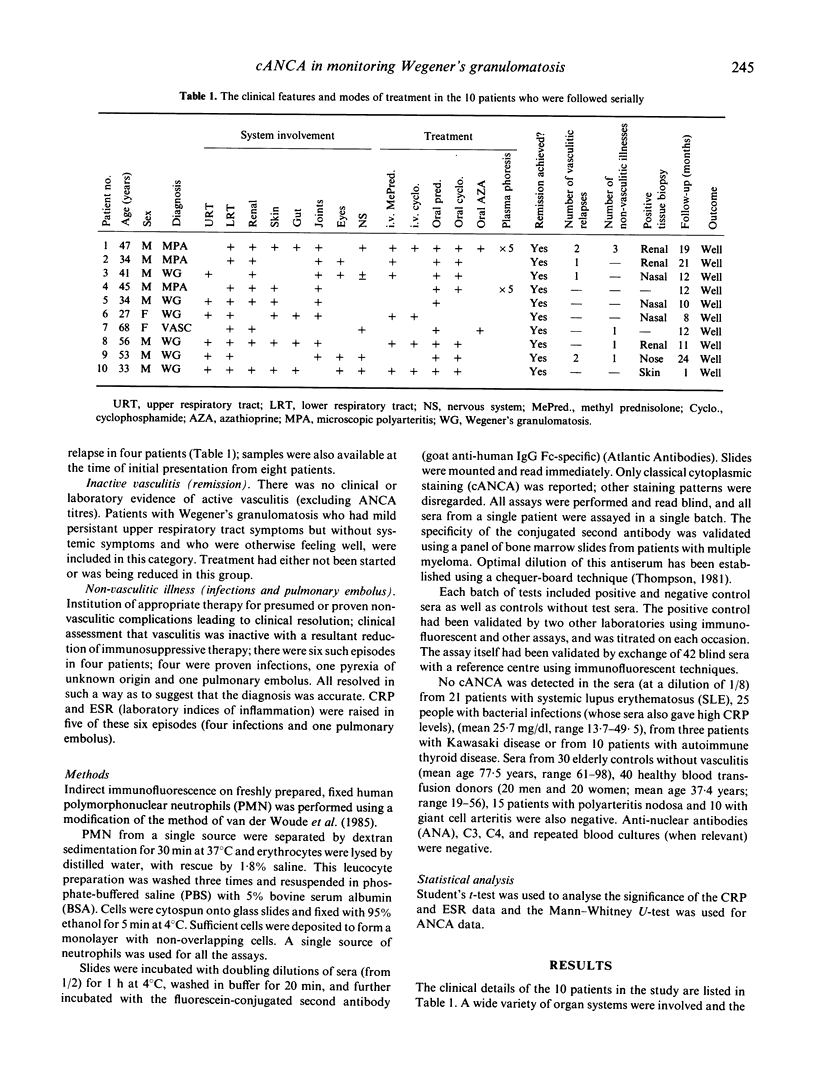
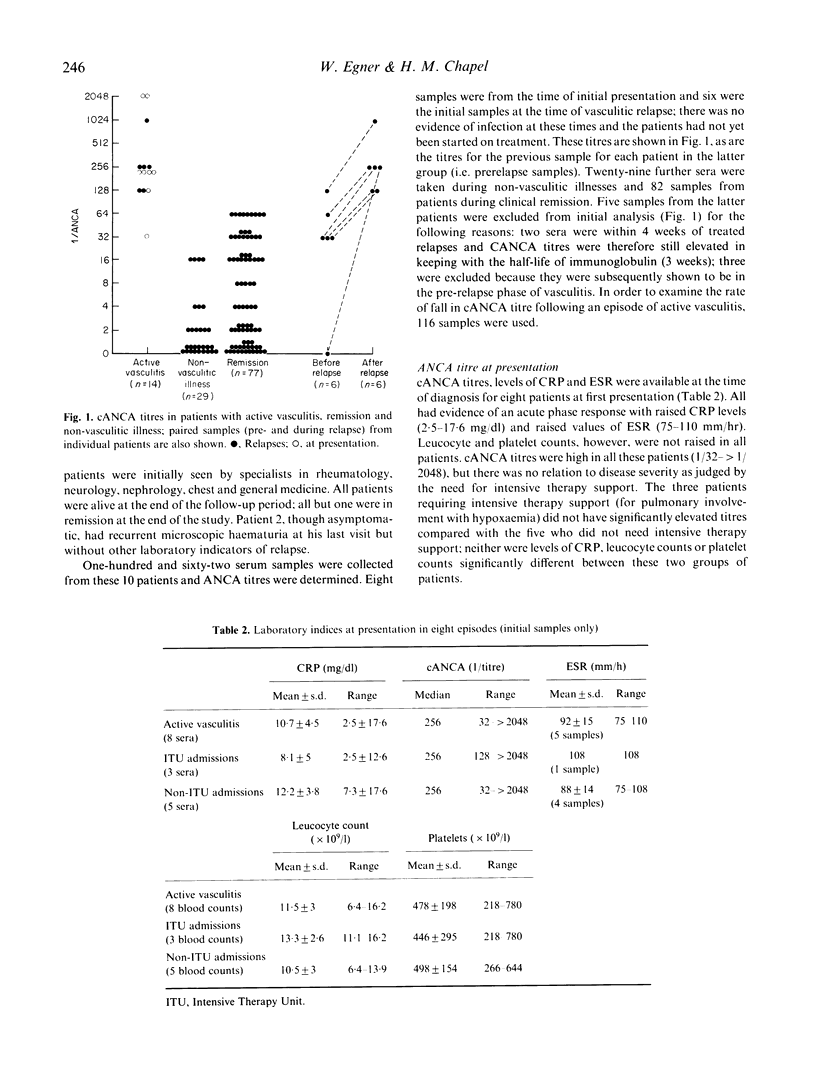
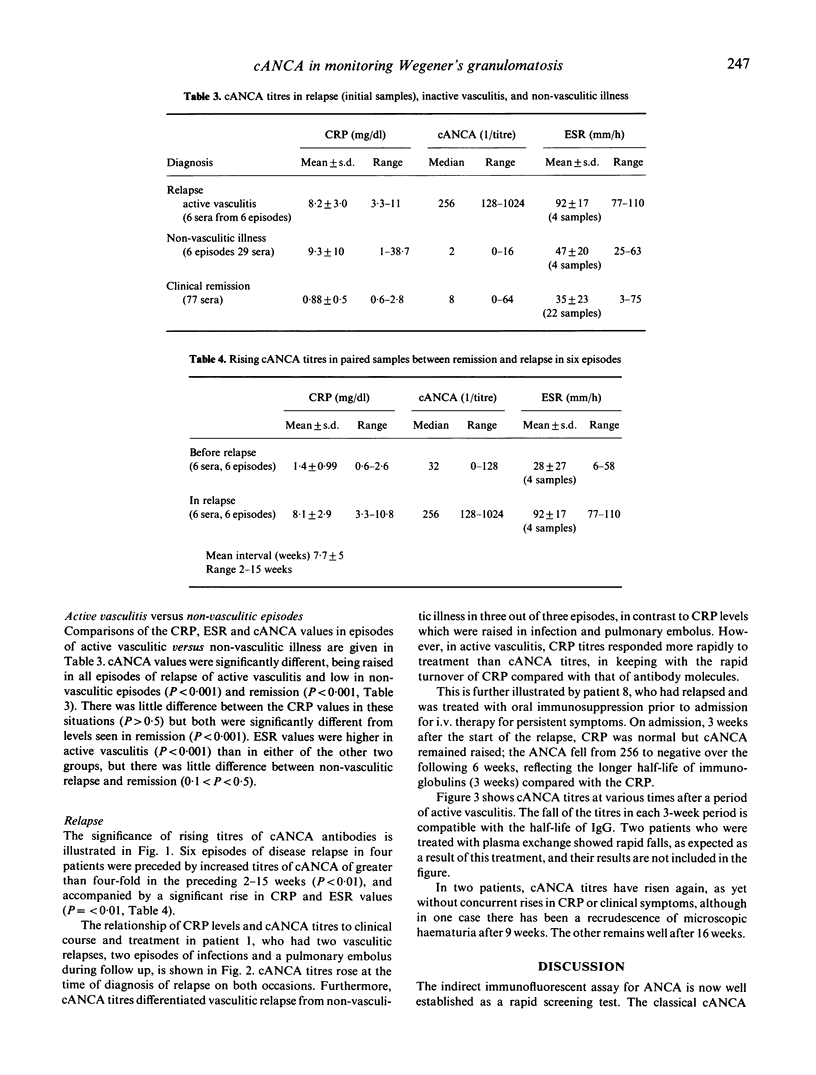
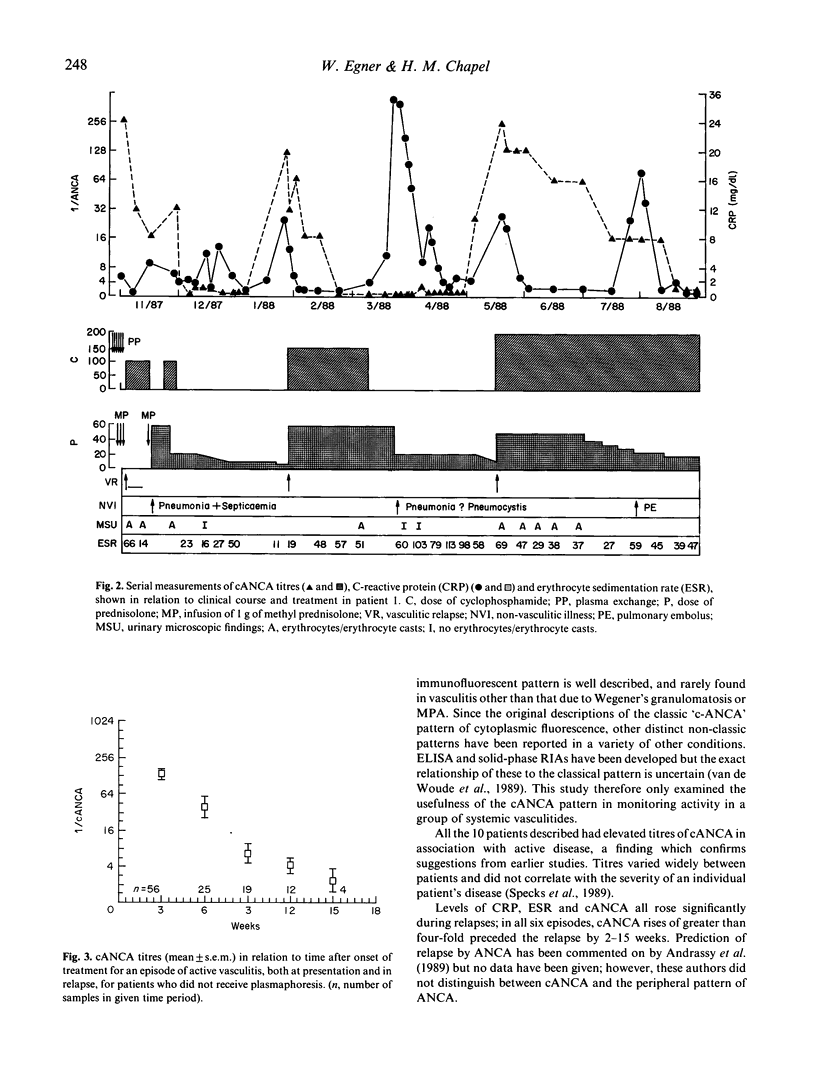
Titration of antibodies against neutrophil cytoplasmic antigens (cANCA), as detected by indirect immunofluorescence, is shown to be clinically useful for monitoring disease activity in Wegener's granulomatosis and microscopic polyarteritis. Ten patients were followed (eight from presentation) prospectively for up to 2 years; during this time there were six episodes of vasculitic relapse in four patients and five infective episodes and one pulmonary embolus in four patients. Titres of cANCA were markedly raised, both at presentation (1/32-1/2048) and at vasculitic relapse (1/125-1/1048) but not in infection or embolism (negative, 1/16). Thus the titre of these antibodies can distinguish nonvasculitic illness from vasculitic relapse, in contrast to C-reactive protein levels which were raised in both. Titres of cANCA fell gradually after vasculitic relapse, in keeping with the half-life of IgG (3 weeks). C-reactive protein is a better measure of recovery.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrassy K., Koderisch J., Rufer M., Erb A., Waldherr R., Ritz E. Detection and clinical implication of anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies in Wegener's granulomatosis and rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1989 Oct;32(4):159–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Haynes B., Katz P. The spectrum of vasculitis: clinical, pathologic, immunologic and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):660–676. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-5-660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind C. R., Savage C. O., Winearls C. G., Pepys M. B. Objective monitoring of disease activity in polyarteritis by measurement of serum C reactive protein concentration. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Apr 7;288(6423):1027–1030. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6423.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind C. R., Winearls C. G., Lockwood C. M., Rees A. J., Pepys M. B. Objective monitoring of activity in Wegener's granulomatosis by measurement of serum C-reactive protein concentration. Clin Nephrol. 1984 Jun;21(6):341–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie J. T. Classification and immunodiagnosis of vasculitis: a new solution or promises unfulfilled? J Rheumatol. 1988;15(5):728–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tervaert J. W., van der Woude F. J., Fauci A. S., Ambrus J. L., Velosa J., Keane W. F., Meijer S., van der Giessen M., van der Hem G. K., The T. H. Association between active Wegener's granulomatosis and anticytoplasmic antibodies. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Nov;149(11):2461–2465. doi: 10.1001/archinte.149.11.2461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Woude F. J., Daha M. R., van Es L. A. The current status of neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Nov;78(2):143–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Woude F. J., Rasmussen N., Lobatto S., Wiik A., Permin H., van Es L. A., van der Giessen M., van der Hem G. K., The T. H. Autoantibodies against neutrophils and monocytes: tool for diagnosis and marker of disease activity in Wegener's granulomatosis. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):425–429. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


