Abstract
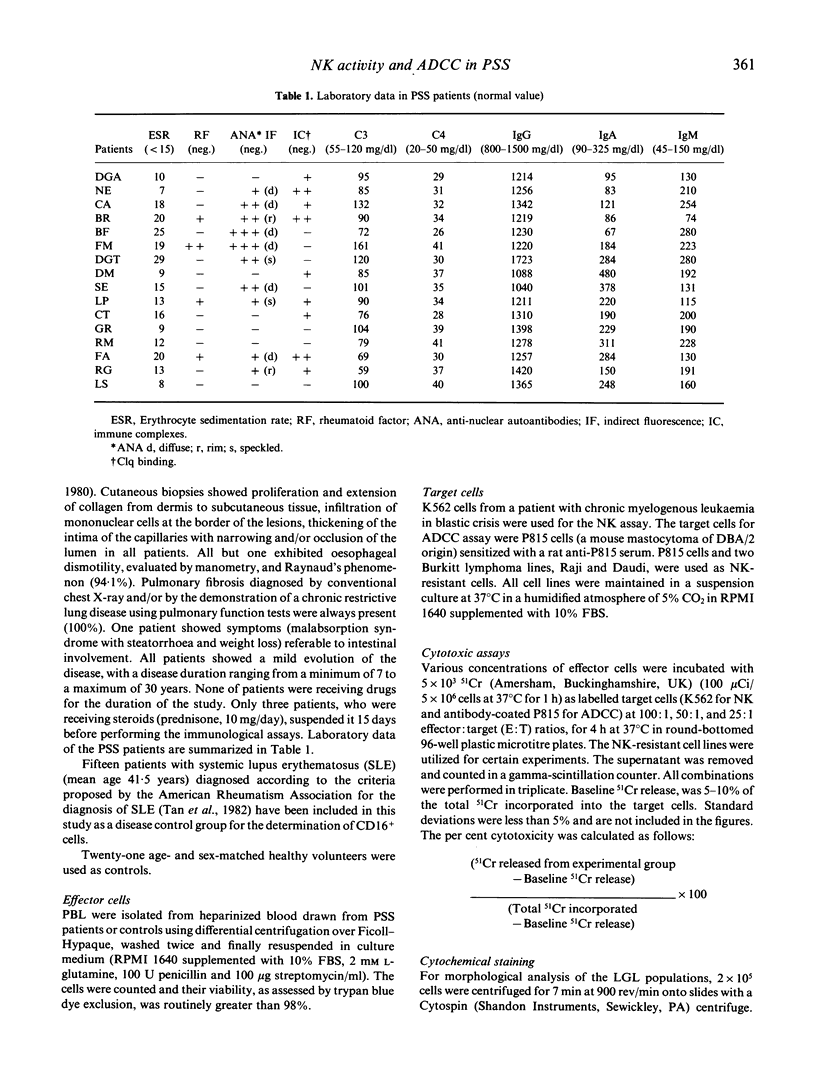
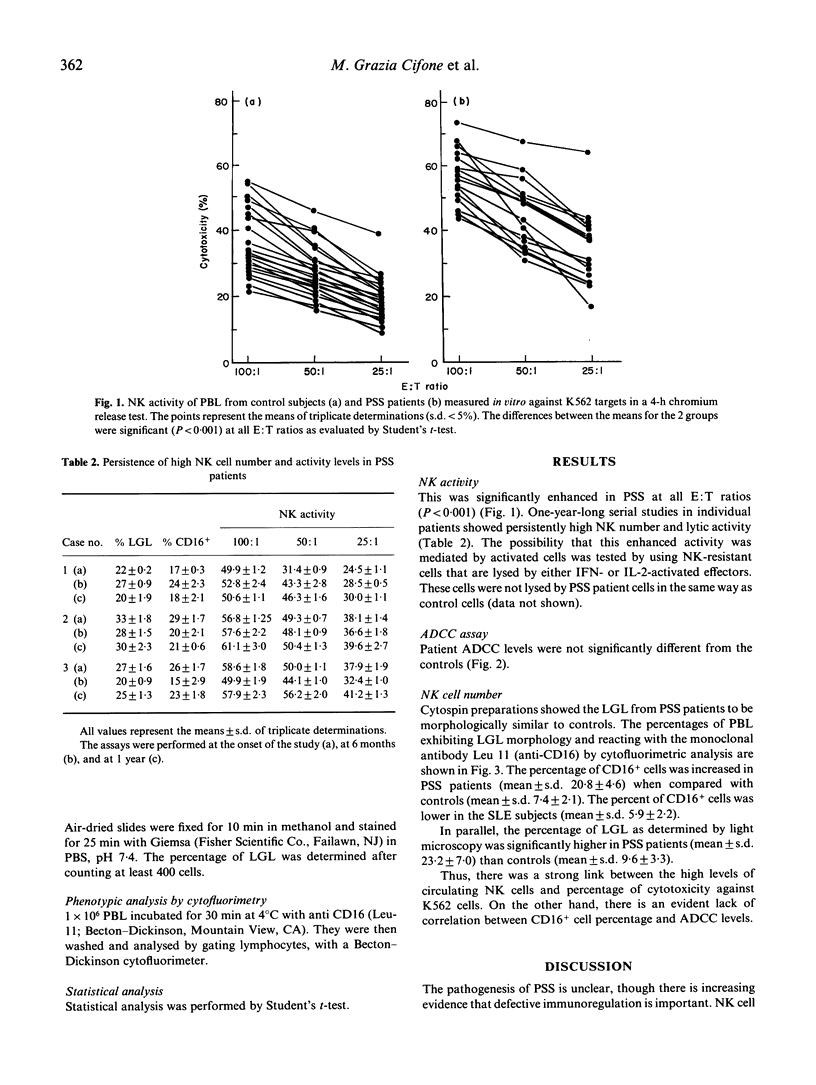
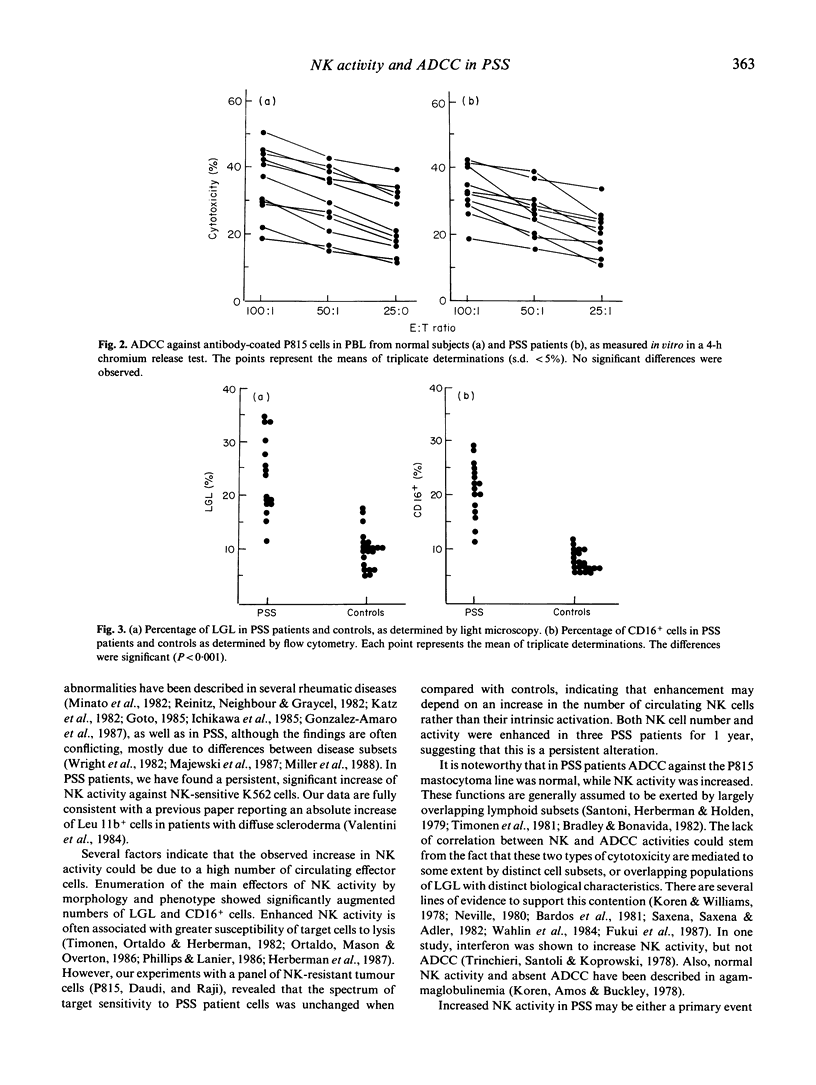
Enhanced natural killer (NK) activity and normal lymphocyte antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) were observed in 16 patients with a diagnosis of progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS). Higher NK activity levels were observed against NK-sensitive K562 target cells, while the NK-resistant P815, Daudi and Raji cell lines were not lysed. Cytofluorimetric studies and morphological analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) showed an increased number of CD16 positive cells and large granular lymphocytes (LGL), indicating that the enhancement observed was probably attributable to an increase in the number of circulating NK cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abruzzo L. V., Mullen C. A., Rowley D. A. Immunoregulation by natural killer cells. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):266–278. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai S., Yamamoto H., Itoh K., Kumagai K. Suppressive effect of human natural killer cells on pokeweed mitogen-induced B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):651–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardos P., Altman J., Guillou P. J., Carnaud C. The cell populations mediating natural killing-(NK) and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity are only partially identical. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):534–539. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Steigerwald J. C., Tan E. M. Association of antinuclear and antinucleolar antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C. A., Turgiss L. R., Welsh R. M. Increase in NK cell number and turnover rate during acute viral infection. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1539–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. P., Bonavida B. Mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity at the single cell level. IV. Natural killing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity can be mediated by the same human effector cell as determined by the two-target conjugate assay. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2260–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famularo G., Giacomelli R., Alesse E., Cifone M. G., Morrone S., Boirivant M., Danese C., Perego M. A., Santoni A., Tonietti G. Polyclonal B lymphocyte activation in progressive systemic sclerosis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(2):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich B., Jimenez S. A. Phenotype of peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis: activated T lymphocytes and the effect of D-penicillamine therapy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Aug;69(2):375–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui H., Overton W. R., Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W. Natural killer cell activity in the rat. VI. Characterization of rat large granular lymphocytes as effector cells in natural killer and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic activities. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Feb;41(2):130–142. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Amaro R., Alcocer-Varela J., Martínez-Cordero E., Alarcón-Segovia D. Natural killer cell-mediated activity in mixed connective tissue disease and its response to induction by interleukin-2. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;4(4):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00915294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Hercend T., Beveridge R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of an antigen expressed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2947–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Malaviya A. N., Rajagopalan P., Good R. A. Subpopulations of human T lymphocytes. IX. Imbalance of T cell subpopulations in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Nov;38(2):342–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Djeu J., Kay H. D., Ortaldo J. R., Riccardi C., Bonnard G. D., Holden H. T., Fagnani R., Santoni A., Puccetti P. Natural killer cells: characteristics and regulation of activity. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:43–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Staal S., Djeu J. Y. Augmentation of natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic target cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Apr 15;19(4):555–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Yoshida M., Takaya M., Uchiyama M., Shimizu H., Arimori S. Circulating natural killer cells in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Feb;28(2):182–187. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoshita T., Whiteside T. L., Rodnan G. P., Taylor F. H. Abnormalities of T lymphocyte subsets in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS, scleroderma). J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Feb;97(2):264–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Zaytoun A. M., Lee J. H., Jr, Panush R. S., Longley S. Abnormal natural killer cell activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: an intrinsic defect in the lytic event. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1966–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Amos D. B., Buckley R. H. Natural killing in immunodeficient patients. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):796–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Williams M. S. Natural killing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity are mediated by different mechanisms and by different cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1956–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano K., Arai S., Munakata T., Tomita Y., Yoshitake Y., Kumagai K. Suppressive effect of human natural killer cells on Epstein-Barr virus-induced immunoglobulin synthesis. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1462–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski S., Blaszczyk M., Wasik M., Jablonska S. Natural killer cell activity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with various forms of systemic scleroderma. Br J Dermatol. 1987 Jan;116(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1987.tb05784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. B., Hiserodt J. C., Hunt L. E., Steen V. D., Medsger T. A., Jr Reduced natural killer cell activity in patients with systemic sclerosis. Correlation with clinical disease type. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Dec;31(12):1515–1523. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato N., Takeda A., Kano S., Takaku F. Studies of the function of natural killer-interferon system in patients with Sjögren syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):581–588. doi: 10.1172/JCI110484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. E. Human killer cells and natural killer cells: distinct subpopulations of Fc receptor-bearing lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2604–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Tamura T., Takano T. Evidence in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus of the presence of antibodies against RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of baboon endogenous virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):747–755. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A., Overton R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells. Analysis of progenitors and effectors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1193–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Jackson A., Warner N. L., Faust J., Rumpold H., Kraft D., Lanier L. L. The Fc receptor for IgG on human natural killer cells: phenotypic, functional, and comparative studies with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Dissection of the lymphokine-activated killer phenomenon. Relative contribution of peripheral blood natural killer cells and T lymphocytes to cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):814–825. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):581–590. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinitz E., Neighbour P. A., Grayzel A. I. Natural killer cell activity of mononuclear cells from rheumatoid patients measured by a conjugate-binding cytotoxicity assay. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Dec;25(12):1440–1444. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robles C. P., Pollack S. B. Regulation of the secondary in vitro antibody response by endogenous natural killer cells: kinetics, isotype preference, and non-identity with T suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2418–2424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield N. F., Rodnan G. P. Serum antinuclear antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Oct;11(5):607–617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoni A., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Correlation between natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor targets in the mouse. I. Distribution of the reactivity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jan;62(1):109–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena R. K., Saxena Q. B., Adler W. H. Identity of effector cells participating in the reverse antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1982 Jun;46(2):459–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Allavena P., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B., Oppenheim J. J. Subsets of human large granular lymphocytes (LGL) exhibit accessory cell functions. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3049–3055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Analysis by a single cell cytotoxicity assay of natural killer (NK) cells frequencies among human large granular lymphocytes and of the effects of interferon on their activity. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2514–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Koprowski H. Spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity in humans: role of interferon and immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1849–1855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Cytotoxic cells induced during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of mice. I. Characterization of natural killer cell induction. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):163–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Kumagai Y., Roumm A. D., Almendinger R., Rodnan G. P. Suppressor cell function and T lymphocyte subpopulations in peripheral blood of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jul;26(7):841–847. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. K., Hughes P., Rowell N. R. Spontaneous lymphocyte-mediated (NK cell) cytotoxicity in systemic sclerosis: a comparison with antibody-dependent lymphocyte (K cell) cytotoxicity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Aug;41(4):409–413. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Alsheikhly A., Perlmann P., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Enumeration and characterization of human killer and natural killer cells by a modified single-cell assay. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jun;19(6):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


