Abstract
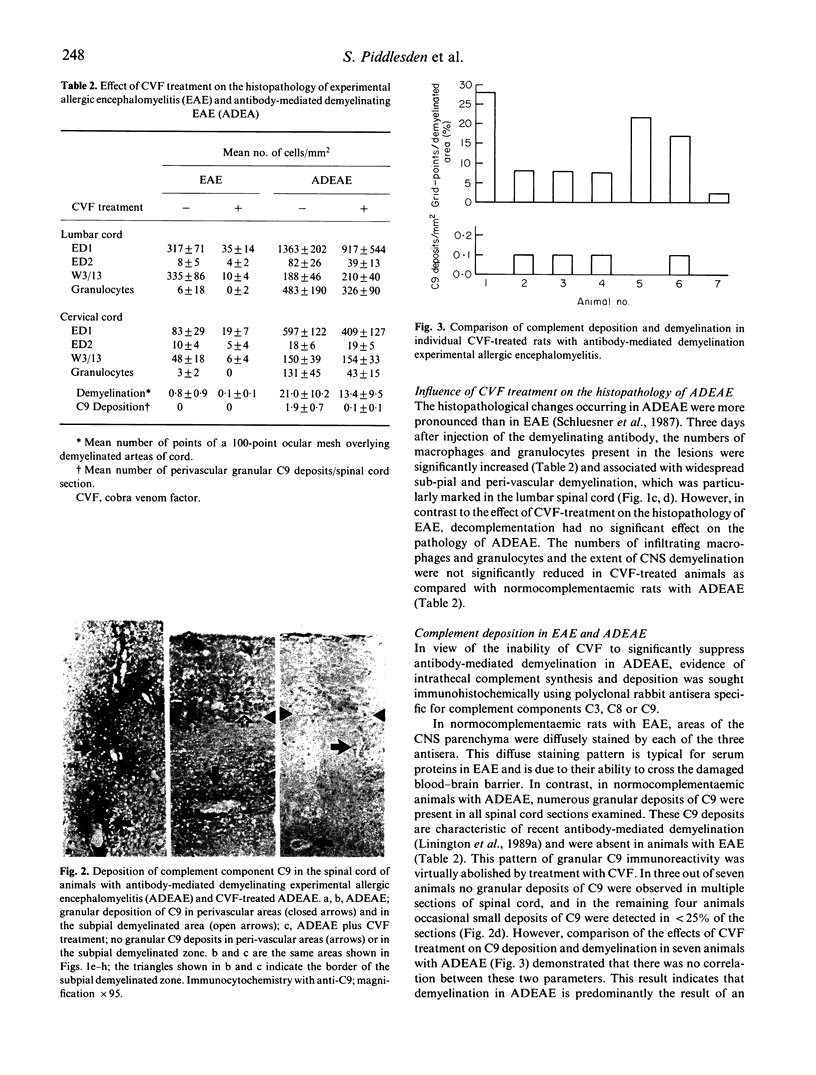
The effects of decomplementation by cobra venom factor (CVF) on the pathogenesis of inflammation and demyelination in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) and acute antibody-mediated demyelinating EAE (ADEAE) have been quantified histologically and immunocytochemically. In rats immunized with 50 micrograms of myelin basic protein in Freund's complete adjuvant containing 100 micrograms heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra, clinical signs of EAE were completely suppressed by two injections of CVF given 9 and 12 days post-immunization. Suppression of clinical disease was associated with a dramatic reduction in peri-vascular inflammation in the CNS, although immunohistochemical staining identified small numbers of infiltrating T cells and macrophages. In contrast, CVF treatment had no significant effect on the clinical severity of ADEAE and although C9 deposition within the CNS was virtually abolished, there was no statistically significant decrease in the extent of demyelination or inflammation. These observations indicate that in the absence of complement components C3 and C5 an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic response plays an important role in the pathogenesis of antibody-mediated demyelination. The major role of the complement cascade in EAE appears to be the generation of pro-inflammatory factors that enhance the inflammatory response within the CNS in animals facing a mild encephalitogenic challenge.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunner C., Lassmann H., Waehneldt T. V., Matthieu J. M., Linington C. Differential ultrastructural localization of myelin basic protein, myelin/oligodendroglial glycoprotein, and 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase in the CNS of adult rats. J Neurochem. 1989 Jan;52(1):296–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb10930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Prineas J. W., Raine C. S. Attachment of myelin to coated pits on macrophages in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Oct-Nov;61(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Kniskern P. J., Jackson J. J. Myelin basic proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:323–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetland G., Johnson E., Falk R. J., Eskeland T. Synthesis of complement components C5, C6, C7, C8 and C9 in vitro by human monocytes and assembly of the terminal complement complex. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Oct;24(4):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höllerhage H. G., Walter G. F., Stolke D. Complement-derived polypeptide C3adesArg as a mediator of inflammation at the blood-brain barrier in a new experimental cat model. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(3):307–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00687583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J., Laffafian I., Morgan B. P. Purification of C8 and C9 from rat serum. Complement Inflamm. 1990;7(1):42–51. doi: 10.1159/000463125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H., Brunner C., Bradl M., Linington C. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: the balance between encephalitogenic T lymphocytes and demyelinating antibodies determines size and structure of demyelinated lesions. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;75(6):566–576. doi: 10.1007/BF00686201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Cochrane C. G., Carpenter C. B., Behan P. O. Allergic encephalomyelitis: effect of complement depletion with cobra venom. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):285–289. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Bradl M., Lassmann H., Brunner C., Vass K. Augmentation of demyelination in rat acute allergic encephalomyelitis by circulating mouse monoclonal antibodies directed against a myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):443–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Lassmann H., Morgan B. P., Compston D. A. Immunohistochemical localisation of terminal complement component C9 in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;79(1):78–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00308961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Morgan B. P., Scolding N. J., Wilkins P., Piddlesden S., Compston D. A. The role of complement in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Brain. 1989 Aug;112(Pt 4):895–911. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.4.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnington C., Webb M., Woodhams P. L. A novel myelin-associated glycoprotein defined by a mouse monoclonal antibody. J Neuroimmunol. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(6):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(84)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. T., Vanguri P., Shin M. L. Studies on demyelination in vitro: the requirement of membrane attack components of the complement system. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Mallat M. Primary cultures of murine astrocytes produce C3 and factor B, two components of the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morariu M. A., Dalmasso A. P. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in cobra venom factor-treated and C4-deficient guinea pigs. Ann Neurol. 1978 Nov;4(5):427–430. doi: 10.1002/ana.410040507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Weigle W. O. Cellular events in the induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):604–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H., Day N. K., Gewurz H., Good R. A. Prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with cobra venom factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):555–560. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluesener H. J., Sobel R. A., Linington C., Weiner H. L. A monoclonal antibody against a myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein induces relapses and demyelination in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4016–4021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolding N. J., Morgan B. P., Houston A., Campbell A. K., Linington C., Compston D. A. Normal rat serum cytotoxicity against syngeneic oligodendrocytes. Complement activation and attack in the absence of anti-myelin antibodies. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Feb;89(2-3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolding N. J., Morgan B. P., Houston W. A., Linington C., Campbell A. K., Compston D. A. Vesicular removal by oligodendrocytes of membrane attack complexes formed by activated complement. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):620–622. doi: 10.1038/339620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J., Brostoff S., Mason D. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the absence of a classical delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. Severe paralytic disease correlates with the presence of interleukin 2 receptor-positive cells infiltrating the central nervous system. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1058–1075. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanguri P., Koski C. L., Silverman B., Shin M. L. Complement activation by isolated myelin: activation of the classical pathway in the absence of myelin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3290–3294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel C. W., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cobra venom factor: improved method for purification and biochemical characterization. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Oct 12;73(1):203–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




