Abstract
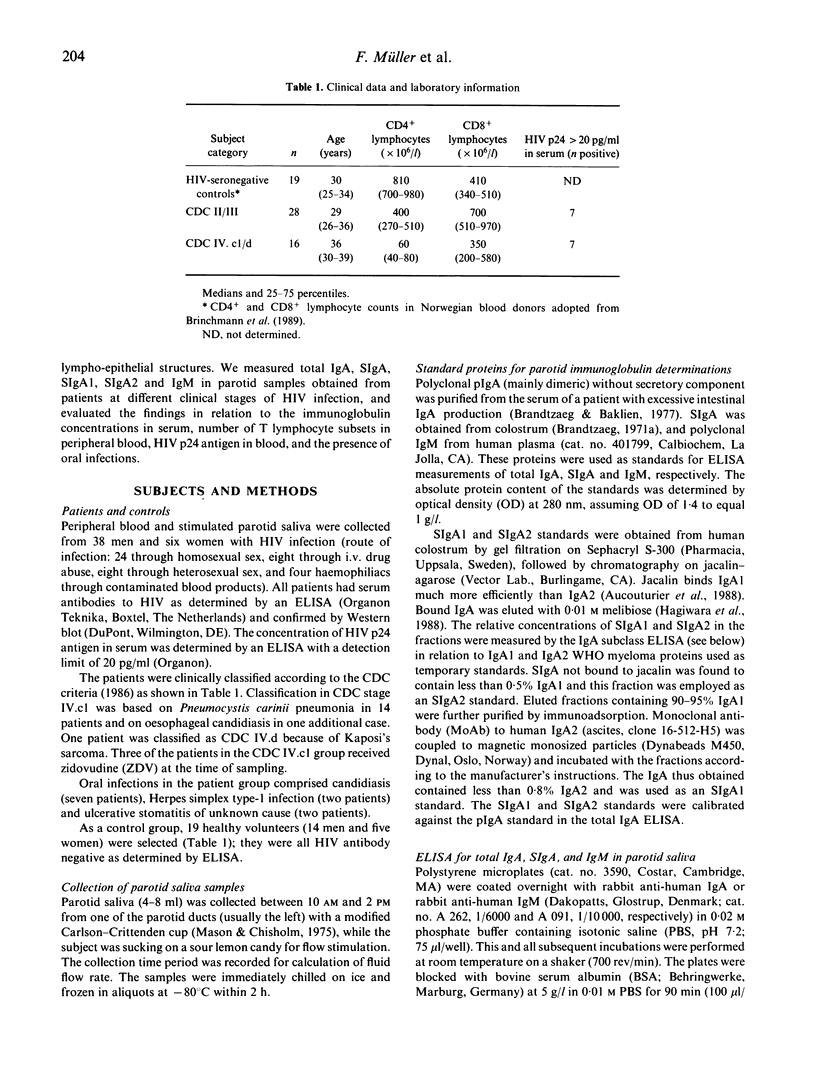
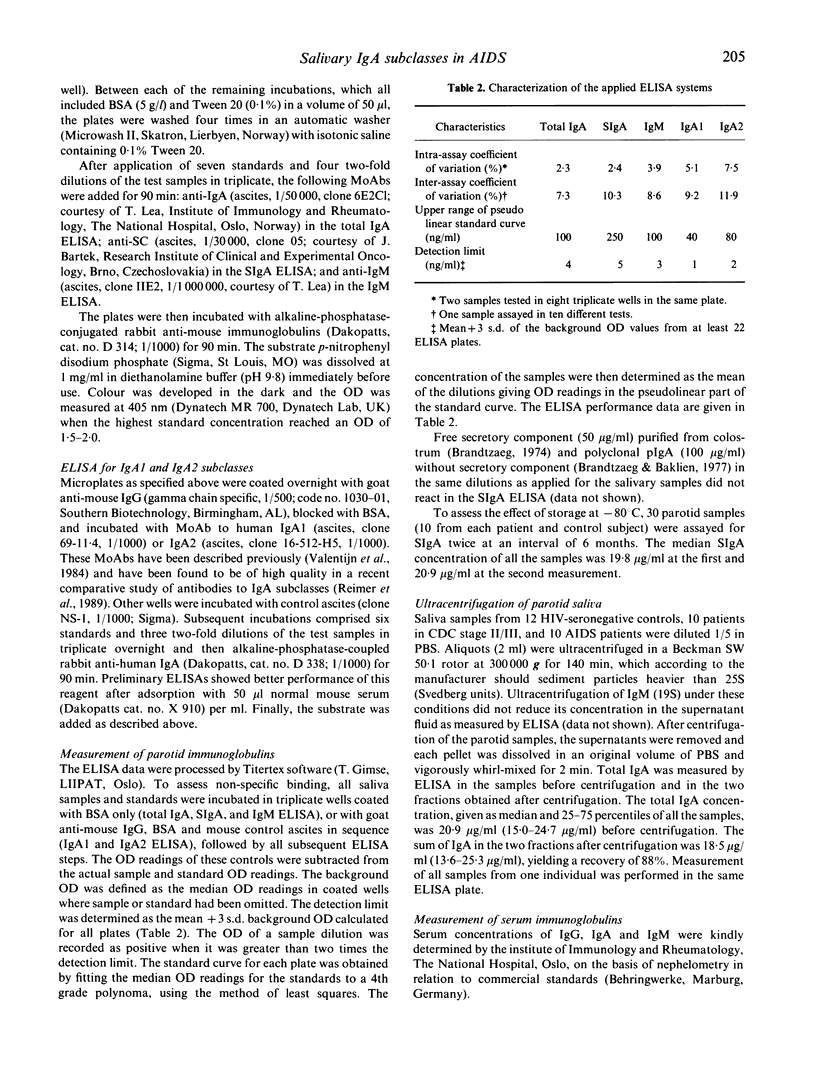
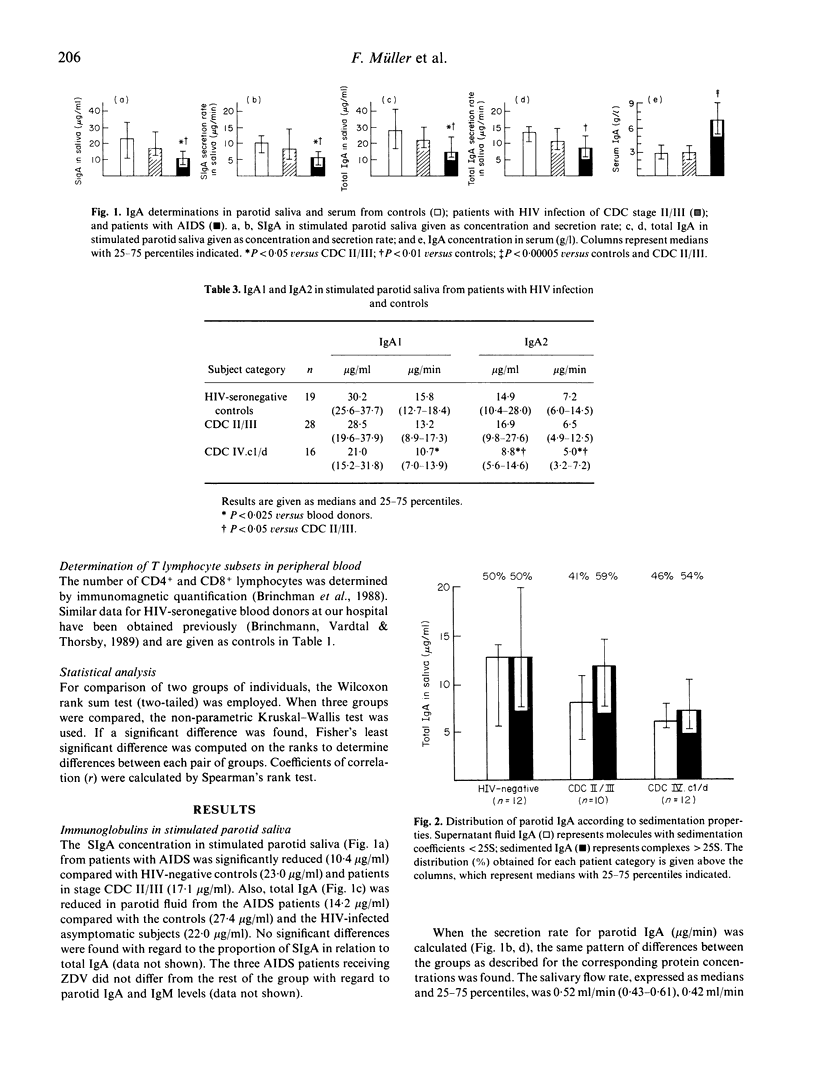
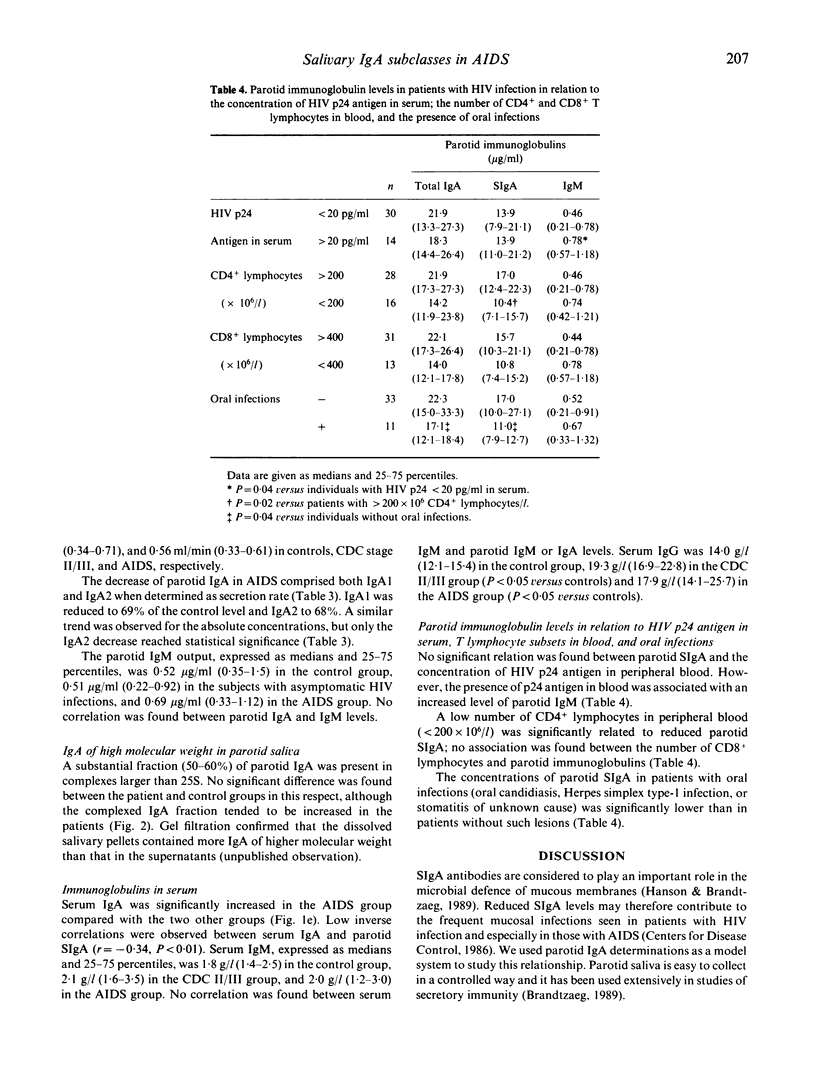
Secretory IgA (SIgA), the isotypes IgA1 and IgA2, and IgM were measured by ELISA in stimulated parotid saliva from patients with AIDS (n = 16), subjects with asymptomatic HIV infection (n = 28), and HIV-seronegative healthy controls (n = 19). SIgA was significantly reduced in the AIDS group (10.4 micrograms/ml) compared with the asymptomatic HIV-infected subjects (17.1 micrograms/ml) and the controls (23.0 micrograms/ml). This decrease comprised both IgA1 and IgA2 to a similar extent on a relative basis. The SIgA decrease in AIDS patients was in striking contrast to their serum IgA level, which was significantly increased (6.9 g/l) compared with the asymptomatic HIV-infected subjects (2.9 g/l) as well as the controls (2.8 g/l). Low parotid output of SIgA in patients with HIV infection was associated with low numbers of CD4+ lymphocytes in peripheral blood as well as the presence of oral infections. The parotid output of IgM was similar in all groups. A low level of SIgA in the external secretions of patients with AIDS may well contribute to their frequent mucosal infections of opportunistic microorganisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald D. W., Barr C. E., Torosian J. P., McLane M. F., Essex M. Secretory IgA antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus in the parotid saliva of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):793–796. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald D. W., Zon L., Groopman J. E., McLane M. F., Essex M. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III) in saliva of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients and in persons at risk for AIDS. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aucouturier P., Duarte F., Mihaesco E., Pineau N., Preud'homme J. L. Jacalin, the human IgA1 and IgD precipitating lectin, also binds IgA2 of both allotypes. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 26;113(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K. Characterization of the IgA immunocyte population and its product in a patient with excessive intestinal formation of IgA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):77–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Human secretory component. I. Purification of free secretory component from colostrum. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(5):579–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Human secretory immunoglobulin M. An immunochemical and immunohistochemical study. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):559–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Human secretory immunoglobulins. 3. Immunochemical and physicochemical studies of secretory IgA and free secretory piece. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):165–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Human secretory immunoglobulins. II. Salivary secretions from individuals with selectively excessive or defective synthesis of serum immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jan;8(1):69–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinchmann J. E., Vartdal F., Gaudernack G., Markussen G., Funderud S., Ugelstad J., Thorsby E. Direct immunomagnetic quantification of lymphocyte subsets in blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jan;71(1):182–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinchmann J. E., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. T lymphocyte subset changes in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Delacroix D. L. Intravascular and mucosal immunoglobulin A: two separate but related systems of immune defense? Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jun;106(6):892–899. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-6-892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dive C., Rambaud J. C., Vaerman J. P. IgA subclasses in various secretions and in serum. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Vaerman J. P. Secretory component (SC): preferential binding to heavy (greater than 11S) IgA polymers and IgM in serum, in contrast to predominance of 11S and free SC forms in secretions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Sep;49(3):717–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara K., Collet-Cassart D., Kobayashi K., Vaerman J. P. Jacalin: isolation, characterization, and influence of various factors on its interaction with human IgA1, as assessed by precipitation and latex agglutination. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jan;25(1):69–83. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Brandtzaeg P., Radl J., Haaijman J. J. Different subclass distribution of IgA-producing cells in human lymphoid organs and various secretory tissues. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3631–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Scholes J. V., Tierney A. R. Intestinal plasma cell alterations in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Feb;32(2):129–138. doi: 10.1007/BF01297100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T. Immunoglobulin estimation of blood and saliva in human recurrent oral ulceration. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Apr;14(4):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Elson C. O., Kiyono H. Regulation of IgA synthesis and immune response by T cells and interleukins. J Clin Immunol. 1989 May;9(3):175–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00916814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R., Arnold R. R., Michalek S. M., Prince S. J., Babb J. L. Selective induction of an immune response in human external secretions by ingestion of bacterial antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):731–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI108986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Black C. M., Wells T. W. Specificity and association constants of 33 monoclonal antibodies to human IgA epitopes. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jun 1;21(3):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spickett G. P., Dalgleish A. G. Cellular immunology of HIV-infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentijn R. M., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Vermeer B. J., Weening J. J., Kauffmann R. H., Daha M. R., van Es L. A. Circulating and mesangial secretory component-binding IgA-1 in primary IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1984 Nov;26(5):760–766. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


