Abstract
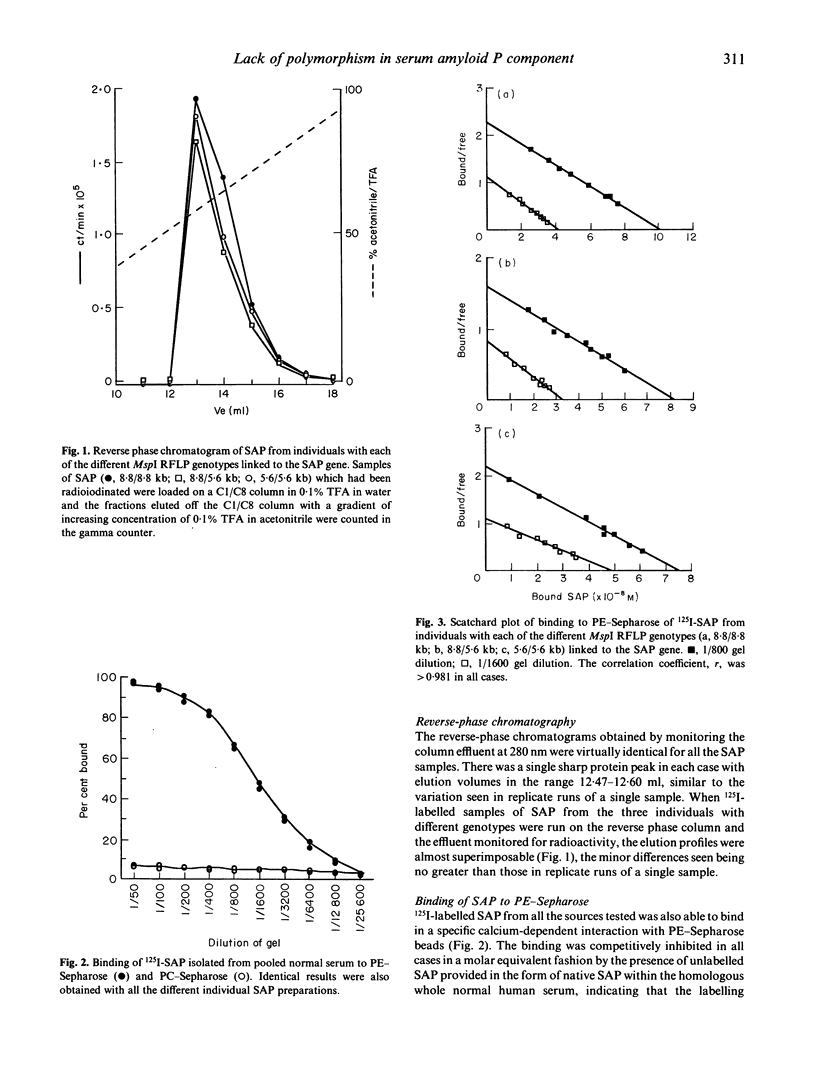
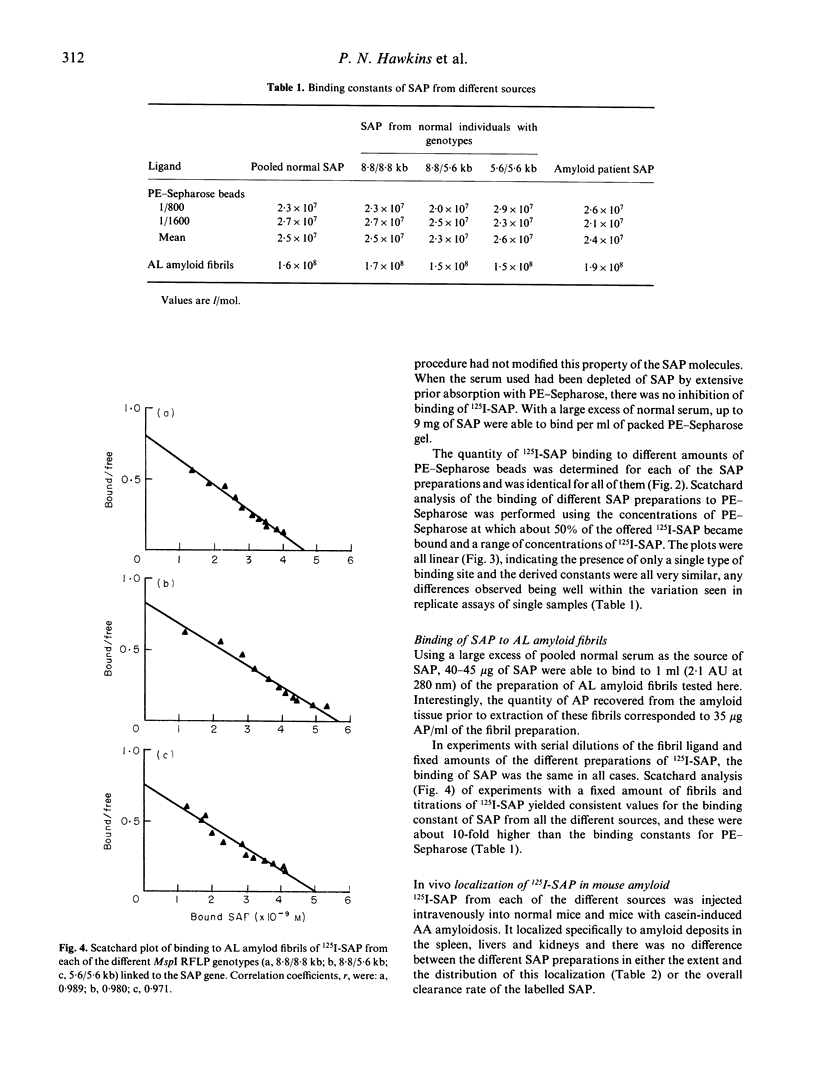
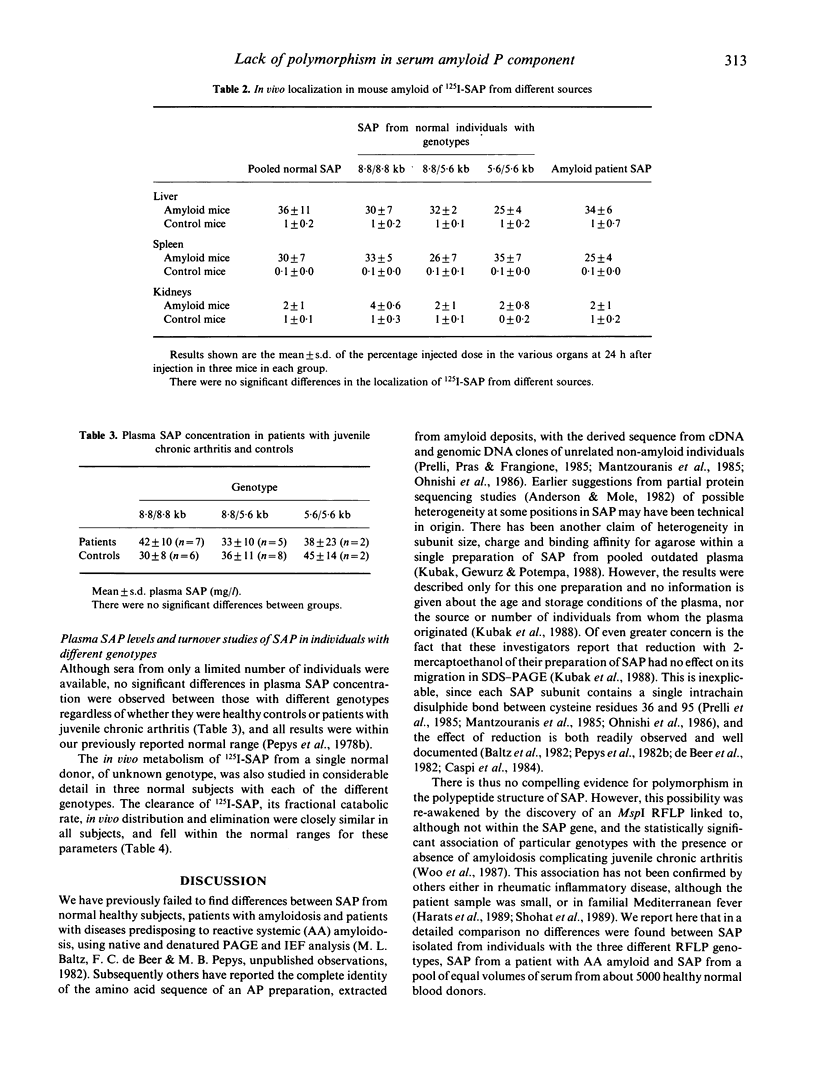
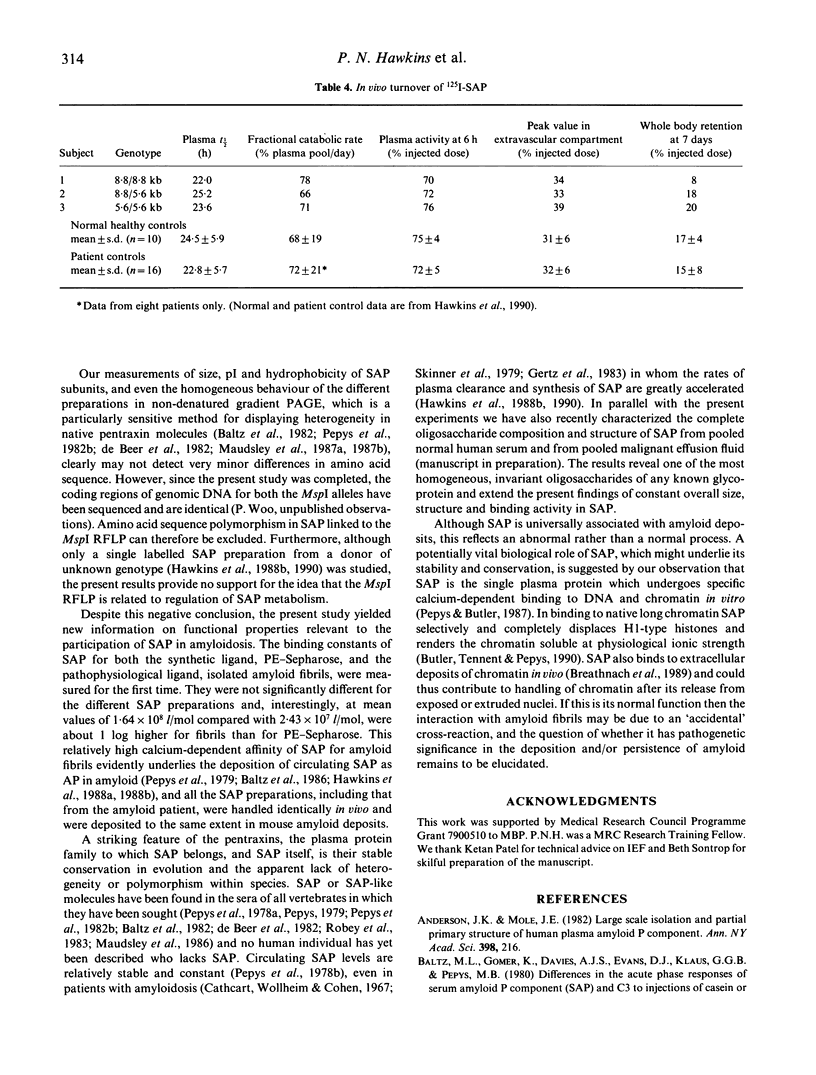
Pure serum amyloid P component (SAP) was isolated from a normal donor pool, from individuals with the different genotypes of an MspI restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) linked to the SAP gene, and from a patient with AA amyloidosis. The SAP preparations were all identical and all behaved as a single homogeneous species in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, isoelectric focussing, reverse-phase chromatography, binding in vitro to phosphoethanolamine-Sepharose (binding constant 2.4 x 10(7) l/mol) and AL amyloid fibrils (1.6 x 10(8) l/mol), and binding to amyloid deposits in vivo in mice with casein-induced amyloidosis. The in vivo metabolism of 125I-SAP from a single donor was normal and identical in three healthy individuals representing the three different MspI RFLP genotypes. There is thus no frequent polymorphism of SAP in normal subjects, and SAP altered with respect to the characteristics studied here is not a necessary condition for pathogenesis of systemic AA amyloidosis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. K., Mole J. E. Large scale isolation and partial primary structure of human plasma amyloid P-component. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:216–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., Caspi D., Evans D. J., Rowe I. F., Hind C. R., Pepys M. B. Circulating serum amyloid P component is the precursor of amyloid P component in tissue amyloid deposits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Dec;66(3):691–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., Gomer K., Davies A. J., Evans D. J., Klaus G. G., Pepys M. B. Differences in the acute phase responses of serum amyloid P-component (SAP) and C3 to injections of casein or bovine serum albumin in amyloid-susceptible and -resistant mouse strains. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):355–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Feinstein A., Munn E. A., Milstein C. P., Fletcher T. C., March J. F., Taylor J., Bruton C., Clamp J. R. Phylogenetic aspects of C-reactive protein and related proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:49–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Kofler H., Sepp N., Ashworth J., Woodrow D., Pepys M. B., Hintner H. Serum amyloid P component binds to cell nuclei in vitro and to in vivo deposits of extracellular chromatin in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1433–1438. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Tennent G. A., Pepys M. B. Pentraxin-chromatin interactions: serum amyloid P component specifically displaces H1-type histones and solubilizes native long chromatin. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):13–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspi D., Baltz M. L., Snel F., Gruys E., Niv D., Batt R. M., Munn E. A., Buttress N., Pepys M. B. Isolation and characterization of C-reactive protein from the dog. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):307–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart E. S., Wollheim F. A., Cohen A. S. Immunoassay of P-component in amyloidotic sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1123–1125. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E., Prelli F., Larrondo-Lillo M., van Duinen S., Shelanski M. L., Frangione B. Isolation and characterization of amyloid P component from Alzheimer's disease and other types of cerebral amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische F. E., Wernstedt C., Westermark G. T., Westermark P., Pepys M. B., Rennie J. A., Gilbey S. G., Watkins P. J. Insulin as an amyloid-fibril protein at sites of repeated insulin injections in a diabetic patient. Diabetologia. 1988 Mar;31(3):158–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00276849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertz M. A., Skinner M., Cohen A. S., Kyle R. A. Nephelometric measurement of human serum amyloid P component (SAP). J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Nov;102(5):773–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harats N., Kluve-Beckerman B., Skinner M., Passo M., Quinn L., Benson M. D. Lack of association of a restriction fragment length polymorphism for serum amyloid P gene with reactive amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Oct;32(10):1325–1327. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Myers M. J., Epenetos A. A., Caspi D., Pepys M. B. Specific localization and imaging of amyloid deposits in vivo using 123I-labeled serum amyloid P component. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):903–913. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Myers M. J., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B. Diagnostic radionuclide imaging of amyloid: biological targeting by circulating human serum amyloid P component. Lancet. 1988 Jun 25;1(8600):1413–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Wootton R., Pepys M. B. Metabolic studies of radioiodinated serum amyloid P component in normal subjects and patients with systemic amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1862–1869. doi: 10.1172/JCI114917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind C. R., Collins P. M., Caspi D., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. Specific chemical dissociation of fibrillar and non-fibrillar components of amyloid deposits. Lancet. 1984 Aug 18;2(8399):376–378. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90544-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubak B. M., Gewurz H., Potempa L. A. Identification of multiple forms of the P component of amyloid isolated from human serum. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;87(2):194–203. doi: 10.1159/000234672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., McAdam K. P. Human amyloid P component: an elastase inhibitor. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Sep;20(3):219–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantzouranis E. C., Dowton S. B., Whitehead A. S., Edge M. D., Bruns G. A., Colten H. R. Human serum amyloid P component. cDNA isolation, complete sequence of pre-serum amyloid P component, and localization of the gene to chromosome 1. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7752–7756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather S. J., Ward B. G. High efficiency iodination of monoclonal antibodies for radiotherapy. J Nucl Med. 1987 Jun;28(6):1034–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley S., Baltz M. L., Munn E. A., Buttress N., Herbert J., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Isolation and characterisation of goat C-reactive protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 16;924(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley S., Hind C. R., Munn E. A., Buttress N., Pepys M. B. Isolation and characterization of guinea-pig serum amyloid P component. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):317–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley S., Rowe I. F., de Beer F. C., Munn E. A., Herbert J., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Identification and isolation of two pentraxins from bovine serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Mar;67(3):662–673. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi S., Maeda S., Shimada K., Arao T. Isolation and characterization of the complete complementary and genomic DNA sequences of human serum amyloid P component. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):849–858. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Dyck R. F., Holford S., Breathnach S. M., Black M. M., Tribe C. R., Evans D. J., Feinstein A. Biology of serum amyloid P component. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:286–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Butler P. J. Serum amyloid P component is the major calcium-dependent specific DNA binding protein of the serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Markham R. E., Thomas H. C., Williams B. D., Petrie A. Comparative clinical study of protein SAP (amyloid P component) and C-reactive protein in serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):119–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., De Beer F. C., Milstein C. P., March J. F., Feinstein A., Butress N., Clamp J. R., Taylor J., Bruton C., Fletcher T. C. C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component in the plaice (Pleuronectes platessa L.), a marine teleost, are homologous with their human counterparts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;704(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dyck R. F., de Beer F. C., Skinner M., Cohen A. S. Binding of serum amyloid P-component (SAP) by amyloid fibrils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Nov;38(2):284–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. Isolation of serum amyloid P-component (protein SAP) in the mouse. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):637–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Pras M., Frangione B. The primary structure of human tissue amyloid P component from a patient with primary idiopathic amyloidosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12895–12898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Tanaka T., Liu T. Y. Isolation and characterization of two major serum proteins from the dogfish, Mustelus canis, C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3889–3894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Vaitukaitis J. L., Cohen A. S., Benson M. D. Serum amyloid P-component levels in amyloidosis, connective tissue diseases, infection, and malignancy as compared to normal serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Oct;94(4):633–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snel F. W., Niewold T. A., Baltz M. L., Hol P. R., Van Ederen A. M., Pepys M. B., Gruys E. Experimental amyloidosis in the hamster: correlation between hamster female protein levels and amyloid deposition. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):296–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachino G., Heck L. W., Gelfand J. A., Kaplan M. M., Burke J. F., Berninger R. W., McAdam K. P. Inhibition of human neutrophil and Pseudomonas elastases by the amyloid P-component: a constituent of elastic fibers and amyloid deposits. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Dec;44(6):529–534. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.6.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Shirahama T., Skinner M., Norén P., Cohen A. S. Amyloid P-component (protein AP) in localized amyloidosis as revealed by an immunocytochemical method. Histochemistry. 1981;71(2):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00507821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., O'Brien J., Robson M., Ansell B. M. A genetic marker for systemic amyloidosis in juvenile arthritis. Lancet. 1987 Oct 3;2(8562):767–769. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92501-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer F. C., Baltz M. L., Munn E. A., Feinstein A., Taylor J., Bruton C., Clamp J. R., Pepys M. B. Isolation and characterization of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component in the rat. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



