Abstract
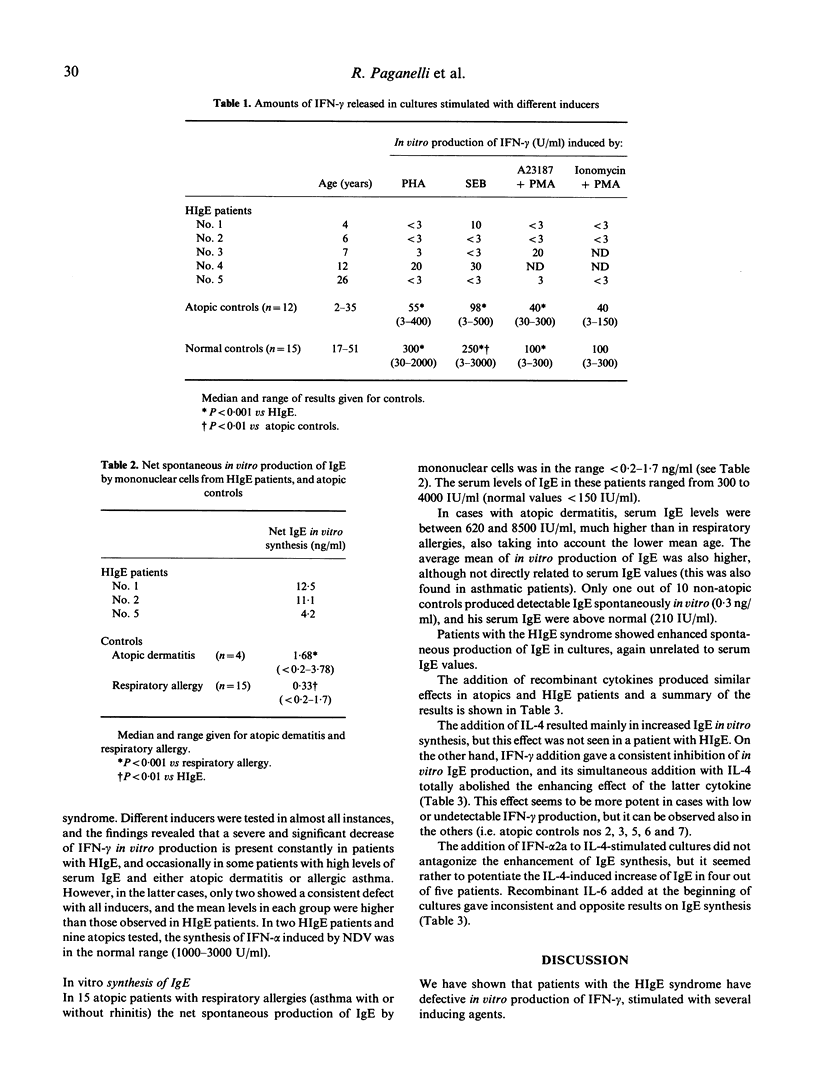
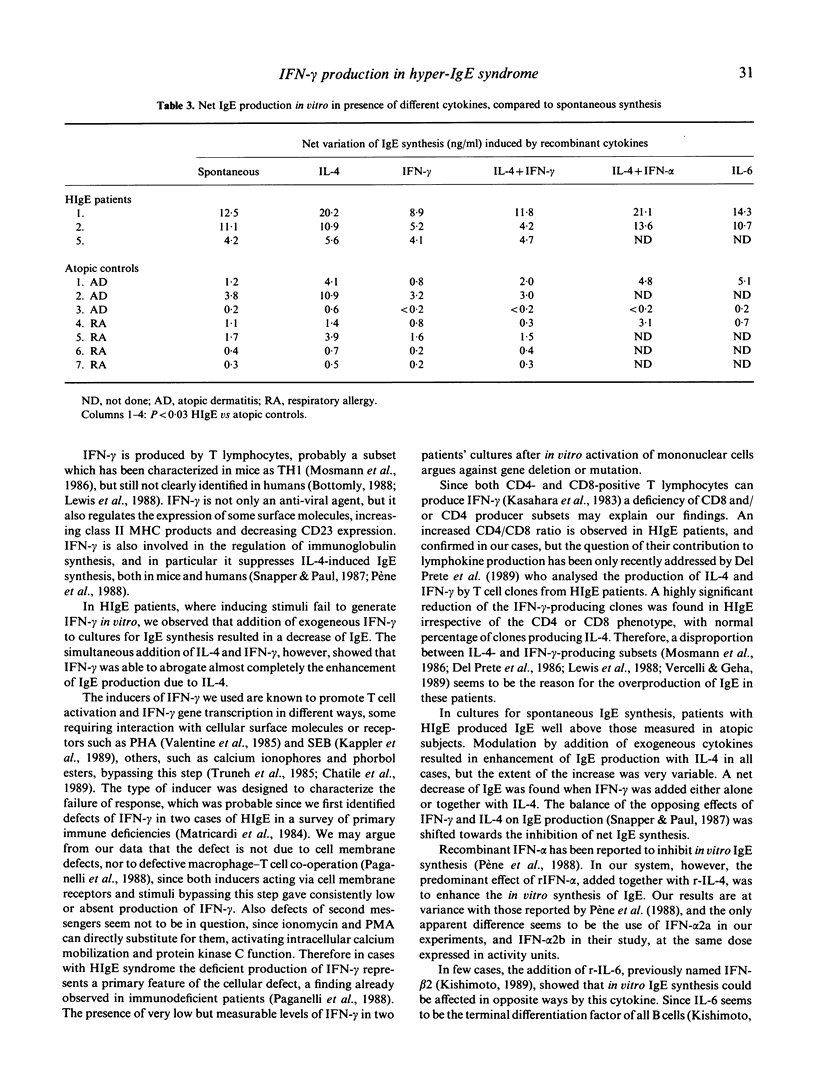
We measured the in vitro production of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in five cases of hyper-IgE syndrome (HIgE), induced by mitogens, calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. The biosynthesis of IFN-gamma was severely reduced or undetectable in HIgE, while it was near normal in most atopic patients. The in vitro spontaneous production of IgE was increased overall in HIgE patients, although no correlation was found with serum IgE levels. Recombinant interleukin-4 (IL-4) induced a further increase in IgE synthesis, and its effect was totally antagonized by recombinant IFN-gamma; the same pattern of response was also observed in atopic subjects with high production of IgE. IFN-alpha synergized with IL-4 on IgE synthesis, whereas recombinant IL-6 gave opposite changes in individual cases tested. We propose that IFN-gamma deficiency may be responsible for some of the features of HIgE patients, including IgE levels and infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., Kirkpatrick C. H., Goldsmith P. K., Gallin J. I. IgE antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans in patients with the syndrome of hyperimmunoglobulin E and recurrent infections. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2437–2443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguniewicz M., Jaffe H. S., Izu A., Sullivan M. J., York D., Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Recombinant gamma interferon in treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis and elevated IgE levels. Am J Med. 1990 Apr;88(4):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomly K. A functional dichotomy in CD4+ T lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1988 Sep;9(9):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Wray B. B., Belmaker E. Z. Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics. 1972 Jan;49(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatila T., Silverman L., Miller R., Geha R. Mechanisms of T cell activation by the calcium ionophore ionomycin. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1283–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Tiri A., Maggi E., De Carli M., Macchia D., Parronchi P., Rossi M. E., Pietrogrande M. C., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Defective in vitro production of gamma-interferon and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by circulating T cells from patients with the hyper-immunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1830–1835. doi: 10.1172/JCI114368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H., Gallin J. I. The hyperimmunoglobulin E recurrent-infection (Job's) syndrome. A review of the NIH experience and the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Jul;62(4):195–208. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198307000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Hyper immunoglobulin E syndrome. Immunodefic Rev. 1989;1(2):155–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemady Z., Blomberg F., Gellis S., Rocklin R. E. IgE production in vitro by human blood mononuclear cells: a comparison between atopic and nonatopic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Mar;71(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Frankel R., Wood N., Geha R. S. Potentiation of human immunoglobulin E synthesis by plasma immunoglobulin E binding factors from patients with the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):952–957. doi: 10.1172/JCI112395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Young M. C., Wood N., Geha R. S. Induction of IgE synthesis in normal human B cells. Sequential requirements for activation by an alloreactive T cell clone and IgE-potentiating factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):713–723. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matricardi P. M., Capobianchi M. R., Paganelli R., Facchini J., Sirianni M. C., Seminara R., Dianzani F., Aiuti F. Interferon production in primary immunodeficiencies. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Sep;4(5):388–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00917142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter L., Wilhelm J. A., Roth F., Schopfer K. Abnormal humoral immune response to Staphylococcus aureus in patients with Staphylococcus aureus hyper IgE syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):450–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganelli R., Capobianchi M. R., Ensoli B., D'Offizi G. P., Facchini J., Dianzani F., Aiuti F. Evidence that defective gamma interferon production in patients with primary immunodeficiencies is due to intrinsic incompetence of lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Apr;72(1):124–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganelli R., Quinti I., Carbonari M., Pontesilli O., D'Offizi G. P., Letta T., Aiuti F. IgG anti-IgE in circulating immune complexes in the hyper-IgE syndrome. Clin Allergy. 1986 Nov;16(6):513–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1986.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Bonnefoy J. Y., Spits H., Yokota T., Arai N., Arai K., Banchereau J. IgE production by normal human lymphocytes is induced by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferons gamma and alpha and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinti I., Brozek C., Wood N., Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Circulating IgG autoantibodies to IgE in atopic syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Apr;77(4):586–594. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold U., Wehrmann W., Kukel S., Kreysel H. W. Evidence that defective interferon-gamma production in atopic dermatitis patients is due to intrinsic abnormalities. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):374–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci M., Del Prete G. F., Maggi E., Lanzavecchia A., Sala P. G., Romagnani S. In vitro synthesis of human IgE: reappraisal of a 5-year study. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):32–37. doi: 10.1159/000233749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truneh A., Albert F., Golstein P., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Early steps of lymphocyte activation bypassed by synergy between calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):318–320. doi: 10.1038/313318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine M. A., Tsoukas C. D., Rhodes G., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Phytohemagglutinin binds to the 20-kDa molecule of the T3 complex. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Aug;15(8):851–854. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Geha R. S. Regulation of IgE synthesis in humans. J Clin Immunol. 1989 Mar;9(2):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00916934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


