Abstract
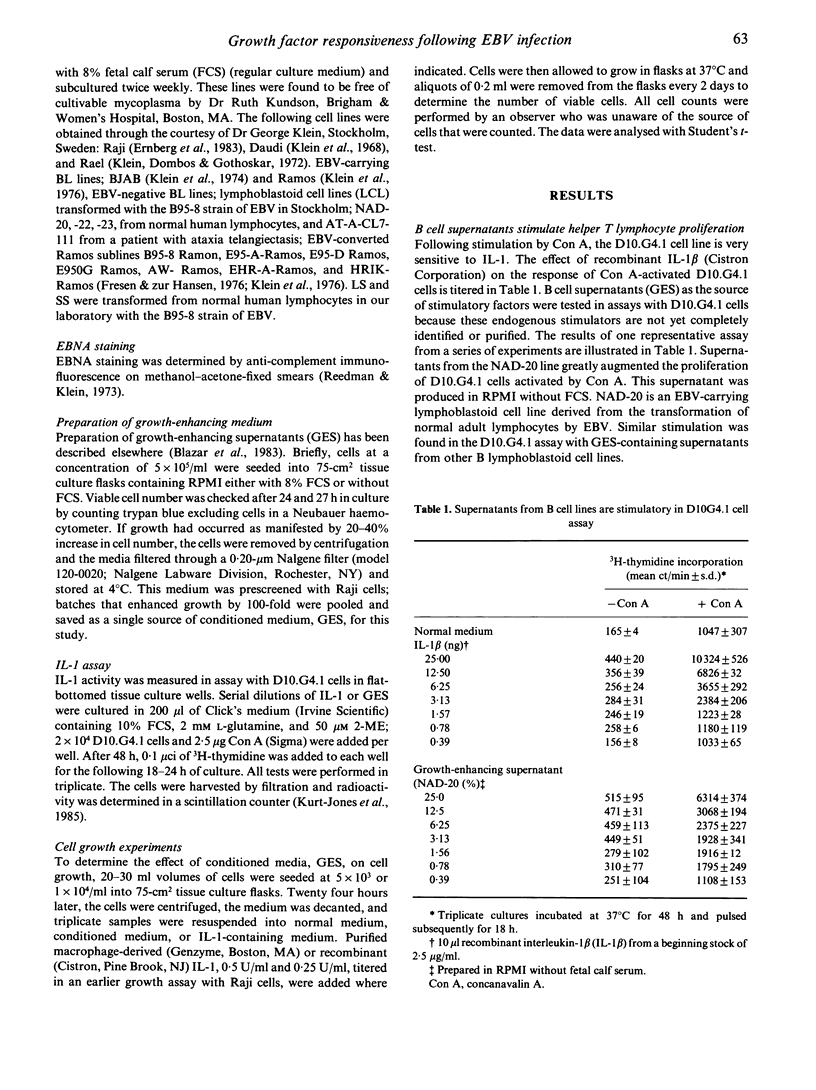
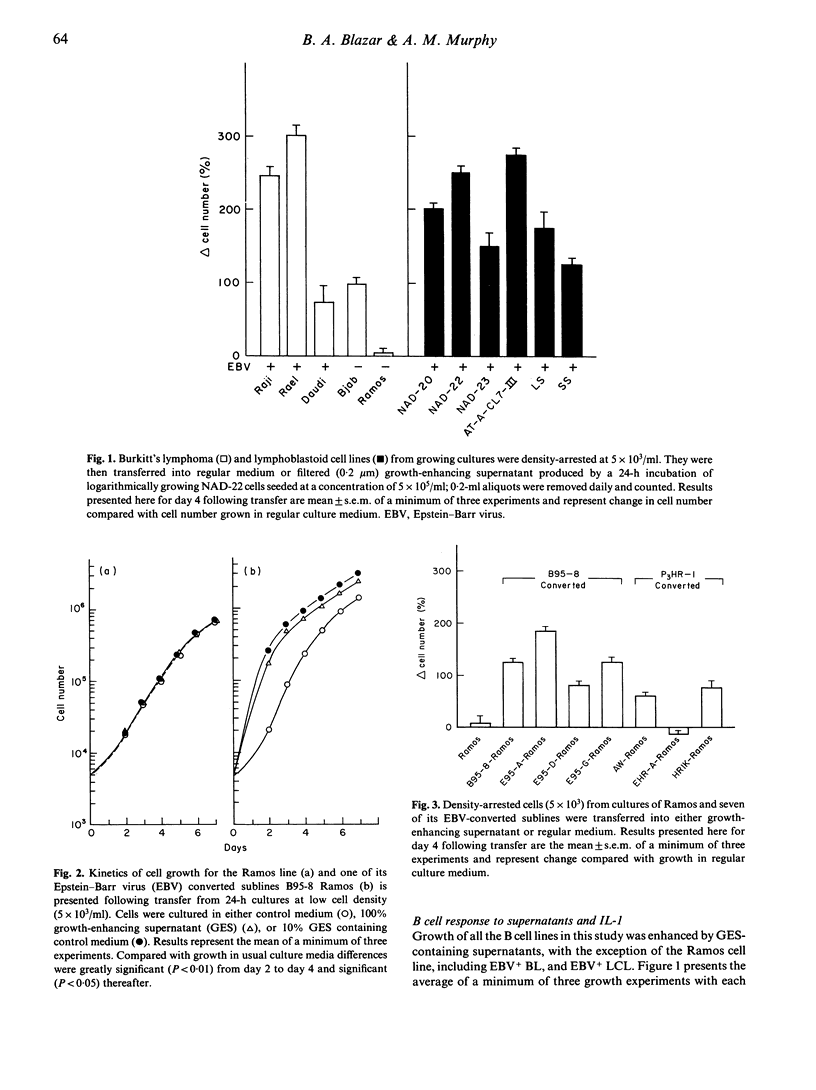
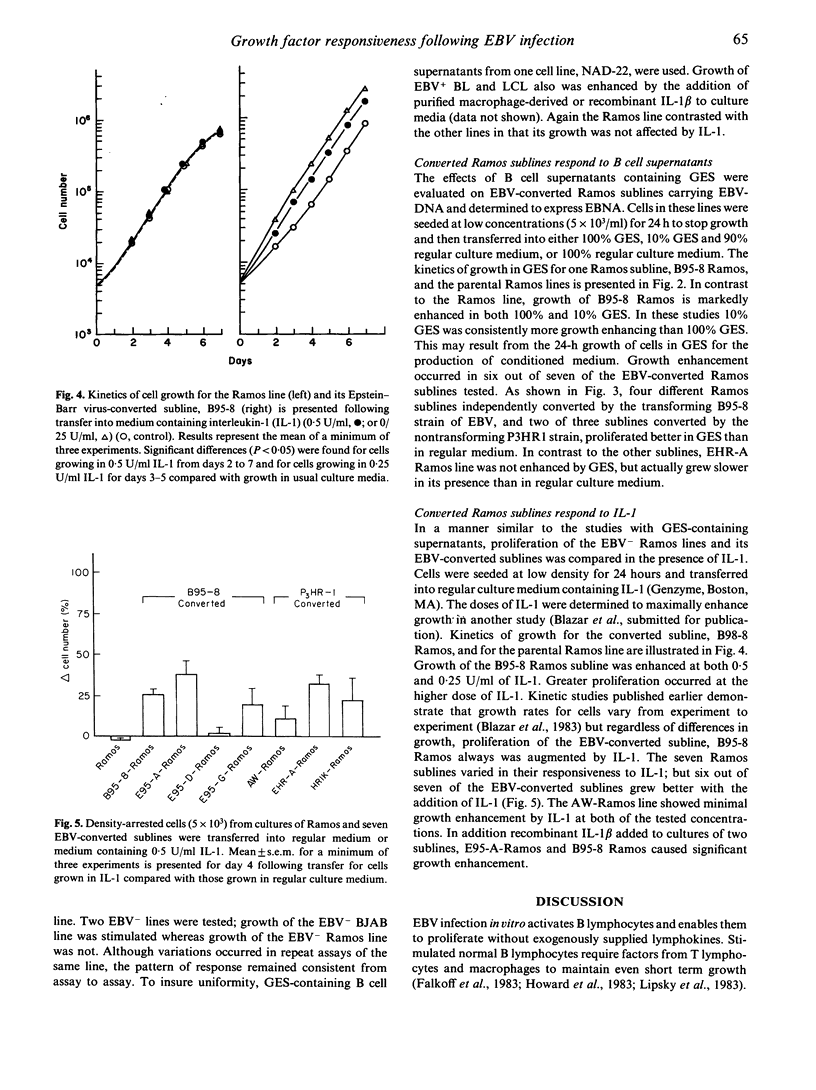
Immortalized B lymphocytes produce a factor(s) that stimulates growth of B cell lines carrying Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Stimulatory supernatants derived from B cells also exhibit interleukin-1 (IL-1) activity in costimulator assays with the D10.G4.1 helper T cell line. Experiments with purified macrophage-derived IL-1 and recombinant IL-1 beta demonstrate that IL-1 stimulates proliferation of the cell lines that respond to the factors from B lymphocyte lines. One B cell line, Ramos, an EBV-Burkitt's lymphoma, contrasts with other B cell lines in that it is refractory to the growth enhancing effects of B cell conditioned medium and macrophage-derived IL-1. When EBV was introduced into Ramos cells, growth was enhanced by the factor(s) in B cell conditioned medium (six out of seven lines); growth of EBV-converted Ramos lines (six out of seven lines) also was enhanced by IL-1. These findings demonstrate that infection of a non-responsive transformed B lymphocyte by EBV induces cellular responsiveness to factor-mediated growth stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrus J. L., Jr, Jurgensen C. H., Brown E. J., Fauci A. S. Purification to homogeneity of a high molecular weight human B cell growth factor; demonstration of specific binding to activated B cells; and development of a monoclonal antibody to the factor. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1319–1335. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazar B. A., Sutton L. M., Strome M. Immunomodulating activity in supernatants from EBV immortalized lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1986;22(1):62–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00205718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazar B. A., Sutton L. M., Strome M. Self-stimulating growth factor production by B-cell lines derived from Burkitt's lymphomas and other lines transformed in vitro by Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4562–4568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck J., Hämmerling U., Hoffmann M. K., Levi E., Welte K. Purification and biochemical characterization of a human autocrine growth factor produced by Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2923–2928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu E., Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A., Lareau M., Geha R. S. Role of interleukin 1 in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1311–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J., McCormick K. J., Andersson-Anvret M., Aman P., Killander D. Relationship between the amounts of EBV-DNA and EBNA per cell, clonability and tumorigenicity in two ebv-negative lymphoma lines and their EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1983 Feb 15;31(2):163–169. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkoff R. J., Muraguchi A., Hong J. X., Butler J. L., Dinarello C. A., Fauci A. S. The effects of interleukin 1 on human B cell activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):801–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Hausen H. Establishment of EBNA-expressing cell lines by infection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-genome-negative human lymphoma cells with different EBV strains. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):161–166. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard T. L., Volkman D. J. IL 1-like activity in antigen-presenting human B cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3217–3223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., Aman P., Hughes-Jones N. C. Soluble factor requirements for the autostimulatory growth of B lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1554–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., English L. S., Hughes-Jones N. C. Immortalized B lymphocytes produce B-cell growth factor. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):145–147. doi: 10.1038/310145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Mizel S. B., Lachman L., Ansel J., Johnson B., Paul W. E. Role of interleukin 1 in anti-immunoglobulin-induced B cell proliferation. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1529–1543. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz T., Chu E., Geha R. S. Antigen presentation by human B cells: T cell proliferation induced by Epstein Barr virus B lymphoblastoid cells. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1446–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurgensen C. H., Ambrus J. L., Jr, Fauci A. S. Production of B cell growth factor by normal human B cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4542–4547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L., Gothoskar B. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) producer and non-producer human lymphoblastoid cell lines to superinfection with EB-virus. Int J Cancer. 1972 Jul 15;10(1):44–57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Schlossman S. F. Induction of an activated b lymphocyte-associated surface moiety defined by the B2 monoclonal antibody by ebv conversion of an EBV-negative lymphoma line (Ramos): differential effect of transforming (B95-8) and nontransforming (P3HR-1) EBV substrains. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1985–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Lindahl T., Jondal M., Leibold W., Menézes J., Nilsson K., Sundström C. Continuous lymphoid cell lines with characteristics of B cells (bone-marrow-derived), lacking the Epstein-Barr virus genome and derived from three human lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3283–3286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Zeuthen J., Terasaki P., Billing R., Honig R., Jondal M., Westman A., Clements G. Inducibility of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle and surface marker properties of EBV-negative lymphoma lines and their in vitro EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):639–652. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Beller D. I., Mizel S. B., Unanue E. R. Identification of a membrane-associated interleukin 1 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Conditions required for expression of membrane IL 1 on B cells. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Thompson P. A., Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A. The role of interleukin 1 in human B cell activation: inhibition of B cell proliferation and the generation of immunoglobulin-secreting cells by an antibody against human leukocytic pyrogen. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2708–2714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Kuang Y. D., Tosato G., Hopkins S. J., Oppenheim J. J. B-cell-derived interleukin 1 (IL-1)-like factor. I. Relationship of production of IL-1-like factor to accessory cell function of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human B-lymphoblast lines. Cell Immunol. 1985 Sep;94(2):406–417. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Procopio A., Abe H., Scala G., Ortaldo J. R., Oppenheim J. J. Production of interleukin 1 activity by normal human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1132–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G. Biological differences between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains with regard to lymphocyte transforming ability, superinfection and antigen induction. Exp Cell Res. 1975 May;92(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Nishimoto H., Kawamura N., Hori A., Kishimoto T. B cell-derived BCGF functions as autocrine growth factor(s) in normal and transformed B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistoia V., Cozzolino F., Rubartelli A., Torcia M., Roncella S., Ferrarini M. In vitro production of interleukin 1 by normal and malignant human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1688–1692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Wakasugi H., Ferrara P., Robin P., Capdevielle J., Tursz T., Fradelizi D., Bertoglio J. Purification to homogeneity and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a novel interleukin 1 species derived from a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3304–3310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Kuang Y. D., Hall R. E., Muchmore A. V., Oppenheim J. J. Accessory cell function of human B cells. I. Production of both interleukin 1-like activity and an interleukin 1 inhibitory factor by an EBV-transformed human B cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1637–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira G., Aman P., Koide N., Lundin G., Klein G., Hall K. Cell-surface immunoglobulin and insulin receptor expression in an EBV-negative lymphoma cell line and its EBV-converted sublines. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):122–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G. Comparison between growth characteristics of an Epstein--Barr virus (EBV)-genome-negative lymphoma line and its EBV-converted subline in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3518–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G. Further studies on the differences in serum dependence in EBV negative lymphoma lines and their in vitro EBV converted, virus-genome carrying sublines. Eur J Cancer. 1977 Nov;13(11):1269–1275. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(77)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendeman S., Thorley-Lawson D. A. The activation antigen BLAST-2, when shed, is an autocrine BCGF for normal and transformed B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1637–1642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchibayashi N., Kikutani H., Barsumian E. L., Hauptmann R., Schneider F. J., Schwendenwein R., Sommergruber W., Spevak W., Maurer-Fogy I., Suemura M. Recombinant soluble Fc epsilon receptor II (Fc epsilon RII/CD23) has IgE binding activity but no B cell growth promoting activity. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3901–3908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa K., Kikutani H., Owaki H., Yamasaki K., Yokota A., Nakamura H., Barsumian E. L., Hardy R. R., Suemura M., Kishimoto T. A B cell-specific differentiation antigen, CD23, is a receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon R) on lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2576–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Unanue E. R. Identification of a macrophage antigen-processing event required for I-region-restricted antigen presentation to T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1869–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


