Abstract
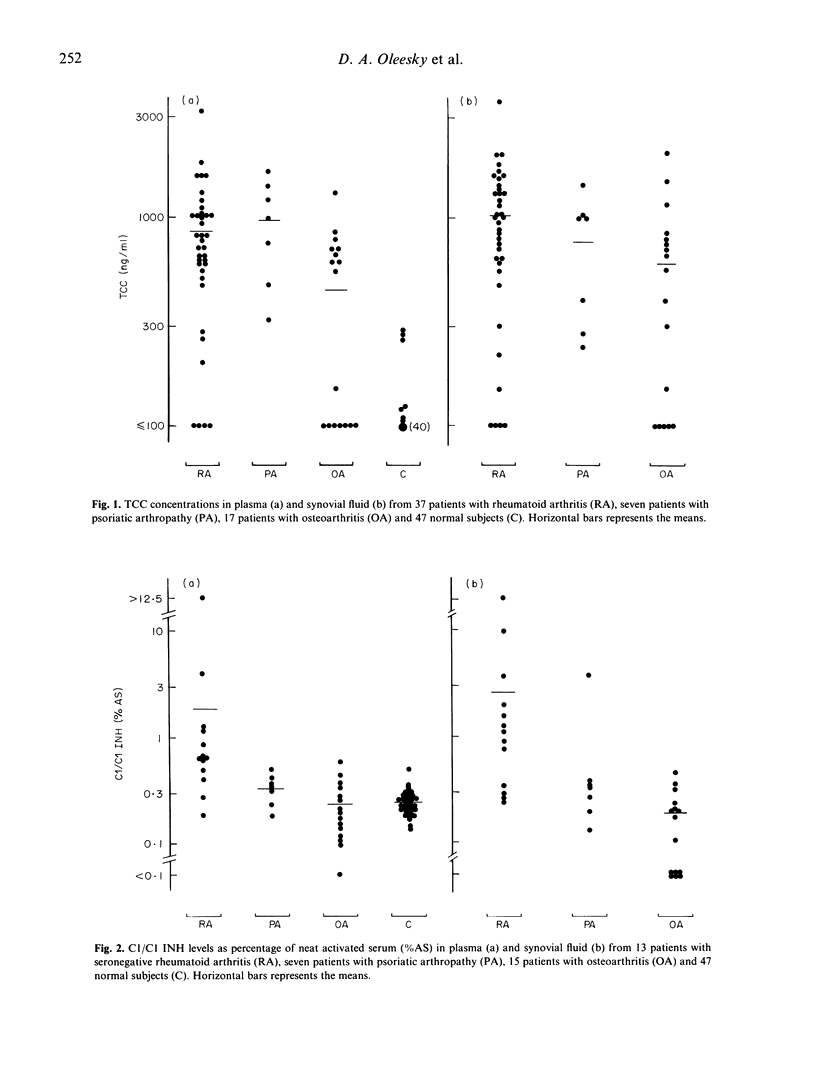
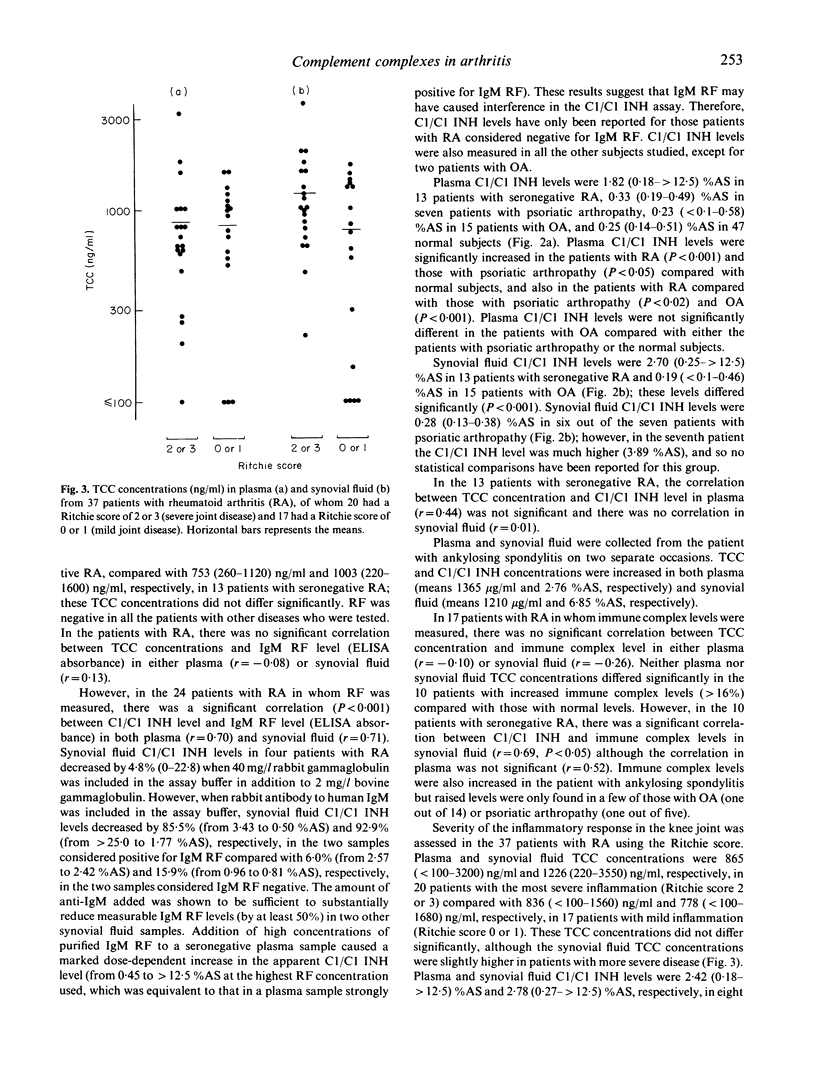
Terminal complement complex (TCC) and C1r-C1s-C1 inhibitor complex (C1/C1 INH) concentrations were measured in plasma and synovial fluid from patients with arthritis and related to other measures of disease activity. Both TCC and C1/C1 INH concentrations were significantly increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared with patients with osteoarthritis (plasma and synovial fluid, P less than 0.05) and normal subjects (plasma only, P less than 0.001). In the patients with RA, there was no correlation between plasma or synovial fluid TCC concentrations and IgM rheumatoid factor, immune complex or C1/C1 INH levels. However, in 10 patients with seronegative RA, C1/C1 INH and immune complex levels correlated significantly in synovial fluid (r = 0.69, P less than 0.05) although not in plasma (r = 0.52). Plasma and synovial fluid TCC and C1/C1 INH concentrations did not differ in rheumatoid patients with severe compared with mild joint disease (categorized by the Ritchie score). These results confirm a role for complement activation in RA but suggest that several mechanisms are involved in its pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barratt J., Naish R. A simple radiolabelled rheumatoid factor binding assay for the measurement of circulating immune complexes. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(2):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund K., Laurell A. B., Nived O., Sjoholm A. G., Sturfelt G. Complement activation, circulating C1q binding substances and inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis: relations and changes on suppression of inflammation. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1980 Jul;4(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Nemerow G. R., Mayes J. T. Methods to detect and quantitate complement activation. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(2-3):195–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00205873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. H., Houston W. A., Petersen M. M., Williams J. D., Williams B. D., Morgan B. P. Stimulation of human rheumatoid synovial cells by non-lethal complement membrane attack. Immunology. 1990 Feb;69(2):237–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faith A., Pontesilli O., Unger A., Panayi G. S., Johns P. ELISA assays for IgM and IgG rheumatoid factors. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEDBERG H. STUDIES ON THE DEPRESSED HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT ACTIVITY OF SYNOVIAL FLUID IN ADULT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1963;9:165–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Perumal R., Roitt I. M. Intra-articular and circulating immune complexes and antiglobulins (IgG and IgM) in rheumatoid arthritis; correlation with clinical features. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Feb;38(1):1–7. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator-C1s complexes in inflammatory joint disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):521–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John R., Henley R., Barron N. Antibody interference in a two-site immunometric assay for thyrotrophin. Ann Clin Biochem. 1989 Jul;26(Pt 4):346–352. doi: 10.1177/000456328902600409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois P. F., Gawryl M. S. Complement activation occurs through both classical and alternative pathways prior to onset and resolution of adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 May;47(2):152–163. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Lea T., Frøland S. S., Harboe M. Quantification of the terminal complement complex in human plasma by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on monoclonal antibodies against a neoantigen of the complex. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Lea T., Mellbye O. J., Pahle J., Grand O., Harboe M. Complement activation in rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by C3dg and the terminal complement complex. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jun;29(6):715–721. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Paus A. Complement activation in synovial fluid and tissue from patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Nov;29(11):1359–1364. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Daniels R. H., Williams B. D. Measurement of terminal complement complexes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):473–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P. Mechanisms of tissue damage by the membrane attack complex of complement. Complement Inflamm. 1989;6(2):104–111. doi: 10.1159/000463082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peakman M., Senaldi G., Vergani D. Review: assessment of complement activation in clinical immunology laboratories: time for reappraisal? J Clin Pathol. 1989 Oct;42(10):1018–1025. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.10.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Activation of the complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. Fed Proc. 1973 Feb;32(2):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumfeld W. R., Morgan B. P., Campbell A. K. The ninth complement component in rheumatoid arthritis, Behçet's disease and other rheumatic diseases. Br J Rheumatol. 1986 Aug;25(3):266–270. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/25.3.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturfelt G., Sjöholm A. G., Svensson B. Complement components, C1 activation and disease activity in SLE. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;70(1):12–18. doi: 10.1159/000233266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo F. B., West C. D. Quantitation of (C1INH)2 C1r-C1s complexes in glomerulonephritis as an indicator of C1 activation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Feb;42(2):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Cohen S. B., Oleesky D. A., Morgan B. P. Terminal complement complexes and C1/C1 inhibitor complexes in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jul;77(1):25–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


