Abstract
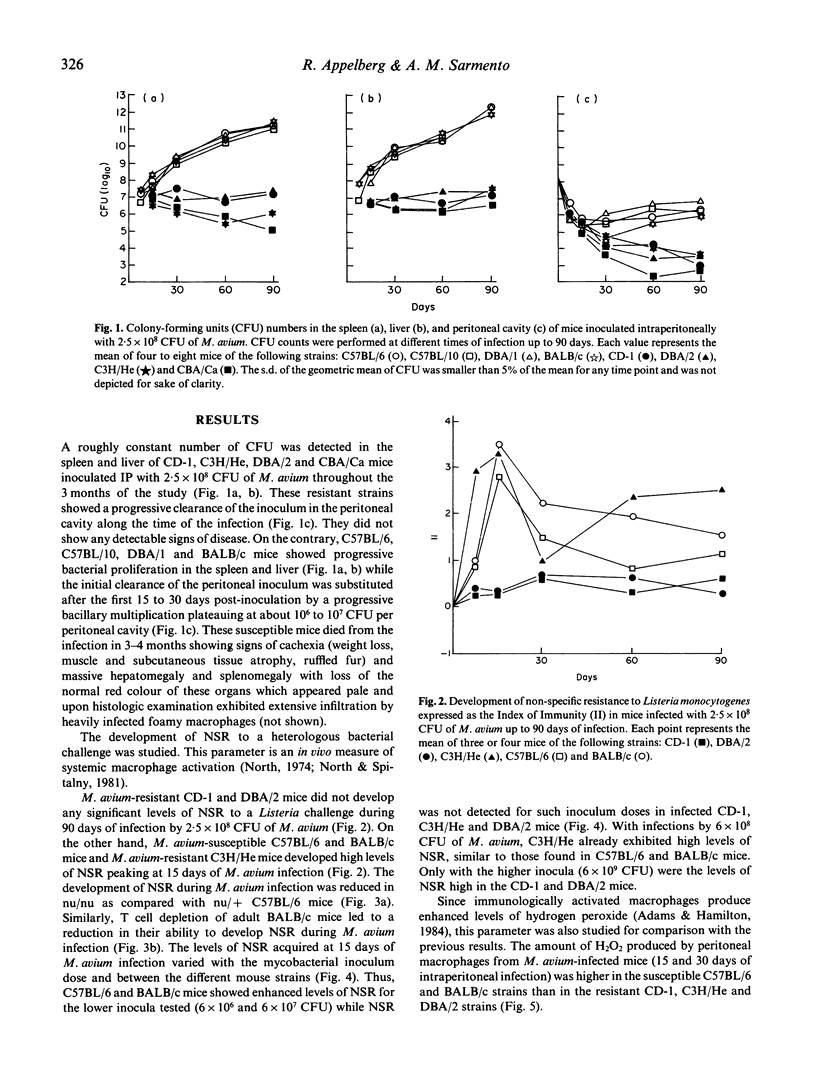
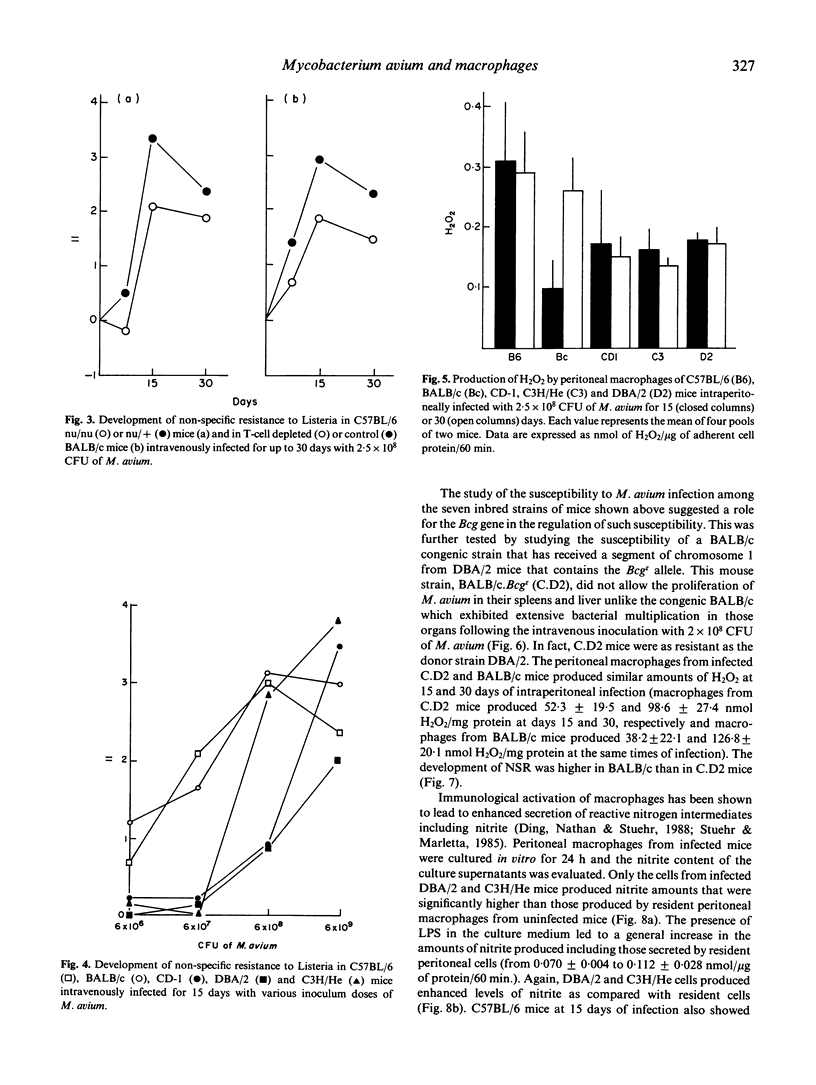
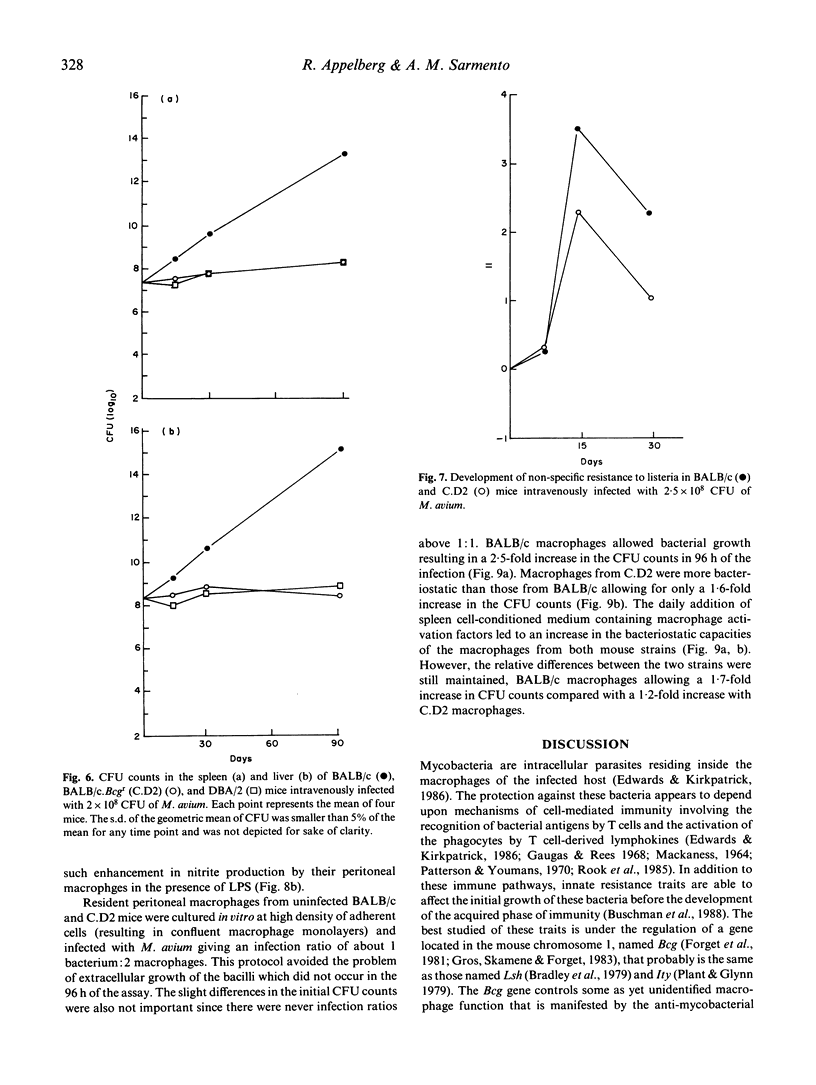
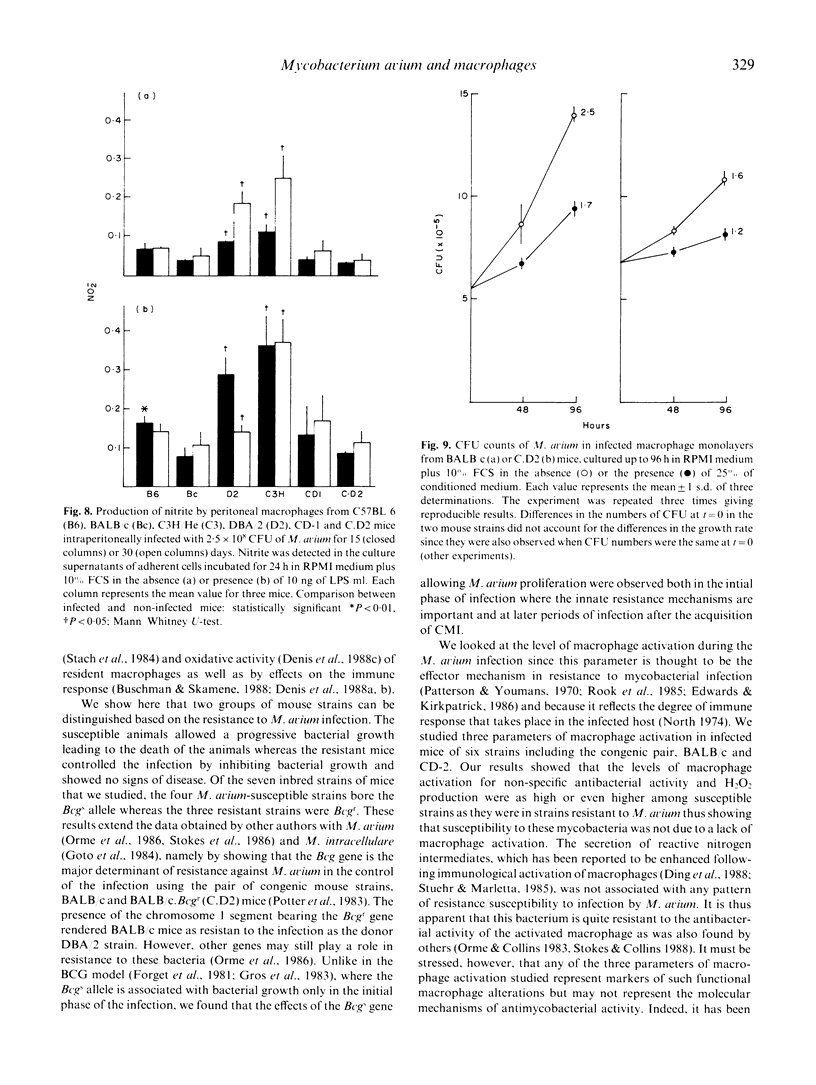
Following the intraperitoneal inoculation of 2.5 x 10(8) colony-forming units of Mycobacterium avium strain ATCC 25291, there was bacillary growth in the liver, spleen and peritoneal cavity of C57BL/6, C57BL/10, DBA/1 and BALB/c mice whereas DBA/2, C3H/He, CBA/Ca and CD-1 mice controlled the infection showing constant or slightly decreasing numbers of viable bacteria in the liver and spleen and effective clearance of the bacilli from the peritoneal cavities. The acquisition of non-specific resistance (NSR) to Listeria monocytogenes during the infection by M. avium was high in C57BL/6, BALB/c and C3H/He mice and negligible in DBA/2 and CD-1 mice. The magnitude of the acquisition of NSR was reduced in T cell-deficient mice and was directly proportional to the dose of the inoculum of M. avium. The production of hydrogen peroxide by phorbol myristate acetate-stimulated peritoneal macrophages of M. avium-infected mice was higher in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice than in CD-1, DBA/2 and C3H/He animals. BALB/c. Bcgr (C.D2) mice, unlike their congenic strain BALB/c, restricted bacterial growth following the intravenous inoculation of 2.5 x 10(8) CFU of M. avium as efficiently as DBA/2 mice. C.D2 and BALB/c peritoneal macrophages from infected mice produced similar amounts of H2O2 but BALB/c mice developed higher levels of NSR to listeria than C.D2 mice. The production of nitrite by peritoneal macrophages from infected mice was found to be enhanced in DBA/2 and C3H/He but not in BALB/c, C57BL/6, DC-1 and C.D2 mice. Resident peritoneal macrophages from C.D2 mice were more bacteriostatic in vitro for M. avium than macrophages from BALB/c mice. The same relative differences between the two macrophage populations were observed when the cells were activated with lymphokines. The results show that the populations were observed when the cells were activated with lymphokines. The results show that the resistance to M. avium infection in mice is under the control of the Bcg gene and that susceptibility may be due to some defect in macrophage antibacterial function not completely overcome by the activation of this phagocyte in the susceptible strains of mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg R., Soares R., Ferreira P., Silva M. T. Induction of non-specific immunosuppression in mice by mycobacterial infections and its relationship to macrophage activation. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Aug;30(2):165–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschman E., Apt A. S., Nickonenko B. V., Moroz A. M., Averbakh M. H., Skamene E. Genetic aspects of innate resistance and acquired immunity to mycobacteria in inbred mice. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(4):319–336. doi: 10.1007/BF02053844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschman E., Skamene E. Immunological consequences of innate resistance and susceptibility to BCG. Immunol Lett. 1988 Nov;19(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. A., Canono B. P., Cook J. L. Mouse macrophages stimulated by recombinant gamma interferon to kill tumor cells are not bactericidal for the facultative intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1371–1375. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1371-1375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Buschman E., Forget A., Pelletier M., Skamene E. Pleiotropic effects of the Bcg gene. II. Genetic restriction of responses to mitogens and allogeneic targets. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3988–3993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Forget A., Pelletier M., Skamene E. Pleiotropic effects of the Bcg gene. I. Antigen presentation in genetically susceptible and resistant congenic mouse strains. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2395–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Forget A., Pelletier M., Skamene E. Pleiotropic effects of the Bcg gene: III. Respiratory burst in Bcg-congenic macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):370–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D., Kirkpatrick C. H. The immunology of mycobacterial diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;134(5):1062–1071. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget A., Skamene E., Gros P., Miailhe A. C., Turcotte R. Differences in response among inbred mouse strains to infection with small doses of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.42-47.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugas J., Rees R. J. Enhancing effect of antilymphocytic serum on mycobacterial infections in mice. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):408–409. doi: 10.1038/219408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Nakamura R. M., Takahashi H., Tokunaga T. Genetic control of resistance to Mycobacterium intracellulare infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.135-140.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M., Yates M. D. Infections caused by opportunist mycobacteria: a review. J R Soc Med. 1986 Apr;79(4):226–229. doi: 10.1177/014107688607900411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Specific amino acid (L-arginine) requirement for the microbiostatic activity of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1172/JCI113427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Cellular mechanisms of genetically controlled host resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1966–1972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. T cell dependence of macrophage activation and mobilization during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.66-71.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Resistance of various strains of mycobacteria to killing by activated macrophages in vivo. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1452–1454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Stokes R. W., Collins F. M. Genetic control of natural resistance to nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.56-62.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. J., Youmans G. P. Demonstration in tissue culture of lymphocyte-mediated immunity to tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):600–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.600-603.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Locating salmonella resistance gene on mouse chromosome 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., O'Brien A. D., Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., Wax J. S. A BALB/c congenic strain of mice that carries a genetic locus (Ityr) controlling resistance to intracellular parasites. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1234–1235. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1234-1235.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Champion B. R., Steele J., Varey A. M., Stanford J. L. I-A restricted activation by T cell lines of anti-tuberculosis activity in murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):414–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruch W., Cooper P. H., Baggiolini M. Assay of H2O2 production by macrophages and neutrophils with homovanillic acid and horse-radish peroxidase. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 28;63(3):347–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stach J. L., Gros P., Forget A., Skamene E. Phenotypic expression of genetically-controlled natural resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes R. W., Collins F. M. Growth of Mycobacterium avium in activated macrophages harvested from inbred mice with differing innate susceptibilities to mycobacterial infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2250–2254. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2250-2254.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes R. W., Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Role of mononuclear phagocytes in expression of resistance and susceptibility to Mycobacterium avium infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.811-819.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi I., Shiratsuchi H., Okuda Y., Yamamoto Y. An analysis of in vitro T cell responsiveness in nontuberculous mycobacterial infection. Chest. 1988 Oct;94(4):822–829. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.4.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. R., Collins F. M. Development of suppressor T cells in mice heavily infected with mycobacteria. Immunology. 1980 Mar;39(3):367–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. R., Collins F. M. The specificity of suppressor T cells induced by chronic Mycobacterium avium infection in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jan;43(1):10–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Stikkelbroeck J. J., van den Barselaar M. T., Sluiter W., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Divergent changes in antimicrobial activity after immunologic activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1665–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



