Abstract
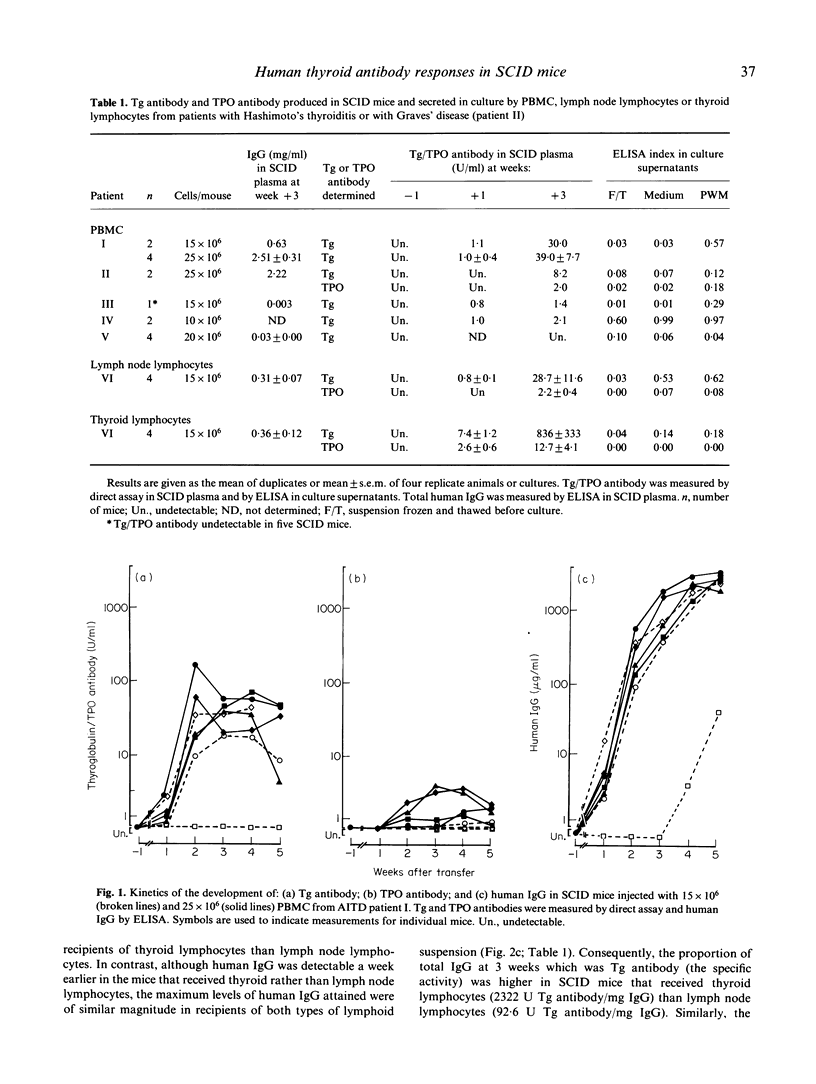
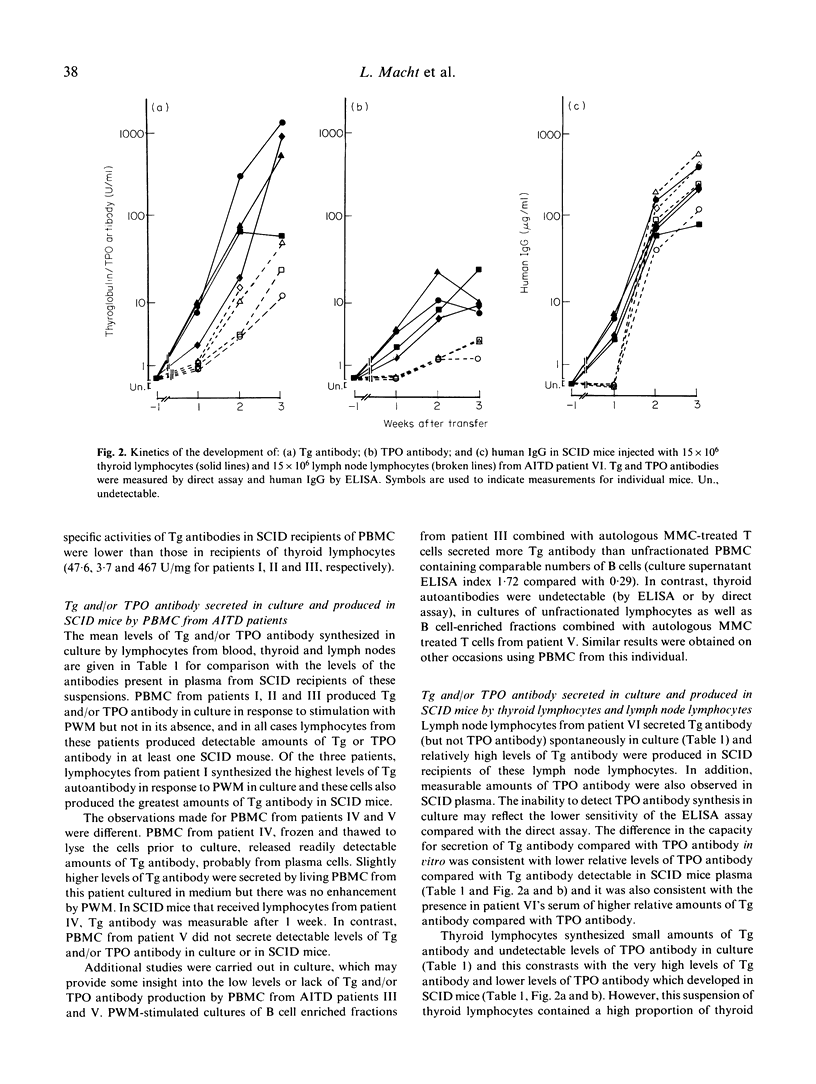
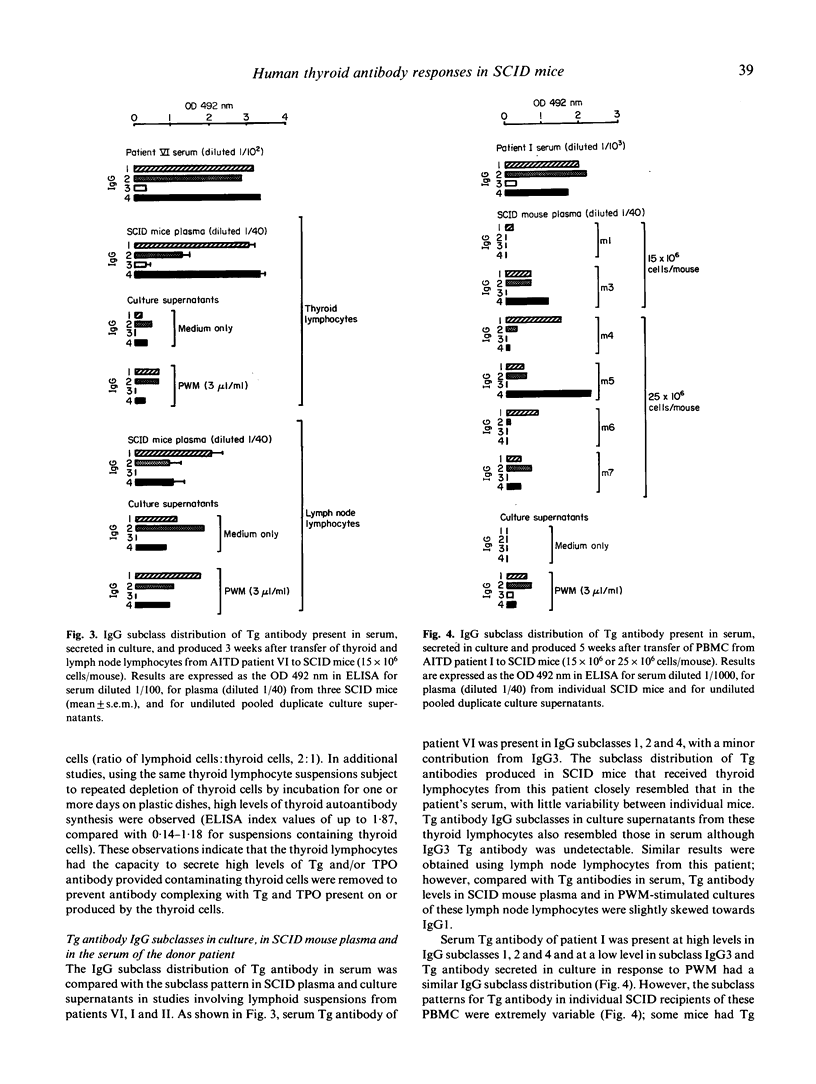
We have studied the ability of lymphocytes from the blood, thyroid and lymph nodes of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) to produce autoantibodies to thyroglobulin (Tg) and/or thyroid peroxidase (TPO) in SCID mice. Human IgG class Tg and/or TPO antibodies were detectable in plasma from SCID mice 7 days after transfer of 15-25 x 10(6) cells/mouse and the highest levels were recorded 2-3 weeks later. In contrast, Tg and/or TPO antibodies were undetectable in recipients of lymphocytes from thyroid antibody negative controls. AITD thyroid lymphocytes produced the most antibody in recipient mice and lower levels were observed in recipients of AITD blood and lymph node lymphocytes. The amounts of Tg and/or TPO antibody detected were in accordance with the ability of thyroid and lymph node lymphocytes to secrete these autoantibodies spontaneously in culture (indicating the presence of cells activated in the patient) and with the capacity of blood lymphocytes (probably B memory cells) to secrete Tg and/or TPO antibodies in culture in response to pokeweed mitogen. Tg antibodies in plasma from SCID recipients of thyroid lymphocytes were of subclasses IgG1, IgG2 and IgG4 and the proportions closely resembled those of the donor's serum Tg antibodies. Blood lymphocytes transferred to SCID recipients were also able to produce Tg antibodies of subclasses 1, 2 and 4 but the subclass distribution varied between mice and the reason for this is not clear at present. Since SCID mice provide an environment in which B lymphocytes from patients with AITD can be activated without mitogen to secrete thyroid antibodies, this model will provide a powerful system for elucidating the mechanisms regulating the secretion of human antibodies to Tg and TPO.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton M. C., McLachlan S. M., Pegg C. A., Dickinson A., Baylis P., Young E. T., Proctor S. J., Rees Smith B. Thyroid autoantibody synthesis by lymphocytes from different lymphoid organs: fractionation of B cells on density gradients. Immunology. 1985 Jun;55(2):271–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYSE E. A., OLD L. J., CHOUROULINKOV I. CYTOTOXIC TEST FOR DEMONSTRATION OF MOUSE ANTIBODY. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall G. N., Kruger S. R. Antithyroglobulin (ATG) production by peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Apr;48(4):712–714. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-4-712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beever K., Bradbury J., Phillips D., McLachlan S. M., Pegg C., Goral A., Overbeck W., Feifel G., Smith B. R. Highly sensitive assays of autoantibodies to thyroglobulin and to thyroid peroxidase. Clin Chem. 1989 Sep;35(9):1949–1954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callard R. E., McCaughan G. W., Babbage J., Souhami R. L. Specific in vitro antibody responses by human blood lymphocytes: apparent nonresponsiveness of PBL is due to a lack of recirculating memory B cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):153–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. T., Byfield P. G., Himsworth R. L., Shepherd P. Human autoantibodies to thyroglobulin are directed towards a restricted number of human specific epitopes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):516–523. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardo E., Davies T. F. Antigen-specific B-cell function in human autoimmune thyroiditis. J Clin Immunol. 1983 Oct;3(4):392–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00915801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchosal M. A., McConahey P. J., Robinson C. A., Dixon F. J. Transfer of human systemic lupus erythematosus in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):985–988. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuma N., McLachlan S. M., Petersen V. B., Kau P., Bradbury J., Devey M., Bleasdale K., Grabowski P., Smith B. R. Human thyroglobulin autoantibodies of subclasses IgG2 and IgG4 bind to different epitopes on thyroglobulin. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):129–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krams S. M., Dorshkind K., Gershwin M. E. Generation of biliary lesions after transfer of human lymphocytes into severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1919–1930. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Clark S., Stimson W. H., Clark F., Smith B. R. Studies of thyroglobulin autoantibody synthesis using a micro-ELISA assay. Immunol Lett. 1982 Jan;4(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Dickinson A., Baylis P., Proctor S., Rees Smith B. Enrichment and depletion of thyroglobulin autoantibody synthesizing lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Aug;53(2):397–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Fawcett J., Atherton M. C., Thompson P., Baylis P., Smith B. R. Thyroid autoantibody synthesis by cultures of thyroid and peripheral blood lymphocytes. II. Effect of thyroglobulin on thyroglobulin antibody synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):620–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Feldt-Rasmussen U., Young E. T., Middleton S. L., Dlichert-Toft M., Siersboek-Nielsen K., Date J., Carr D., Clark F., Rees Smith B. IgG subclass distribution of thyroid autoantibodies: a 'fingerprint' of an individual's response to thyroglobulin and thyroid microsomal antigen. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1987 Mar;26(3):335–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1987.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., McGregor A., Smith B. R., Hall R. Thyroid-autoantibody synthesis by Hashimoto thyroid lymphocytes. Lancet. 1979 Jan 20;1(8108):162–163. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90559-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Pegg C. A., Atherton M. C., Middleton S. L., Dickinson A., Clark F., Proctor S. J., Proud G., Rees Smith B. Subpopulations of thyroid autoantibody secreting lymphocytes in Graves' and Hashimoto thyroid glands. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Aug;65(2):319–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan S. M., Proud G., Pegg C. A., Clark F., Rees Smith B. Functional analysis of T and B cells from blood and thyroid tissue in Hashimoto's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Mar;59(3):585–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees Smith B., McLachlan S. M., Furmaniak J. Autoantibodies to the thyrotropin receptor. Endocr Rev. 1988 Feb;9(1):106–121. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-1-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardt C. W., McLachlan S. M., Matheson J., Smith B. R. An enzyme-linked immunoassay for thyroid microsomal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):155–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M. Enhancement by irradiated T cells of human plasma cell production: dissection of helper and suppressor functions in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. L., Justen J. M., Giraldo A. A., Krco C. J., Kong Y. C. Activation of cytotoxic T cells and effector cells in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis by shared determinants of mouse and human thyroglobulins. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 May;39(2):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. M., McLachlan S. M., Parkes A., Clark F., Howel D., Rees Smith B. The IgG subclass distribution of thyroglobulin antibody synthesized in culture. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Aug;18(2):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tighe H., Silverman G. J., Kozin F., Tucker R., Gulizia R., Peebles C., Lotz M., Rhodes G., Machold K., Mosier D. E. Autoantibody production by severe combined immunodeficient mice reconstituted with synovial cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1843–1848. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Black C. M., Cohen S. B., Tomlinson R., Banga J. P., Reimer C. B. Affinity purification of IgG subclasses and the distribution of thyroid auto-antibody reactivity in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jul;30(1):73–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., McGregor A. M., Lazarus J. H., Hall R. Thyroid antibodies are produced by thyroid-derived lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):196–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


