Abstract
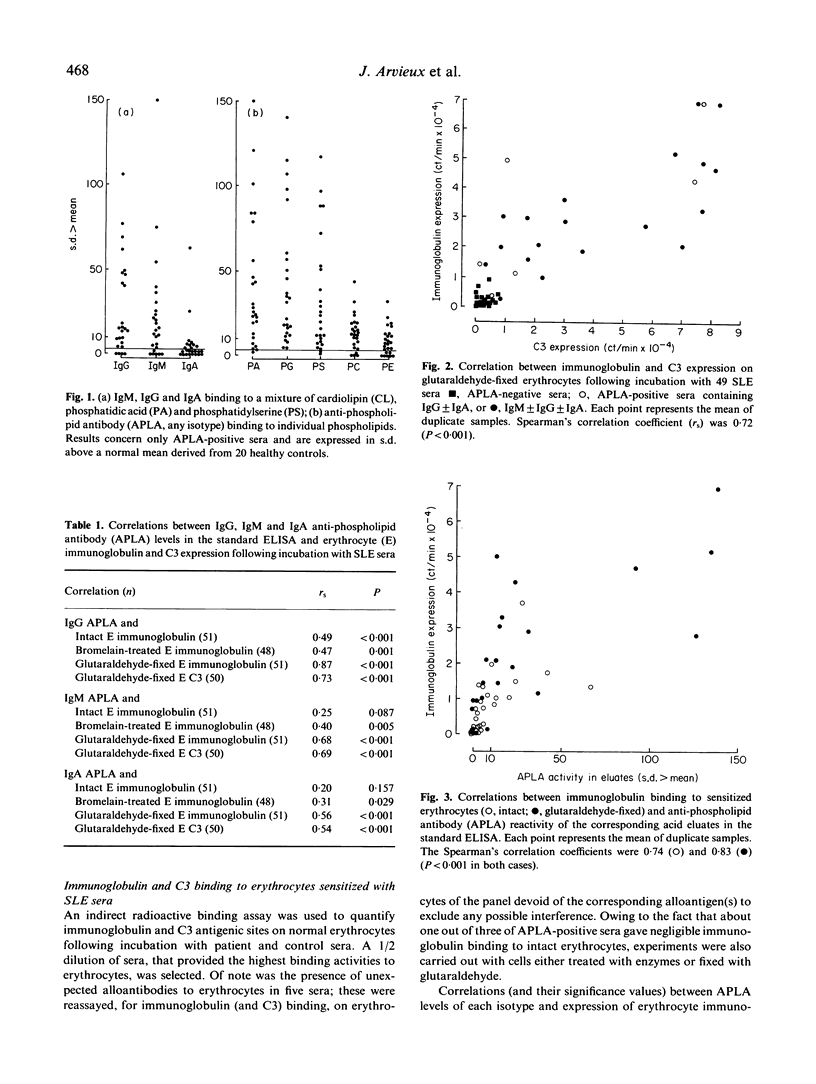
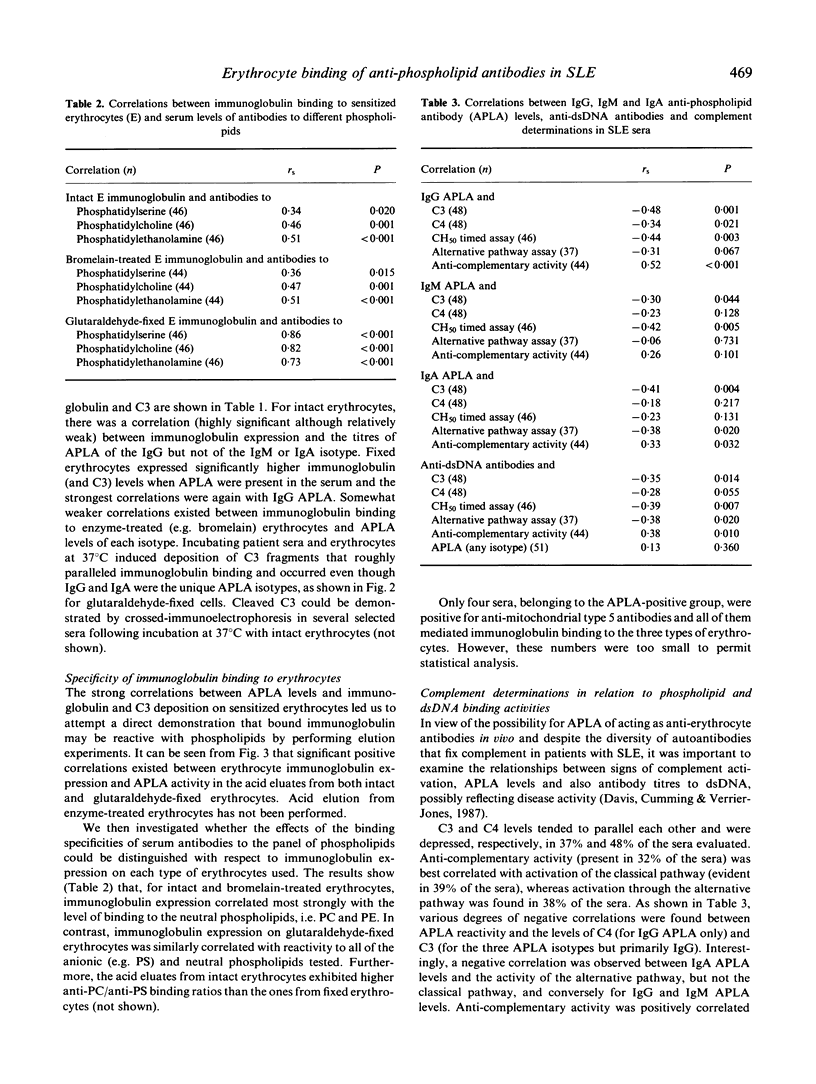
We studied 51 sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus to determine the relationship of their anti-phospholipid activity to their anti-erythrocyte and complement activation properties. Forty-nine per cent of the sera had anti-phospholipid activity as demonstrated by ELISA using a panel of anionic phospholipids, and most of these also bound to neutral phospholipids, albeit to a lesser extent. A cellular radioimmunoassay was used for the detection of immunoglobulin and C3 binding to normal erythrocytes (intact, enzyme-treated or glutaraldehyde-fixed) following incubation with patient sera. The levels of IgG anti-phospholipid correlated with hypocomplementaemia and with immunoglobulin binding (paralleled by a deposition of C3 fragments) to the three types of erythrocytes, although most strongly to fixed cells. Immunoglobulin binding to intact erythrocytes correlated primarily with reactivity against neutral phospholipids. The specificity for phospholipid epitopes of immunoglobulin adsorbed onto erythrocytes was confirmed by acid elution followed by testing in ELISA. These data suggest that some anti-phospholipid antibody subsets may bind to erythrocytes in vivo, thus accounting for the observed association of these antibodies with positive direct antiglobulin tests.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., de Groot E. R., Feltkamp T. E. Immunology of DNA. III. Crithidia luciliae, a simple substrate for the determination of anti-dsDNA with the immunofluorescence technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P., Cumming R. H., Verrier-Jones J. Relationship between anti-DNA antibodies complement consumption and circulating immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):226–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Maassen C., Hemker H. C., de Baets M. H., van Breda-Vriesman P. J., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA) directed not to cardiolipin but to a plasma protein cofactor. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1544–1547. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91374-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond A., Rudge A. C., Loizou S., Bowcock S. J., Walport M. J. Reduced numbers of complement receptor type 1 on erythrocytes are associated with increased levels of anticardiolipin antibodies. Findings in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Mar;32(3):259–264. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Chan J. K., Asherson R. A., Aber V. R., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Predictive value of the anticardiolipin antibody test. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Nov;146(11):2153–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Patel S. P., Hughes G. R. Evaluation of the anti-cardiolipin antibody test: report of an international workshop held 4 April 1986. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):215–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Wasley G. D., Hughes G. R. Use of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and of inhibition studies to distinguish between antibodies to cardiolipin from patients with syphilis or autoimmune disorders. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazeltine M., Rauch J., Danoff D., Esdaile J. M., Tannenbaum H. Antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence of an association with positive Coombs' and hypocomplementemia. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jan;15(1):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. H., Mowbray J. F., Porter K. A. Detection of circulating immune complexes in pathological human sera. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):762–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Sueishi M., Funaki H., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Anti-phospholipid antibodies and biological false positive serological test for syphilis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou S., Mackworth-Young C. G., Cofiner C., Walport M. J. Heterogeneity of binding reactivity to different phospholipids of antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and with syphilis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. Antiphospholipid antibodies: more than just a disease marker? Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90020-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Furthmayr H., Tomita M. The red cell membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:667–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg R., Gårdlund B., Thorstensson R., Lidman K. Further immunological studies of sera containing anti-mitochondrial antibodies, type M 5. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Dec;58(3):639–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg R., Nived O., Sturfelt G., Unander M., Arfors L. Anticardiolipin and complement activation: relation to clinical symptoms. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987 Jun;14 (Suppl 13):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Meng Q. H., Tannenbaum H. Lupus anticoagulant and antiplatelet properties of human hybridoma autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2598–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Tannenbaum M., Tannenbaum H., Ramelson H., Cullis P. R., Tilcock C. P., Hope M. J., Janoff A. S. Human hybridoma lupus anticoagulants distinguish between lamellar and hexagonal phase lipid systems. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9672–9677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Yount W. J., Walport M. J., Winfield J. B., Parker C. J., Fuller C. R., Taylor R. P., Myones B. L., Lachmann P. J. Disease-associated loss of erythrocyte complement receptors (CR1, C3b receptors) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases involving autoantibodies and/or complement activation. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2005–2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vismara A., Meroni P. L., Tincani A., Harris E. N., Barcellini W., Brucato A., Khamashta M., Hughes G. R., Zanussi C., Balestrieri G. Relationship between anti-cardiolipin and anti-endothelial cell antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):247–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter H., Krob E. J. Fixation with even small quantities of glutaraldehyde affects red blood cell surface properties in a cell- and species-dependent manner. Studies by cell partitioning. Biosci Rep. 1989 Dec;9(6):727–735. doi: 10.1007/BF01114811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann C. E., Wallace D. J., Peter J. B., Knight P. J., Bear M. B., Klinenberg J. R. Studies of IgG, IgM and IgA antiphospholipid antibody isotypes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jan;15(1):74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


